Abstract
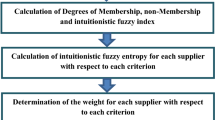
In this communication, based on the concept of \((\delta , \gamma )\)-norm entropy, an \((\delta , \gamma )\)-norm intuitionistic fuzzy entropy measure is introduced in the settings of intuitionistic fuzzy set theory. Some of its major properties are also proved. The performance of the proposed entropy measure is demonstrated using numerical examples. Based on the proposed intuitionistic fuzzy (IF) entropy, a new multiple-attribute decision-making method (MADM) considering the merits of subjective and objective weights has been introduced. Two methods of finding the weights of attributes are discussed. The proposed MADM method is effectively explained with the help of supplier selection example.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atanassov KT (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20:87–96
Atanassov KT, Gargov G (1989) Interval valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 31(3):343–349
Aczel J, Daroczy Z (1975) On measures of information and their characterization. Academic Press, New York
Burillo P, Bustince H (2001) Entropy on intuitionistic fuzzy sets and on interval-valued fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 118:305–316
Boekee DE, Vander Lubbe JCA (1980) The R-norm information measure. Inf Control 45:136–155
Boran FE, Genc S, Akay D (2011) Personnel selection based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Hum Factors Ergon Manuf Serv Ind 21:493–503
Chen T, Li C (2010) Determining objective weights with intuitionistic fuzzy entropy measures: a comparative analysis. Inf Sci 180:4207–4222
Chu ATW, Kalaba RE, Spingarn K (1979) A comparison of two methods for determining the weights of belonging to fuzzy sets. J Optimiz Theor App 27:531–538
Choo EU, Wedley WC (1985) Optimal criterion weights in repetitive multicriteria decision making. J Oper Res Soc 36:983–992
De Luca A, Termini S (1972) A definition of non-probabilistic entropy in the setting of fuzzy set theory. Inf Control 20:301–312
De SK, Biswas R, Roy AR (2000) Some operations on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 114:477–484
Fan ZP (1996) Complicated multiple attribute decision making: theory and applications. Ph.D. Dissertation, Northeastern university, Shenyang, China
Hung WL, Yang MS (2006) Fuzzy entropy on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 21(4):443–451
Hooda DS (2004) On generalized measures of fuzzy entropy. Mathematica Slovaca 54:315–325
Hwang CL, Lin MJ (1987) Group decision making under multiple criteria: methods and applications. Springer, Berlin
Hung W (2003) A note on entropy of intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 11(5):627–633
Hwang CM, Yang MS (2008) On entropy of fuzzy sets. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 16(4):519–527
Joshi R, Kumar S (2017) An \((R, S)\)-norm fuzzy information measure with its applications in multiple attribute decision making. Computational and applied mathematics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-017-0491-4
Joshi R, Kumar S (2016) \((R, S)\)-norm information measure and a relation between coding and questionnaire theory. Open Syst Inf Dyn 23(3):1–12
Joshi R, Kumar S (2017b) Parametric \((R, S)\)-norm entropy on intuitionistic fuzzy sets with a new approach in multiple attribute decision making. Fuzzy Inf Eng 9:181–203
Kim SH, Choi SH, Kim IK (1999) An interactive procedure for multiple attribute decision making with incomplete information: range based approach. Eur J Oper Res 118:139–152
Liu M, Ren H (2014) A new intuitionistic fuzzy entropy and application in multi-attribute decision-making. Information 5:587–601
Mao J, Yao D, Wang C (2013) A novel cross-entropy and entropy measures of IFSs and their applications. Knowl Based Syst 48:37–45
Opricovic S (1998) Multi-criteria optimization of civil engineering systems. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Belgrade, Belgrade, Serbia
Pal NR, Bustince H, Pagola M, Mukherjee U, Goswami D, Beliakov G (2013) Uncertainties with Atanassov’s intuitionistic fuzzy sets: fuzziness and lack of knowledge. Inf Sci 228:61–74
Szmidt E, Kacprzyk J (2002) Using intuitionistic fuzzy sets in group decision-making. Control Cybern 31:1037–1054
Shannon CE (1948) The mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J 27(379–423):623–656
Saaty TL (1980) The analytic hierarchy process. McGraw Hill, New York
Szmidt E, Kacprzyk J (2001) Entropy for intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 118(3):467–477
Taneja IJ (1975) A study of generalized measures of information theory. Ph.D. Thesis, New Delhi
Vlachos IK, Sergiadis GD (2007) Intuitionistic fuzzy information—applications to pattern recognition. Pattern Recognit Lett 28:197–206
Verma R, Sharma BD (2014) On intuitionistic fuzzy entropy of order-\(\alpha \). Adv Fuzzy Syst 2014:1–8 (Article ID 789890)
Wang J, Wang P (2012) Intuitionistic linguistic fuzzy multi-critria decision-making method based on intuitionistic fuzzy entropy. Control Decis 27:1694–1698
Wang W, Xin X (2005) Distance measure between intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Pattern Recognit Lett 26:2063–2069
Xia M, Xu Z (2012) Entropy/cross entropy-based group decision making under intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Inf Fusion 13:31–47
Xu ZS (2007) Intuitionistic fuzzy aggregation operators. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 15:1179–1187
Xu ZS, Yager RR (2006) Some geometric aggregation operators based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Int J Gen Syst 35:417–433
Yazdani M, Chatterjee P, Zavadskas EK, Hashemkhani Zolfani S (2016a) Integrated QFD-MCDM framework for green supplier selection. J Clean Prod 142:3728–3740
Yazdani M, Hashemkhani Zolfani S, Zavadskas EK (2016b) New integration of MCDM methods and QFD in the selection of green suppliers. J Bus Econ Manag 17:1097–1113
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8:338–353
Zhang H, Zhang W, Mei C (2009) Entropy on interval-valued fuzzy sets based on distance and its relationship with similarity measure. Knowl Based Syst 22(6):449–454
Zeng W, Yu F, Yu X, Chen H, Wu S (2009) Entropy on intuitionistic fuzzy set based on similarity measure. Int J Innovative Comput Inf Control 5(12):4737–4744
Zhao N, Xu Z, Liu F (2015) Uncertainty measures for hesitant fuzzy information. Int J Intell Syst 00:1–19
Zhao N, Xu Z (2016) Entropy measures for interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy information from a comparative perspective and their application to decision making. Informatica 27(1):203–228
Zadeh LA (1975) The concept of linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning-I. Inf Sci 8:199–249
Zhao J, Xiao-Yue You, Hu-Chen Liu, Song-Man Wu (2017) An extended VIKOR method using intuitionistic fuzzy sets and combination weights for supplier selection. Symmetry. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym9090169
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions and comments which enhanced our knowledge and improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Anibal Tavares de Azevedo.
Appendix: proofs of properties
Appendix: proofs of properties
Proof of Theorem 3.2
Bifurcate \(X=\{q_1, q_2, \ldots , q_n\}\) into two parts \(X_1\) and \(X_2\), such that
This implies that for all \(q_i\in X_1\),
and for all \(q_i\in X_2\),
Using (3.5), we have
Similarly,
This proves the theorem. \(\square \)
Proof of Theorem 3.3
Proof of Theorem 3.3 follows directly from the proofs of Properties E1 and E2. \(\square \)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, R., Kumar, S. An intuitionistic fuzzy \((\delta , \gamma )\)-norm entropy with its application in supplier selection problem. Comp. Appl. Math. 37, 5624–5649 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-018-0656-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-018-0656-9
Keywords
- \(\delta \)-Norm entropy
- \((\delta, \gamma)\)-Norm entropy
- Intuitionistic fuzzy entropy
- Multi-attribute decision-making
- VIKOR