Abstract
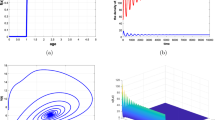
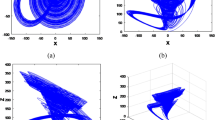
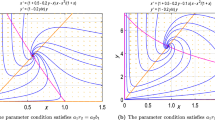
This paper presents a prey–predator harvesting model with time delay for bifurcation analysis. We consider the parameters of the proposed model with imprecise data as form of interval in nature, due to the lack of precise numerical information of the biological parameters such as prey population growth rate and predator population decay rate. The proposed prey–predator harvesting model is presented with Holling type of predation and time delay under impreciseness of parameters by introducing parametric functional form of interval number. Our study reveals that along with delay and harvesting efforts role on the stability of the system, interval parameters also play a significant role. Computer simulations of numerical examples are given to explain our proposed imprecise model and for observing of chaotic behaviors.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoekstra J, Bergh JCJMV (2005) Harvesting and conservation in a predator–prey system. J Econ Dyn Control 29:1097–1120
Palma A, Olivares E (2012) Optimal harvesting in a predator–prey model with Allee effect and sigmoid functional response. Appl Math Comput 36:1864–1874
Gupta RP, Chandra P (2013) Bifurcation analysis of modified Leslie-Gower predator–prey model with Michaelis–Menten type prey harvesting. J Math Anal Appl 338:278–295
Pal D, Mahapatra GS, Samanta GP (2012) A proportional harvesting dynamical model with fuzzy intrinsic growth rate and harvesting quantity. Pac Asian J Math 6:199–213
Duncan S, Hepburn C, Papachristodoulou A (2011) Optimal harvesting of fish stocks under a time-varying discount rate. J Theor Biol 269:166–173
Anita L, Anita S, Arnautu V (2009) Optimal harvesting for periodic age-dependent population dynamics with logistic term. Appl Math Comput 215:2701–2715
Chen F, Ma Z, Zhang H (2012) Globala symptotical stability of the positive equilibrium of the Lotka-Volterra prey–predator model incorporating a constant number of prey refuges. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 13:2790–2793
Chen L, Chen F, Wang Y (2013) Influence of predator mutual interference and prey refuge on Lotka–Volterra predator–prey dynamics. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 18:3174–3180
Wang H, Morrison W, Sing A, Weiss H (2009) Modeling inverted biomass pyramids and refuges in ecosystems. Ecol Model 220:1376–1382
Rebaza J (2012) Dynamics of prey threshold harvesting and refuge. J Comput Appl Math 236:1743–1752
Das KP, Roy S, Chattopadhyay J (2009) Effect of disease-selective predation on prey infected by contact and external sources. Biosystems 95:188–199
Bairagi N, Chaudhuri S, Chattopadhyay J (2009) Harvesting as a disease control measure in an eco-epidemiological system: a theoretical study. Math Biosci 217:134–144
Hethcote HW, Wang W, Han L, Ma Z (2004) A predator–prey model with infected prey. Theor Popul Biol 66:259–268
Pal AK, Samanta GP (2010) Stability analysis of an eco-epidemiological model incorporating a Prey Refuge. Nonlinear Anal Model Control 15:473–491
Samanta GP (2011) Analysis of a nonautonomous dynamical model of diseases through droplet infection and direct contact. Appl Math Comput 217:5870–5888
Gopalsamy K (1983) Harmless delay in model systems. Bull Math Biol 45:295–309
Kar TK (2003) Selective harvesting in a prey–predator fishery with time delay. Math Comput Model 38:449–458
Yongzhen P, Shuping L, Changguo L (2011) Effect of delay on a predator–prey model with parasite infection. Nonlinear Dyn 63:311–321
Qu Y, Wei J (2007) Bifurcation analysis in a time-delay model for prey–predator growth with stage-structure. Nonlinear Dyn 49:285–294
Shao Y (2010) Analysis of a delayed predator–prey system with impulsive diffusion between two patches. Math Comput Model 52:120–127
Jiao J, Chen I, Yang X, Cai S (2009) Dynamical analysis of a delayed predator–prey model with impulsive diffusion between two patches. Math Comput Simul 80:522–532
MacDonald M (1989) Biological delay systems: linear stability theory. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Misra AK, Dubey B (2010) A ratio-dependent predator–prey model with delay and harvesting. J Biol Syst 18:437–453
Zhang J (2012) Bifurcation analysis of a modified Holling–Tanner predator–prey model with time delay. Appl Math Model 36:1219–1231
Bandyopadhyay M, Banerjee S (2006) A stage-structured prey–predator model with discrete time delay. Appl Math Comput 182:1385–1398
Bassanezi RC, Barros LC, Tonelli A (2000) Attractors and asymptotic stability for fuzzy dynamical systems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 113:473–483
Barros LC, Bassanezi RC, Tonelli PA (2000) Fuzzy modelling in population dynamics. Ecol Model 128:27–33
Peixoto M, Barros LC, Bassanezi RC (2008) Predator–prey fuzzy model. Ecol Model 214:39–44
Tuyako MM, Barros LC, Bassanezi RC (2009) Stability of fuzzy dynamic systems. Int J Uncertain Fuzzyness Knowl Based Syst 17:69–83
Pal D, Mahapatra GS, Samanta GP (2013) Quota harvesting model for a single species population under fuzziness. Int J Math Sci 12:33–46
Abundo M (1991) Stochastic model for predator–prey systems: basic properties, stability and computer simulation. J Math Biol 29:495–511
Rudnicki R (2003) Long-time behaviour of a stochastic prey–predator model. Stoch Process Appl 108:93–107
Liu M, Wang K (2012) Extinction and global asymptotical stability of a nonautonomous predator–prey model with random perturbation. Appl Math Model 36:5344–5353
Vasilova M (2013) Asymptotic behavior of a stochastic Gilpin–Ayala predator–prey system with time-dependent delay. Math Comput Model 57:764–781
Aguirre P, Olivares EG, Torres S (2013) Stochastic predator–prey model with Allee effect on prey. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 14:768–779
Mahapatra GS, Mandal TK (2012) Posynomial parametric geometric programming with interval valued coefficient. J Optim Theory Appl 154:120–132
Pal D, Mahapatra GS, Samanta GP (2013) Optimal harvesting of prey–predator system with interval biological parameters: a bioeconomic model. Math Biosci 24:181–187
Kuang Y, Freedman HI (1988) Uniqueness of limit cycles in Gause-type models of predator–prey systems. Math Biosci 88:67–84
Freedman HI, Hari Rao V Sree (1983) The trade-of between mutual interference and time lags in predator–prey systems. Bull Math Biol 45:991–1003
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the Editor and Referees for their encouragement and constructive comments in revising the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pal, D., Mahapatra, G.S. & Samanta, G.P. Bifurcation analysis of predator–prey model with time delay and harvesting efforts using interval parameter. Int. J. Dynam. Control 3, 199–209 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-014-0083-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-014-0083-8