Abstract
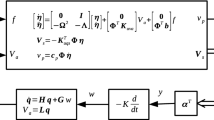
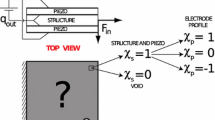
This work presents an optimal design methodology for piezoelectric material positioning in structures aiming at vibration measurements. The main objective is to find the optimal location of piezoelectric sensors using a suitable topology optimization strategy. The sensors location is determined by an optimization formulation that defines where the material should have piezoelectric properties. The objective of the optimization is maximizing observability, measured by means of the trace of the Gramian matrix. The control strategy development is based on a truncated modal system model. A case study and its results are presented and discussed, showing that the optimal placement of the piezoelectric sensors in a cantilever beam can be suitably achieved through the proposed approach.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvelid M (2008) Optimal position and shape of applied damping material. J Sound Vib 310(4):947–965
Balamurugan V, Narayanan S (2002) Finite element formulation and active vibration control study on beams using smart constrained layer damping (SCLD) treatment. J Sound Vib 249(2):227–250
Becker J, Fein O, Maess M, Gaul L (2006) Finite element-based analysis of shunted piezoelectric structures for vibration damping. Comput Struct 84(31):2340–2350
Bendsoe MP, Sigmund O (2013) Topology optimization: theory, methods, and applications. Springer Science and Business Media, New York
Carbonari RC, Silva EC, Nishiwaki S (2007) Optimum placement of piezoelectric material in piezoactuator design. Smart Mater Struct 16(1):207
Da Silveira OAA, Fonseca JSO, Santos IF (2015) Actuator topology design using the controllability gramian. Struct Multidiscip Optim 51(1):145–157
Donoso A, Bellido JC (2009) Distributed piezoelectric modal sensors for circular plates. J Sound Vib 319(1):50–57
Gawronski W (2004) Advanced structural dynamics and active control of structures. Springer Science and Business Media, New York
Gawronski W, Lim K (1996) Balanced actuator and sensor placement for flexible structures. Int J Control 65(1):131–145
Goncalves JF, Fonseca JS, Silveira OA (2016) A controllability-based formulation for the topology optimization of smart structures. Smart Struct Syst 17(5):773–793
Gupta V, Sharma M, Thakur N (2010) Optimization criteria for optimal placement of piezoelectric sensors and actuators on a smart structure: a technical review. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 21(12):1227–1243
Hać A, Liu L (1993) Sensor and actuator location in motion control of flexible structures. J Sound Vib 167(2):239–261
Kang Z, Wang R, Tong L (2011) Combined optimization of bi-material structural layout and voltage distribution for in-plane piezoelectric actuation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200(13):1467–1478
Kumar KR, Narayanan S (2008) Active vibration control of beams with optimal placement of piezoelectric sensor/actuator pairs. Smart Mater Struct 17(5):055008
Lee YS (2011) Comparison of collocation strategies of sensor and actuator for vibration control. J Mech Sci Technol 25(1):61–68
Lin ZQ, Gea HC, Liu ST (2011) Design of piezoelectric energy harvesting devices subjected to broadband random vibrations by applying topology optimization. Acta Mech Sin 27(5):730–737
Marcelo Tusset A, Piccirillo V, Bueno AM, Manoel Balthazar J, Sado D, Felix JLP, Brasil RMLRdF (2016) Chaos control and sensitivity analysis of a double pendulum arm excited by an rlc circuit based nonlinear shaker. J Vib Control 22(17):3621–3637
Mecchi ACL, Nader G, Silva ECN, Adamowski JC (2004) Development and characterization of a unimorph-type piezoelectric actuator applied to a michelson interferometer. Mechatronics 1(2):653–661
Moheimani SR, Fleming AJ (2006) Piezoelectric transducers for vibration control and damping. Springer Science and Business Media, New York
Pereira MdFV, Balthazar JM, dos Santos DA, Tusset AM, de Castro DF, Prado IAA (2017) A note on polynomial chaos expansions for designing a linear feedback control for nonlinear systems. Nonlinear Dyn 87(3):1653–1666
Peruzzi N, Chavarette FR, Balthazar JM, Tusset AM, Perticarrari ALPM, Brasil R (2016) The dynamic behavior of a parametrically excited time-periodic mems taking into account parametric errors. J Vib Control 22(20):4101–4110
Preumont A (2011) Vibration control of active structures: an introduction, vol 179. Springer Science and Business Media, New York
Qi H, Fang D, Yao Z (1997) Fem analysis of electro-mechanical coupling effect of piezoelectric materials. Comput Mater Sci 8(4):283–290
Qiu Zc, Zhang Xm, Wu Hx, Zhang Hh (2007) Optimal placement and active vibration control for piezoelectric smart flexible cantilever plate. J Sound Vib 301(3):521–543
Rubio WM, Silva EC, Paulino GH (2009) Toward optimal design of piezoelectric transducers based on multifunctional and smoothly graded hybrid material systems. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 20(14):1725–1746
Schwantz M (2002) Encyclopedia of smart materials. Wiley-Interscience Publication, New York
Tzou H, Tseng C (1990) Distributed piezoelectric sensor/actuator design for dynamic measurement/control of distributed parameter systems: a piezoelectric finite element approach. J Sound Vib 138(1):17–34
Vasques C, Rodrigues JD (2006) Active vibration control of smart piezoelectric beams: comparison of classical and optimal feedback control strategies. Comput Struct 84(22):1402–1414
Wang S (2004) A finite element model for the static and dynamic analysis of a piezoelectric bimorph. Int J Solids Struct 41(15):4075–4096
Wang X, Kang Z, Wang Y (2011) Topology design of slender piezoelectric actuators with repetitive component patterns. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 22(18):2161–2172
Wu B, Xu Z, Li Z (2007) A note on computing eigenvector derivatives with distinct and repeated eigenvalues. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng 23(3):241–251
Xu B, Ou J, Jiang J (2013) Integrated optimization of structural topology and control for piezoelectric smart plate based on genetic algorithm. Finite Elem Anal Design 64:1–12
Zorić ND, Simonović AM, Mitrović ZS, Stupar SN (2013) Optimal vibration control of smart composite beams with optimal size and location of piezoelectric sensing and actuation. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 24(4):499–526
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Brazilian agencies CAPES and CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Eduardo Souza de Cursi.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menuzzi, O., Fonseca, J.S.O., Perondi, E.A. et al. Piezoelectric sensor location by the observability Gramian maximization using topology optimization. Comp. Appl. Math. 37 (Suppl 1), 237–252 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-017-0517-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-017-0517-y