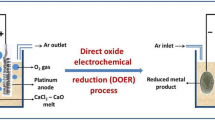
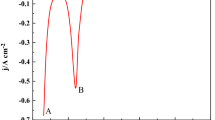
Abstract
Powder compacted and sintered Nb2O5 pellets were cathodically polarised against graphite anode in calcium chloride melt at 1173 K to study the influence of various factors on the electrochemical reduction of the oxide. The parameters were; duration and temperature of electrolysis, open porosity of pellets, nature of anode, mode of electrolysis and configuration of the oxide cathode. The experiments were also conducted in KCl, KCl-25 mol% CaCl2 and NaCl melts to understand the effect of melt composition on the electroreduction. Different Ca–Nb–O and Nb–O intermediates were found in the pellets electrolysed for different durations of time in CaCl2 melt which eventually reduced to Nb. The current efficiency of the process decreased with increasing duration of electrolysis. Decrease in electrolysis temperature from 1173 to 1073 K led to the decrease in the rate of reduction of the oxide pellets. Pellets with high open porosity reduced faster. Carbon contamination of the melt was relatively less when pyrolytic graphite was used as anode. Of all the melts studied, the reduction was found to be better in calcium chloride melt, that too when alumina crucible was used as container of the melt.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.J. Fray, T.W. Farthing, G.Z. Chen, Removal of Oxygen from Metal Oxides and Solid Solutions by Electrolysis in a Fused Salt, International Patent No. WO 9964638 (1999)
G.Z. Chen, D.J. Fray, T.W. Farthing, Nature 407, 361 (2000)
C. Schwandt, D.J. Fray, Electrochim. Acta 51, 66 (2005)
K.S. Mohandas, L. Shakila, N. Sanil, D. Sri Maha Vishnu, K. Nagarajan, in Molten Salts & Ionic Liquids, vol. 3, ed. by F. Kongoli (Flogen Stars Outreach, Montréal, 2011), p. 253
D. Sri Maha Vishnu, N. Sanil, L. Shakila, R. Sudha, K.S. Mohandas, K. Nagarajan, Electrochim. Acta 159, 124 (2015)
K.S. Mohandas, D.J. Fray, in Molten Salts and Ionic Liquids, vol. 3, ed. by F. Kongoli (Flogen Stars Outreach, Montréal, 2011), p. 219
E. Gordo, G.Z. Chen, D.J. Fray, Electrochim. Acta 49, 2195 (2004)
D. Sri Maha Vishnu, N. Sanil, L. Shakila, R. Sudha, K.S. Mohandas, K. Nagarajan, J. Electrochem. Soc. 160, D394 (2013)
D. Sri Maha Vishnu, N. Sanil, G. Panneerselvam, S.K. Mahato, K.V. Soja, K.S. Mohandas, K. Nagarajan, J. Electrochem. Soc. 160, D583 (2013)
K.S. Mohandas, N. Sanil, L. Shakila, D. Sri Maha Vishnu, K. Nagarajan, in Molten Salts and Ionic liquids, vol. 3, ed. by F. Kongoli, (Flogen Stars Outreach, Montréal, 2011), p. 239
D. Sri Maha Vishnu, N. Sanil, N. Murugesan, L. Shakila, C. Ramesh, K.S. Mohandas, K. Nagarajan, J. Nucl. Mater. 427, 200 (2012)
D. Sri Maha Vishnu, Studies on the Molten Salt Electro-deoxidation of Niobium, Titanium, Silicon and Uranium Oxides, Ph.D. Thesis, Homi Bhabha National Institute, Mumbai, December, 2013, p. 108–120
K.S. Mohandas, D.J. Fray, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 40, 685 (2009)
Q.S. Song, Q. Xu, X. Kang, J.H. Du, Z.P. Xi, J. Alloys. Compd. 490, 241 (2010)
X.Y. Yan, D.J. Fray, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 33, 685 (2002)
T. Wu, W. Xiao, X. Jin, C. Liu, D. Wang, G.Z. Chen, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 10, 1809 (2008)
X.Y. Yan, D.J. Fray, J. Mater. Res. 18, 346 (2003)
X.Y. Yan, D.J. Fray, J. Electrochem. Soc. 152, D12 (2005)
X.Y. Yan, D.J. Fray, J. Electrochem. Soc. 152, E308 (2005)
Q. Xu, L. Deng, Y. Wu, T. Ma, J. Alloys Compd. 396, 288 (2005)
S.L. Wang, Y. Xue, H. Sun, J. Electroanal. Chem. 595, 109 (2006)
S.M. Jeong, H.Y. Yoo, J.M. Hur, C.S. Seo, J. Alloys Compd. 452, 27 (2008)
G. Qiu, X. Feng, M. Liu, W. Tan, F. Liu, Electrochim. Acta 53, 4074 (2008)
Q.S. Song, Q. Xu, R. Tao, X. Kang, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 7, 272 (2012)
D. Sri Maha Vishnu, N. Sanil, L. Shakila, G. Panneerselvam, R. Sudha, K.S. Mohandas, K. Nagarajan, Electrochim. Acta 100, 51 (2013)
D. Sri Maha Vishnu, N. Sanil, L. Shakila, K.S. Mohandas, K. Nagarajan, Galvanostatic electrodeoxidation of niobium pentoxide in molten calcium chloride medium, in: 3rd International Symposium on Materials Chemistry, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Trombay, Mumbai, 7–11 December, 2010, p. 135
K. Yasuda, T. Nohira, Y.H. Ogata, Y. Ito, J. Electrochem. Soc. 152, D208 (2005)
K.S. Mohandas, Trans. Inst. Min Metall. C 122, 195 (2013)
K. Ono, Mater. Trans., JIM 45, 1660 (2004)
R. Bhagat, D. Dye, S.L. Raghunathan, R.J. Talling, D. Inman, B.K. Jackson, K.K. Rao, R.J. Dashwood, Acta Mater. 58, 5057 (2010)
G.Z. Chen, D.J. Fray, T.W. Farthing, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 32, 1041 (2001)
C. Schwandt, G.R. Doughty, D.J. Fray, Key Eng. Mater. 436, 13 (2010)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. G. Panneerselvam and Mr. S.K. Mahato for recording the XRD patterns and microscopic images of the samples, Mrs. Annie and Mrs. Soja K. Vijay for residual oxygen analysis of the samples and Mrs. L. Shakila and Mr. V. Arun Kumar for their help during some of the experiments. The first author sincerely acknowledges the grant of financial assistance from IGCAR, Department of Atomic Energy, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Available online at http://link.springer.com/journal/40195c.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sri Maha Vishnu, D., Sanil, N., Mohandas, K.S. et al. Factors Influencing the Direct Electrochemical Reduction of Nb2O5 Pellets to Nb Metal in Molten Chloride Salts. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 30, 218–227 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-016-0503-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-016-0503-1