Abstract
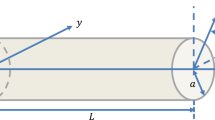
The following research work deals with the size-dependent dynamic instability of suspended nanowires in the presence of Casimir force and surface effects. Specifically, the Casimir-induced instability of nanostructures with circular cross-section and cylinder-plate geometry is studied. Following the Gurtin–Murdoch model and nonlocal elasticity, the governing equation of motion for nanowires is derived. To express the Casimir attraction of cylinder-plate geometry, two approaches, e.g. proximity force approximation (PFA) for small separations and Dirichlet asymptotic approximation for large separations are studied. To overcome the difficulties for solving a nonlinear problem, a step-by-step numerical method is utilized. The effects of nonlocal parameter, surface energy and vacuum fluctuations on the dynamic instability characteristic and adhesion time of nanowires are studied. It is observed that the phase portrait of Casimir-induced nanowires exhibit periodic and homoclinic orbits.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang ZL (2004) Mechanical properties of nanowires and nanobelts. Dekker Encycl Nanosci Nanotechnol 2:1773–1786
Craighead HG (2000) Nanoelectromechanical systems. Science 290:1532–1535
Wang MCP, Gates BD (2009) Directed assembly of nanowires. Mater Today 12:34–43
Khajeansari A, Baradaran GH, Yvonnet J (2012) An explicit solution for bending of nanowires lying on Winkler–Pasternak elastic substrate medium based on the Euler–Bernoulli beam theory. Int J Eng Sci 52:115–128
Serre P, Ternon C, Stambouli V, Periwal P, Baron T (2013) Fabrication of silicon nanowire networks for biological sensing. Sens Actuators B 182:390–395
Patolsky F, Zheng G, Lieber CM (2006) Nanowire-based biosensors. Anal Chem 78(13):4260–4269
Husain A, Hone J, Postma HWC, Huang XMH, Drake T, Barbic M, Scherer A, Roukes ML (2003) Nanowire-based very-high-frequency electromechanical resonator. Appl Phys Lett 83:1240
Feng XL, He R, Yang P, Roukes ML (2007) Very high frequency silicon nanowire electromechanical resonators. Nano Lett 7(7):1953–1959
Farrokhabadi A, Abadian N, Rach R, Abadyan M (2014) Theoretical modelling of the Casimir force-induced instability in freestanding nanowires with circular cross-section. Phys E 63:67–80
Zou J, Marcet Z, Rodriguez AW, Reid MTH, McCauley AP, Kravchenko II, Lu T, Bao Y, Johnson SG, Chan HB (2013) Casimir forces on a silicon micromechanical chip. Nat Commun 4:1845
Lombardo FC, Mazzitelli FD, Villar PI (2008) Numerical evaluation of the Casimir interaction between cylinders. Phys Rev D 78:085009
Emig T, Jaffe RL, Kardar M, Scardicchio A (2006) Casimir interaction between a plate and a cylinder. Phys Rev Lett 96:080403
Terças H, Ribeiro S, Mendonça JT (2015) Quasi-polaritons in Bose-Einstein condensates induced by Casimir–Polder interaction with graphene. J Phys Condens Matter 27:214011
Ali S, Terças H, Mendonça JT (2011) Nonlocal plasmon excitation in metallic nanostructures. Phys Rev B 83:153401
Bordag M, Mohideen U, Mostepanenko VM (2001) New developments in the Casimir effect. Phys Rep 353:1–205
Casimir HBG (1948) On the attraction between two perfectly conducting plates. Proc K Ned Akad Wet 51:793
Guo JG, Zhao YP (2004) Influence of van der Waals and Casimir Forces on Electrostatic Torsional Actuators. J Microelectromech Syst 13(6):1027
Lin WH, Zhao YP (2005) Nonlinear behavior for nanoscales electrostatic actuators with Casimir force. Chaos Solitons Fractals 23:1777
Casimir HBG, Polder D (1948) The influence of retardation of the London-van der Waals forces. Phys Rev 73:360
Teo LP (2011) First analytic correction to the proximity force approximation in the Casimir effect between two parallel cylinders. Phys Rev D 84:065027
Teo LP (2011) Casimir, interaction between a cylinder and a plate at finite temperature: exact results and comparison to proximity force approximation. Phys Rev D 84:025022
Barretta R, Feo L, Luciano R, Marotti de Sciarra F (2015) Variational formulations for functionally graded nonlocal Bernoulli–Euler nanobeams. Compos Struct 129:80–89
Sedighi HM, Daneshmand F, Abadyan M (2015) Modified model for instability analysis of symmetric FGM double-sided nano-bridge: corrections due to surface layer, finite conductivity and size effect. Compos Struct 132:545–557
Sedighi HM (2014) The influence of small scale on the Pull-in behavior of nonlocal nano-Bridges considering surface effect, Casimir and van der Waals attractions. Int J Appl Mech. doi:10.1142/S1758825114500306
Koochi A, Kazemi A, Khandani F, Abadyan M (2012) Influence of surface effects on size-dependent instability of nano-actuators in the presence of quantum vacuum fluctuations. Phys Scr 85(3):035804
Abdi J, Koochi A, Kazemi AS, Abadyan M (2011) Modeling the effects of size dependence and dispersion forces on the pull-in instability of electrostatic cantilever NEMS using modified couple stress theory. Smart Mater Struct 20:055011
Karimipour I, Tadi Beni Y, Koochi A, Abadyan M (2015) Using couple stress theory for modeling the size-dependent instability of double-sided beam-type nanoactuators in the presence of Casimir force. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng. doi:10.1007/s40430-015-0385-6
AkbarzadehKhorshidi M, Shariati M (2015) Free vibration analysis of sigmoid functionally graded nanobeams based on a modified couple stress theory with general shear deformation theory. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng. doi:10.1007/s40430-015-0388-3
Sedighi HM (2014) Size-dependent dynamic pull-in instability of vibrating electrically actuated micro-beams based on the strain gradient elasticity theory. Acta Astronaut 95:111–123
Shojaeian M, Tadi Beni Y, Ataei H (2016) Electromechanical buckling of functionally graded electrostatic nanobridges using strain gradient theory. Acta Astronaut 118:62–71
Ansari R, Gholami R, Sahmani S (2013) Size-dependent vibration of functionally graded curved microbeams based on the modified strain gradient elasticity theory. Arch Appl Mech 83(10):1439–1449
Daneshmand F (2014) Combined strain-inertia gradient elasticity in free vibration shell analysis of single walled carbon nanotubes using shell theory. Appl Math Comput 243:856–869
Wang ZQ, Zhao YP, Huang ZP (2010) The effects of surface tension on the elastic properties of nano structures. Int J Eng Sci 48:140–150
Dingrevillea R, Qua J, Cherkaoui M (2005) Surface free energy and its effect on the elastic behavior of nano-sized particles, wires and films. J Mech Phys Solids 53(8):1827–1854
Gurtin ME, Murdoch AI (1978) Surface stress in solids. Int J Solids Struct 14:431–440
Sedighi HM (2015) Modeling of surface stress effects on the dynamic behavior of actuated non-classical nano-bridges. Trans Can Soc Mech Eng 39(2):137–151
Eltaher MA, Mahmoud FF, Assie AE, Meletis EI (2013) Coupling effects of nonlocal and surface energy on vibration analysis of nanobeams. Appl Math Comput 224:760–774
Fu Y, Zhang J (2011) Size-dependent pull-in phenomena in electrically actuated nanobeams incorporating surface energies. Appl Math Model 35(2):941–951
Koochi A, Hosseini-Toudeshky H, Ovesy HR, Abadyan M (2013) Modeling the influence of surface effect on instability of nano-cantilever in presence of Van der Waals force. Int J Struct Stab Dyn 13:1250072
Zhang WM, Yan H, Peng ZK, Meng G (2014) Electrostatic pull-in instability in MEMS/NEMS: a review. Sens Actuators A 214:187–218
Bordag M, Mohideen U, Mostepanenko VM (2001) New developments in the Casimir effect. Phys Rep 353:1
Lamoreaux SK (2005) The Casimir force: background, experiments, and applications. Rep Prog Phys 68:201–236
Chan HB, Bao Y, Zou J, Cirelli RA, Klemens F, Mansfield WM, Pai CS (2008) Measurements of the Casimir force between a gold sphere and a silicon surface with nanoscale v trench arrays. Phys Rev Lett 101:030401
Li H, Kardar M (1991) Fluctuation-induced forces between rough surfaces. Phys Rev Lett 67:3275
Buscher R, Emig T (2005) Geometry and spectrum of Casimir forces. Phys Rev Lett 94:133901
Rahi SJ, Emig T, Jaffe RL, Kardar M (2008) Casimir forces between cylinders and plates. Phys Rev A 78:012104
Bulgac A, Magierski P, Wirzba A (2006) Scalar Casimir effect between Dirichlet spheres or a plate and a sphere. Phys Rev D 73:025007
Abbasnejad B, Rezazadeh G, Shabani R (2013) Stability analysis of a capacitive fgm micro-beam using modified couple stress theory. Acta Mech Solida Sin 26(4):427–440
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Kátia Lucchesi Cavalca Dedini.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sedighi, H.M., Bozorgmehri, A. Nonlinear vibration and adhesion instability of Casimir-induced nonlocal nanowires with the consideration of surface energy. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 39, 427–442 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-016-0530-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-016-0530-x