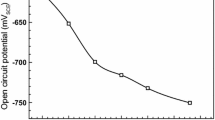
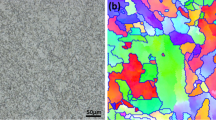
Abstract
Susceptibilities to stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of X80 pipeline steel in relatively concentrated carbonate/bicarbonate solutions with different chloride ion concentrations or pH value at a passive potential of −200 mV vs SCE were investigated by slow strain rate tensile test. In order to explore the SCC mechanism and the evaluation criterion for the SCC susceptibility of the steel in passive state, electrochemical measurements were taken. Potentiodynamic polarization curves were obtained at different potential sweep rates, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements were taken after fast polarization to the passive potential. The effects of chloride ion and pH on SCC behaviors of X80 steel at the passive potential were also discussed. The results showed that the SCC mechanism of X80 pipeline steel was greatly influenced by the passive film formed in these solutions. The SCC behaviors followed the film suppressed anodic dissolution mechanism in these circumstances, because the filming process accounted for a considerable proportion of the overall electrode process. The criteria for evaluating the SCC susceptibility of the steel at passive potential were proposed and validated. Decreasing in the concentration of chloride ion or increasing in pH value resulted in the reduction in SCC susceptibility. The existence of chloride ion greatly lowered the passivation tendency and the film stability, while its concentration determined the dissolution rate of the steel matrix. Higher pH value was responsible for the stable and tenacious passive films and the high repassivation capability. It was also inclined to lower the anodic dissolution rate at crack tips by retarding the cathodic oxygen reduction.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Manfredi, J.L. Otegui, Eng. Fail. Anal. 9, 495 (2002)
L. Zhang, X.G. Li, C.W. Du, Y.Z. Huang, Mater. Des. 30, 2259 (2009)
M.C. Yan, J.Q. Wang, E.H. Han, W. Ke, Corros. Sci. 50, 1331 (2008)
R.N. Parkins, W.K. Blanchard Jr., B.S. Delanty, Corrosion 50, 394 (1994)
G.A. Zhang, Y.F. Cheng, Electrochim. Acta 55, 316 (2009)
Z.Y. Liu, C.W. Du, X. Zhang, F.M. Wang, X.G. Li, Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 26, 489 (2013)
B.Y. Fang, A. Atrens, J.Q. Wang, E.H. Han, Z.Y. Zhu, W. Ke, J. Mater. Sci. 38, 127 (2003)
R.N. Parkins, Corrosion 43, 130 (1987)
V.A. Alves, C.M.A. Brett, Corros. Sci. 44, 1949 (2002)
W.S. Li, J.L. Luo, Corros. Sci. 44, 1695 (2002)
J.W. Schultze, M.M. Lohrengel, Electrochim. Acta 45, 2499 (2000)
A.Q. Fu, Y.F. Cheng, Corros. Sci. 52, 612 (2010)
G.Z. Meng, C. Zhang, Y.F. Cheng, Corros. Sci. 50, 3116 (2008)
B.T. Lu, F. Song, M. Gao, M. Elboujdaini, Corros. Sci. 52, 4064 (2010)
D.G. Li, Y.R. Feng, Z.Q. Bai, J.W. Zhu, M.S. Zheng, Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 2837 (2008)
D.G. Li, Y.R. Feng, Z.Q. Bai, J.W. Zhu, M.S. Zheng, Electrochim. Acta 52, 7877 (2007)
R.N. Parkins, Corrosion 52, 363 (1996)
R.N. Parkins, Corros. Sci. 20, 147 (1980)
Z.Y. Liu, L. Lu, Y.Z. Huang, C.W. Du, X.G. Li, Corros. 70(7), 678 (2014)
L. Fan, Z.Y. Liu, C.W. Du, X.G. Li, Acta Metall. Sin. (in Chinese) 49, 689 (2013)
Z.Y. Liu, X.G. Li, C.W. Du, G.L. Zhai, Y.F. Cheng, Corros. Sci. 50, 2251 (2008)
B.R. Linter, G.T. Burstein, Corros. Sci. 41, 117 (1999)
J.K. Heuer, J.F. Stubbins, Corros. Sci. 41, 1231 (1999)
X. Liu, X. Mao, Scr. Metall. Mater. 33, 145 (1995)
Y.F. Cheng, J. Mater. Sci. 42, 2701 (2007)
C.S. Zhang, J.L. Luo, D. Munoz-Paniagua, P.R. Norton, Thin Solid Films 503, 149 (2006)
P. Liang, C.W. Du, X.G. Li, X. Chen, L. Zhang, Int. J. Min. Metall. Mater. 16, 407 (2009)
J. Kruger, Corros. Sci. 29, 149 (1989)
L. Fan, C.W. Du, Z.Y. Liu, X.G. Li, Int. J. Min. Metall. Mater. 20, 645 (2013)
D.H. Davies, G.T. Burstein, Corrosion 36, 416 (1980)
J.Q. Wang, A. Atrens, Corros. Sci. 45, 2199 (2003)
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51471034, 51131001 and 51171025). Many thanks to Dr. Ri Qiu for the fruitful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Available online at http://link.springer.com/journal/40195
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, L., Liu, ZY., Guo, WM. et al. A New Understanding of Stress Corrosion Cracking Mechanism of X80 Pipeline Steel at Passive Potential in High-pH Solutions. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 28, 866–875 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-015-0270-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-015-0270-4