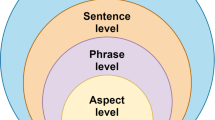
Abstract
Social Media nowadays generate huge loads of data that can be valuable in many contexts. It includes media of all formats by which groups of users interact to generate ideas in a distributed and networked process. Data scientists from Twitter have found that the main reason for attaining fame of Presidential Candidate in the upcoming elections scheduled in Nov, 2016 in US is the reach of social media. Researchers and data scientists can use data on social media to track opinions of people about products and services. Many approaches are working behind the scene to reduce errors in opinion mining and sentiment analysis and to attain a level of accuracy for meeting the growing demands of organizations to evaluate their customers. The way people express their opinions have radically changed in the past few years. This paper explores various techniques of distillation of knowledge from huge amount of unstructured information. Generic features of making use of linguistic patterns in sentiment classification are being explored in this paper. In this study investigation of all opinion extraction techniques to generate positive and negative aspects of data with appropriate feature set can help in reduction of error of misclassification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel Fattah M (2015) New term weighting schemes with combination of multiple classifiers for sentiment analysis. Neurocomputing 167:434–442. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2015.04.051
Alam MH, Ryu W, Lee S (2016) Joint multi-grain topic sentiment: modeling semantic aspects for online reviews. Inf Sci 339:206–223. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2016.01.013
Bhadane C, Dalal H, Doshi H (2015) Sentiment analysis: measuring opinions. Procedia Comput Sci 45:808–814. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2015.03.159
Gao K, Xu H, Wang J (2015) A rule-based approach to emotion cause detection for Chinese micro-blogs. Expert Syst Appl 42(9):4517–4528. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2015.01.064
Gautam G, Yadav D (2014) Sentiment analysis of twitter data using machine learning approaches and semantic analysis. In: 2014 Seventh International Conference on Contemporary Computing (IC3). doi:10.1109/ic3.2014.6897213
Gundla AV, Otari PM (2015) A review on sentiment analysis and visualization of customer reviews. Int J Eng Comput Sci. doi:10.18535/ijecs/v4i10.11
Haenlein M, Kaplan AM (2010) An Empirical analysis of attitudinal and behavioral reactions toward the abandonment of unprofitable customer relationships. J Relat Mark 9(4):200–228. doi:10.1080/15332667.2010.522474
Hu M, Liu B (2004) Mining and summarizing customer reviews. In: Proceedings of the 2004 ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining—KDD ‘04. doi:10.1145/1014052.1014073
Jeyapriya A, Selvi CS (2015) Extracting aspects and mining opinions in product reviews using supervised learning algorithm. In: 2015 2nd International Conference on Electronics and Communication Systems (ICECS). doi:10.1109/ecs.2015.7124967
Khan FH, Qamar U, Bashir S (2016) SentiMI: introducing point-wise mutual information with SentiWordNet to improve sentiment polarity detection. Appl Soft Comput 39:140–153. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2015.11.016
Li Tao, Zhu Shenghuo, Ogihara Mitsunori (2008) Text categorizationvia generalized discriminant analysis. Inf Process Manage 44:1684–1697
Liu B (2011) Opinion mining and sentiment analysis. Web Data Mining 459–526. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-19460-3_11
Pak A, Paroubek P (2011) Twitter for sentiment analysis: when language resources are not available. In: 2011 22nd International Workshop on Database and Expert Systems Applications. doi:10.1109/dexa.2011.86
Panger G (2015) Reassessing the facebook experiment: critical thinking about the validity of Big Data research. Inf Commun Soc 19(8):1108–1126. doi:10.1080/1369118x.2015.1093525
Savchenko AV (2013) Probabilistic neural network with homogeneity testing in recognition of discrete patterns set. Neural Netw 46:227–241
Shi H, Zhan W, Li X (2015) A supervised fine-grained sentiment analysis system for online reviews. Intell Autom Soft Comput 21(4):589–605. doi:10.1080/10798587.2015.1012830
Su Y, Zhang Y, Ji D, Wang Y, Wu H (2013) Ensemble learning for sentiment classification, Chinese lexical semantics. Springer, Berlin, pp 84–93
Vinodhini G, Chandrasekaran R (2016) A comparative performance evaluation of neural network based approach for sentiment classification of online reviews. J King Saud Univ—Comput Inf Sci 28(1):2–12. doi:10.1016/j.jksuci.2014.03.024
Wang H (2013) ReTweeting analysis and prediction in microblogs: an epidemic inspired approach. China Commun 10(3):13–24. doi:10.1109/cc.2013.6488827
Wang W, Wang H, Song Y (2016) Ranking product aspects through sentiment analysis of online reviews. J Exp Theor Artif Intell 1–20. doi:10.1080/0952813x.2015.1132270
Yang CC, Dorbin Ng T (2011) Analyzing and visualizing web opinion development and social interactions with density-based clustering. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern—Part A Syst Hum 41(6):1144–1155. doi:10.1109/tsmca.2011.2113334
Yang SY, Liu A, Mo SY (2014) Twitter financial community modeling using agent based simulation. In: 2014 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence for Financial Engineering and Economics (CIFEr). doi:10.1109/cifer.2014.6924055
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, J., Singh, G. & Singh, R. A review of sentiment analysis techniques for opinionated web text. CSIT 4, 241–247 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-016-0107-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-016-0107-y