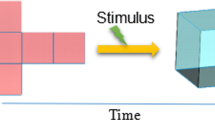
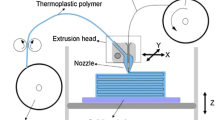
Abstract
In 4D printing, a target 3D object that can self-transform or self-assemble over time is created using a printer with smart materials. Since the advent of 4D printing, much research has been conducted on smart materials and application of 4D printing in diverse areas. However, research and development of 4D printing software is very limited due to the fact that 4D printing technology is still a novelty. Nevertheless, the time characteristics of 4D printing require appropriate 4D printing software to produce effective 4D printing outputs. In this article, we first introduce 4D printing technology and discuss its application in various fields. Then, we focus on the software required for 4D printing. More specifically, we present six types of software solutions needed to fully support corresponding stages in the 4D printing process: simulation, modeling, slicing, host/firmware, monitoring, and printing management software (PMS), respectively. We discuss how each software solution can sufficiently carry out the designated functions at each stage of the 4D printing process and propose that these software solutions can together provide all of the required operations for 4D printing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ko, H., Moon, S. K., and Hwang, J., “Design for Additive Manufacturing in Customized Products,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 11, pp. 2369–2375, 2015.
Moon, S. K., Tan, Y. E., Hwang, J., and Yoon, Y.-J., “Application of 3D Printing Technology for Designing Light-Weight Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Wing Structures,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Tech., Vol. 1, No. 3, pp. 223–228, 2014.
Kang, H. S., Lee, J. Y., Choi, S., Kim, H., Park, J. H., et al., “Smart Manufacturing: Past Research, Present Findings, and Future Directions,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Tech., Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 111–128, 2016.
Kim, M.-S., Chu, W.-S., Kim, Y.-M., Avila, A. P. G., and Ahn, S.-H., “Direct Metal Printing of 3D Electrical Circuit Using Rapid Prototyping,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 10, No. 5, pp. 147–150, 2009.
Chu, W.-S., Kim, C.-S., Lee, H.-T., Choi, J.-O., Park, J.-I., et al., “Hybrid Manufacturing in Micro/Nano Scale: A Review,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Tech., Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 75–92, 2014.
Kim, S., Lee, J., and Choi, B., “3D Printed Fluidic Valves for Remote Operation Via External Magnetic Field,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 17, No. 7, pp. 937–942, 2016.
Ahn, D.-G., “Direct Metal Additive Manufacturing Processes and their Sustainable Applications for Green Technology: A Review,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Tech., Vol. 3, No. 4, pp. 381–395, 2016.
Chua, Z. Y., Ahn, I. H., and Moon, S. K., “Process Monitoring and Inspection Systems in Metal Additive Manufacturing: Status and Applications,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Tech., Vol. 4, No. 2, pp. 235–245, 2017.
Anwar, H., Din, I., and Park, K., “Projector Calibration for 3D Scanning Using Virtual Target Images,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 13, No. 1, pp. 125–131, 2012.
Kim, L.-S., Nakahashi, K., Xu, Z.-Z., Xiao, H., and Lyu, S.-K., “Three-Dimensional Building-Cube Method for Inviscid Compressible Flow Computations,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 13, pp. 2673–2681, 2015.
Jang, S. H., Oh, S. T., Lee, I. H., Kim, H.-C., and Cho, H. Y., “3-Dimensional Circuit Device Fabrication Process Using Stereolithography and Direct Writing,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 7, pp. 1361–1367, 2015.
Lee, C.-M., Woo, W.-S., Baek, J.-T., and Kim, E.-J., “Laser and arc Manufacturing Processes: A Review,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 17, No. 7, pp. 973–985, 2016.
Yoon, H.-S., Lee, J.-Y., Kim, H.-S., Kim, M.-S., Kim, E.-S., et al., “A Comparison of Energy Consumption in Bulk Forming, Subtractive, and Additive Processes: Review and Case Study,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Tech., Vol. 1, No. 3, pp. 261–279, 2014.
Qin, Z., Compton, B. G., Lewis, J. A., and Buehler, M. J., “Structural Optimization of 3D-Printed Synthetic Spider Webs for High Strength,” Nature Communications, Vol. 6, Article No. 7038, 2015.
Ko, H. J., Noh, K. S., and Lee, Y. G., “Survey of Materials for 4D Printing,” Proc. of the Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers Spring & Autumn Conference, pp. 43–43, 2016.
Ge, Q., Dunn, C. K., Qi, H. J., and Dunn, M. L., “Active Origami by 4D Printing,” Smart Materials and Structures, Vol. 23, No. 9, Paper No. 094007, 2014.
Ge, Q., Qi, H. J., and Dunn, M. L., “Active Materials by Four-Dimension Printing,” Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 103, No. 13, Paper No. 131901, 2013.
Khoo, Z. X., Teoh, J. E. M., Liu, Y., Chua, C. K., Yang, S., et al., “3D Printing of Smart Materials: A Review on Recent Progresses in 4D Printing,” Virtual and Physical Prototyping, Vol. 10, No. 3, pp. 103–122, 2015.
Monzón, M., Paz, R., Pei, E., Ortega, F., Suárez, L., et al., “4D Printing: Processability and Measurement of Recovery Force in Shape Memory Polymers,” The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 89, No. 5, pp. 1827–1836, 2017.
Huang, L., Jiang, R., Wu, J., Song, J., Bai, H., et al., “Ultrafast Digital Printing Toward 4D Shape Changing Materials,” Advanced Materials, Vol. 29, No. 7, DOI: 10.1002/adma.201605390, 2017.
Buffington, J., “The Future of Manufacturing: An End to Mass Production,” Frictionless Markets, pp. 49–65, 2016.
Ghi, A. and Rossetti, F., “4D Printing: An Emerging Technology in Manufacturing?” Digitally Supported Innovation, pp. 171–178, 2016.
Campbell, T. A., Tibbits, B., and Garrett, B., “The Next Wave: 4D Printing Programming the Material World,” Atlantic Council Report, 2014.
Pei, E., “4D Printing-Revolution or Fad?” Assembly Automation, Vol. 34, No. 2, pp. 123–127, 2014.
Choi, J., Kwon, O.-C., Jo, W., Lee, H. J., and Moon, M.-W., “4D Printing Technology: A Review,” 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing, Vol. 2, No. 4, pp. 159–167, 2015.
Raviv, D., Zhao, W., McKnelly, C., Papadopoulou, A., Kadambi, A., et al., “Active Printed Materials for Complex Self-Evolving Deformations,” Scientific Reports, Vol. 4, Article No. 7422, 2014.
Mao, Y., Yu, K., Isakov, M. S., Wu, J., Dunn, M. L., et al., “Sequential Self-Folding Structures by 3D Printed Digital Shape Memory Polymers,” Scientific Reports, Vol. 5, Article No. 13616, 2015.
RNCOS, “Global 4D Printing Market Outlook 2027,” http://www.rncos.com/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
MarketsandMarkets, “4D Printing Market by Material, End User & Geography-Global Trends & Forecasts to 2019-2025,” 2015.
Bodaghi, M., Damanpack, A., and Liao, W., “Self-Expanding/Shrinking Structures by 4D Printing,” Smart Materials and Structures, Vol. 25, No. 10, Paper No. 105034, 2016.
Coulter, F. B. and Ianakiev, A., “4D Printing Inflatable Silicone Structures,” 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing, Vol. 2, No. 3, pp. 140–144, 2015.
Pei, E., “4D Printing: Dawn of an Emerging Technology Cycle,” Assembly Automation, Vol. 34, No. 4, pp. 310–314, 2014.
Ahn, S.-H., Lee, K.-T., Kim, H.-J., Wu, R., Kim, J.-S., et al., “Smart Soft Composite: An Integrated 3D Soft Morphing Structure Using Bend-Twist Coupling of Anisotropic Materials,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 13, No. 4, pp. 631–634, 2012.
Alt, H. and Godau, M., “Computing the Fréchet Distance between Two Polygonal Curves,” International Journal of Computational Geometry & Applications, Vol. 5, Nos. 1-2, pp. 75–91, 1995.
Aronov, B., Har-Peled, S., Knauer, C., Wang, Y., and Wenk, C., “Fréchet Distance for Curves, Revisited,” Algorithms-ESA 2006, pp. 52–63, 2006.
Maheshwari, A. and Yi, J., “On Computing Fréchet Distance of Two Paths on a Convex Polyhedron,” Proc. of the Euro CG, pp. 41–44, 2005.
Kwok, T.-H., Wang, C. C., Deng, D., Zhang, Y., and Chen, Y., “Four-Dimensional Printing for Freeform Surfaces: Design Optimization of Origami and Kirigami Structures,” Journal of Mechanical Design, Vol. 137, No. 11, Paper No. 111413, 2015.
Bakarich, S. E., Gorkin, R., and Spinks, G. M., “4D Printing with Mechanically Robust, Thermally Actuating Hydrogels,” Macromolecular Rapid Communications, Vol. 36, No. 12, pp. 1211–1217, 2015.
Teoh, J., Chua, C. K., Liu, Y., An, J., and Li, Y., “Preliminary Investigation of 4D Printing Technology for Deployable UAV Development,” Proc. of the 2nd International Conference on Progress in Additive Manufacturing, 2016.
Naficy, S., Gately, R., Gorkin, R., Xin, H., and Spinks, G. M., “4D Printing of Reversible Shape Morphing Hydrogel Structures,” Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, Vol. 302, No. 1, DOI: 10.1002/mame.201600212, 2017.
Teoh, J., An, J., Chua, C., Lv, M., Krishnasamy, V., et al., “Hierarchically Self-Morphing Structure through 4D Printing,” Virtual and Physical Prototyping, Vol. 12, No. 1, pp. 61–68, 2017.
Okuzaki, H., Kuwabara, T., Funasaka, K., and Saido, T., “Humidity-Sensitive Polypyrrole Films for Electro-Active Polymer Actuators,” Advanced Functional Materials, Vol. 23, No. 36, pp. 4400–4407, 2013.
Lu, H., Liu, Y., Gou, J., Leng, J., and Du, S., “Electrical Properties and Shape-Memory Behavior of Self-Assembled Carbon Nanofiber Nanopaper Incorporated with Shape-Memory Polymer,” Smart Materials and Structures, Vol. 19, No. 7, Paper No. 075021, 2010.
Hu, Y., Wu, G., Lan, T., Zhao, J., Liu, Y., et al., “A Graphene-Based Bimorph Structure for Design of High Performance Photoactuators,” Advanced Materials, Vol. 27, No. 47, pp. 7867–7873, 2015.
Mu, J., Hou, C., Wang, H., Li, Y., Zhang, Q., et al., “Origami-Inspired Active Graphene-Based Paper for Programmable Instant Self-Folding Walking Devices,” Science Advances, Vol. 1, No. 10, DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1500533, 2015.
Deng, D. and Chen, Y., “Origami-Based Self-Folding Structure Design and Fabrication Using Projection Based Stereolithography,” Journal of Mechanical Design, Vol. 137, No. 2, Paper No. 021701, 2015.
Gou, M., Qu, X., Zhu, W., Xiang, M., Yang, J., et al., “Bio-Inspired Detoxification Using 3D-Printed Hydrogel Nanocomposites,” Nature Communications, Vol. 5, DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4774, 2014.
Nguyen, D. G., Funk, J., Robbins, J. B., Crogan-Grundy, C., Presnell, S. C., et al., “Bioprinted 3D Primary Liver Tissues Allow Assessment of Organ-Level Response to Clinical Drug Induced Toxicity in Vitro,” PloS One, Vol. 11, No. 7, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158674, 2016.
Chae, M. P., Hunter-Smith, D. J., De-Silva, I., Tham, S., Spychal, R. T., et al., “Four-Dimensional (4D) Printing: A New Evolution in Computed Tomography-Guided Stereolithographic Modeling. Principles and Application,” Journal of Reconstructive Microsurgery, Vol. 31, No. 6, pp. 458–463, 2015.
Ho, C. M. B., Ng, S. H., and Yoon, Y.-J., “A Review on 3D Printed Bioimplants,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 5, pp. 1035–1046, 2015.
Kapsali, V., Toomey, A., Oliver, R., and Tandler, L., “Biomimetic Spatial and Temporal (4D) Design and Fabrication,” Proc. of the Conference on Biomimetic and Biohybrid Systems, pp. 387–389, 2013.
Vatani, M., Lu, Y., Engeberg, E. D., and Choi, J.-W., “Combined 3D Printing Technologies and Material for Fabrication of Tactile Sensors,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 7, pp. 1375–1383, 2015.
Tsai, E. Y., “4D Printing: Towards Biomimetic Additive Manufacturing,” Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2012.
Mulakkal, M. C., Seddon, A. M., Whittell, G., Manners, I., and Trask, R. S., “4D Fibrous Materials: Characterising the Deployment of Paper Architectures,” Smart Materials and Structures, Vol. 25, No. 9, Paper No. 095052, 2016.
Bakarich, S. E., Gorkin, R., Naficy, S., Gately, R., and Spinks, G. M., “3D/4D Printing Hydrogel Composites: A Pathway to Functional Devices,” MRS Advances, Vol. 1, No. 8, pp. 521–526, 2016.
Gao, B., Yang, Q., Zhao, X., Jin, G., Ma, Y., et al., “4D Bioprinting for Biomedical Applications,” Trends in Biotechnology, Vol. 34, No. 9, pp. 746–756, 2016.
Miao, S., Zhu, W., Castro, N. J., Leng, J., and Zhang, L. G., “Four-Dimensional Printing Hierarchy Scaffolds with Highly Biocompatible Smart Polymers for Tissue Engineering Applications,” Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods, Vol. 22, No. 10, pp. 952–963, 2016.
Kuribayashi-Shigetomi, K., Onoe, H., and Takeuchi, S., “Cell Origami: Self-Folding of Three-Dimensional Cell-Laden Microstructures Driven by Cell Traction Force,” PloS One, Vol. 7, No. 12, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051085, 2012.
Li, Y.-C., Zhang, Y. S., Akpek, A., Shin, S. R., and Khademhosseini, A., “4D Bioprinting: The Next-Generation Technology for Biofabrication Enabled by Stimuli-Responsive Materials,” Biofabrication, Vol. 9, No. 1, Paper No. 012001, 2016.
Malda, J., Visser, J., Melchels, F. P., Jüngst, T., Hennink, W. E., et al., “25th Anniversary Article: Engineering Hydrogels for Biofabrication,” Advanced Materials, Vol. 25, No. 36, pp. 5011–5028, 2013.
Gladman, A. S., Matsumoto, E. A., Nuzzo, R. G., Mahadevan, L., and Lewis, J. A., “Biomimetic 4D Printing,” Nature Materials, Vol. 15, No. 4, pp. 413–418, 2016.
Miao, S., Zhu, W., Castro, N. J., Nowicki, M., Zhou, X., et al., “4D Printing Smart Biomedical Scaffolds with Novel Soybean Oil Epoxidized Acrylate,” Scientific Reports, Vol. 6, Article Number: 27226, 2016.
Arslan-Yildiz, A., El Assal, R., Chen, P., Guven, S., Inci, F., et al., “Towards Artificial Tissue Models: Past, Present, and Future of 3D Bioprinting,” Biofabrication, Vol. 8, No. 1, Paper No. 014103, 2016.
Lee, V. K., Kim, D. Y., Ngo, H., Lee, Y., Seo, L., et al., “Creating Perfused Functional Vascular Channels Using 3D Bio-Printing Technology,” Biomaterials, Vol. 35, No. 28, pp. 8092–8102, 2014.
Inzana, J. A., Olvera, D., Fuller, S. M., Kelly, J. P., Graeve, O. A., et al., “3D Printing of Composite Calcium Phosphate and Collagen Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration,” Biomaterials, Vol. 35, No. 13, pp. 4026–4034, 2014.
Murphy, S. V. and Atala, A., “3D Bioprinting of Tissues and Organs,” Nature Biotechnology, Vol. 32, No. 8, pp. 773–785, 2014.
Mironov, V., Reis, N., and Derby, B., “Bioprinting: A Beginning,” Tissue Engineering, Vol. 12, No. 4, pp. 631–634, 2006.
Nervous System, “Kinematics Dress,” http://n-e-r-v-o-u-s.com/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Frost & Sullivan, “Advances in 4D Printing (Techniacl Insights),” 2014.
Mao, Y., Ding, Z., Yuan, C., Ai, S., Isakov, M., et al., “3D Printed Reversible Shape Changing Components with Stimuli Responsive Materials,” Scientific Reports, Vol. 6, Article No. 24761, 2016.
Wu, J., Yuan, C., Ding, Z., Isakov, M., Mao, Y., et al., “Multi-Shape Active Composites by 3D Printing of Digital Shape Memory Polymers,” Scientific Reports, Vol. 6, Article No. 24224, 2016.
Mao, Y., Yu, K., Isakov, M. S., Wu, J., Dunn, M. L., et al., “Sequential Self-Folding Structures by 3D Printed Digital Shape Memory Polymers,” Scientific Reports, Vol. 5, Article No. 13616, 2015.
Kokkinis, D., Schaffner, M., and Studart, A. R., “Multimaterial Magnetically Assisted 3D Printing of Composite Materials,” Nature Communications, Vol. 6, Article No. 8643, 2015.
Autodesk Research, “4D Printing,” https://www.autodeskresearch. com/projects/4dprinting (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Tibbits, S., McKnelly, C., Olguin, C., Dikovsky, D., and Hirsch, S., “4D Printing and Universal Transformation,” ACADIA 14: Design Agency, pp. 539–548, 2014.
Tibbits, S., “4D Printing: Multi-Material Shape Change,” Architectural Design, Vol. 84, No. 1, pp. 116–121, 2014.
Kwok, T.-H., Wang, C. C., Deng, D., Zhang, Y., and Chen, Y., “Four-Dimensional Printing for Freeform Surfaces: Design Optimization of Origami and Kirigami Structures,” Journal of Mechanical Design, Vol. 137, No. 11, Paper No. 111413, 2015.
Kuksenok, O. and Balazs, A. C., “Stimuli-Responsive Behavior of Composites Integrating Thermo-Responsive Gels with Photo-Responsive Fibers,” Materials Horizons, Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 53–62, 2016.
Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, “Development of a Contents Configuration Management System and a Simulator for 3D Printing Using Smart Materials” https://www.gist.ac.kr/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Yun, G.-Y. and Lee, Y.-G., “Service-Oriented Web for Transformable 4D Printing Components,” Korean Journal of Computational Design and Engineering, Vol. 21, No. 2, pp. 122–129, 2016.
Ham, S. I. and Lee, Y. G., “A Study on the Automatic Design of 4D Printing to Follow the Target Shape,” Korean Journal of Computational Design and Engineering,” Vol. 21, No. 3, pp. 306–312, 2016.
Noh, K.-S., Seo, H.-W., and Lee, Y.-G., “3D Printing Structures that Exhibit Torsions,” Proc. of the 2nd International Conference on Progress in Additive Manufacturing, 2016.
Gibson, I., Rosen, D., and Stucker, B., “Software Issues for Additive Manufacturing,” Additive Manufacturing Technologies, pp. 351–374, 2015.
Hiller, J. D. and Lipson, H., “STL 2.0: A Proposal for a Universal Multi-Material Additive Manufacturing File Format,” Proc. of the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, pp. 266–278, 2009.
Wikipedia, “Additive Manufacturing File Format,” https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Additive_Manufacturing_File_Format/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Sivagurunathan, Y., Harman, M., and Danicic, S., “Slicing; I/O and the Implicit State,” Proc. of the 3rd International Workshop on Automatic Debugging, pp. 59–67, 1997.
Tip, F., “A Survey of Program Slicing Techniques,” Journal of Programming Languages, Vol. 3, pp. 121–189, 1995.
Shah, A., Raza, A., Hassan, B., and Shah, A., “A Review of Slicing Techniques in Software Engineering,” Proc. of the International Conference on Engineering and Technology, pp. 1–15, 2015.
Pyo, S. H. and Choi, J. S., “Trends of 3D Printing Software Technologies,” Electronics and Telecommunications Trends, Vol. 29, No. 1, pp. 1–10, 2014.
Ding, D., Pan, Z., Cuiuri, D., and Li, H., “A Practical Path Planning Methodology for Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing of Thin-Walled Structures,” Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, Vol. 34, pp. 8–19, 2015
Ding, D., Pan, Z., Cuiuri, D., Li, H., Van Duin, S., et al., “Bead Modelling and Implementation of Adaptive Mat Path in Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing,” Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, Vol. 39, pp. 32–42, 2016.
Ding, D., Shen, C., Pan, Z., Cuiuri, D., Li, H., et al., “Towards an Automated Robotic Arc-Welding-Based Additive Manufacturing System from CAD to Finished Part,” Computer-Aided Design, Vol. 73, pp. 66–75, 2016.
Yaman, U., Butt, N., Sacks, E., and Hoffmann, C., “Slice Coherence in a Query-Based Architecture for 3D Heterogeneous Printing,” Computer-Aided Design, Vol. 75, pp. 27–38, 2016.
Steuben, J. C., Iliopoulos, A. P., and Michopoulos, J. G., “Implicit Slicing for Functionally Tailored Additive Manufacturing,” Computer-Aided Design, Vol. 77, pp. 107–119, 2016.
Ding, D., Pan, Z., Cuiuri, D., Li, H., Larkin, N., et al., “Automatic Multi-Direction Slicing Algorithms for Wire Based Additive Manufacturing,” Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, Vol. 37, pp. 139–150, 2016.
Kim, H.-J., Wie, K.-H., Ahn, S.-H., Choo, H.-S., and Jun, C.-S., “Slicing Algorithm for Polyhedral Models Based on Vertex Shifting,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 11, No. 5, pp. 803–807, 2010.
Fabian Schirig, “Slicing Algorithms for 3D-Printing,” http://blog.hkfs. de/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Abe, T. and Sasahara, H., “Development of the Shell Structures Fabrication CAM System for Direct Metal Lamination Using Arc Discharge-Lamination Height Error Compensation by Torch Feed Speed Control,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 1, pp. 171–176, 2015.
Ryu, S. A., Lee, S. K., Park, J. O., An, E. J., and Lee, H. S., “A Preprocessor Functionality for 3D Metal Printing Process,” Proc. of the Society of CAD/CAM Conference, pp. 390–394, 2013.
Subdivision Surfaces, “Loop Subdivision,” http://www.geocities.ws/jason_zxu/subdivision/mid-subdivision.html (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Rypl, D. and Bittnar, Z., “Generation of Computational Surface Meshes of STL Models,” Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, Vol. 192, No. 1, pp. 148–151, 2006.
Chui, C. K. and Jiang, Q., “Surface Subdivision Schemes Generated by Refinable Bivariate Spline Function Vectors,” Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, Vol. 15, No. 2, pp. 147–162, 2003.
Dyn, N., Levine, D., and Gregory, J. A., “A Butterfly Subdivision Scheme for Surface Interpolation with Tension Control,” ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 9, No. 2, pp. 160–169, 1990.
Zorin, D., Schröder, P., and Sweldens, W., “Interactive Multiresolution Mesh Editing,” Proc. of the 24th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, pp. 259–268, 1997.
Zorin, D., “Subdivision Zoo,” Subdivision for Modeling and Animation, Schröder, Peter and Zorin, Denis, pp. 65–104, 2000.
Velho, L. and Zorin, D., “4-8 Subdivision,” Computer Aided Geometric Design, Vol. 18, No. 5, pp. 397–427, 2001.
Zorin, D., Schröder, P., and Sweldens, W., “Interpolating Subdivision for Meshes with Arbitrary Topology,” Proc. of the 23rd Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, pp. 189–192, 1996.
Materialise, “Magics 3D Print Suite” http://www.materialise.com/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
All3DP, “20 Best 3D Printing Software Tools (Most are Free),” https://all3dp.com/best-3d-printing-software-tools/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
All3DP, “16 Best Slicer Software Tools for 3D Printers (Most are Free),” https://all3dp.com/best-3d-slicer-software-3d-printer/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Craft Unique, “Craftware,” https://craftunique.com/craftware (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Ultimaker, “Cura Software,” https://ultimaker.com/en/products/cura-software/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
KISSlicer, “Keep It Simple Slicer,” http://kisslicer.com/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Simplify3D, “Simplify3D 3D Printing Slicing Software,” https://www.simplify3d.com (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Slic3r, “G-Code Generator for 3D Printers,” http://slic3r.org/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
SIEMENS, “PLM Software,” https://www.plm.automation.siemens.com (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Han, H., Bae, H., Kang, H., Son, J., and Kim, H., “Multi Agent 3D Printer and Robot System for Mass Personalization FAAS Platform,” Proc. of the Information and Communication Technology Convergence, pp. 1129–1131, 2016.
Lin, K.-H., Shen, C.-Y., Du, J.-L., Wang, G.-Y., Chen, H.-M., et al., “A Design of Constant Temperature Control System in 3D Printer,” Proc. of the International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan, pp. 1–2, 2016.
Yang, W. M., Ge, R. Z., and Meng, P. F., “Wireless Thermal Printer Based on Internet of Things,” Applied Mechanics and Materials, pp. 2021–2024, 2014.
Gubbi, J., Buyya, R., Marusic, S., and Palaniswami, M., “Internet of Things (IoT): A Vision, Architectural Elements, and Future Directions,” Future Generation Computer Systems, Vol. 29, No. 7, pp. 1645–1660, 2013.
Miorandi, D., Sicari, S., De Pellegrini, F., and Chlamtac, I., “Internet of Things: Vision, Applications and Research Challenges,” Ad Hoc Networks, Vol. 10, No. 7, pp. 1497–1516, 2012.
Atzori, L., Iera, A., and Morabito, G., “The Internet of Things: A Survey,” Computer Networks, Vol. 54, No. 15, pp. 2787–2805, 2010.
HP, “HP Printers-Print and Scan from the HP AiO Printer Remote App,” http://support.hp.com/us-en/document/c03561640 (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Canon, “Canon Print Service,” http://www.canon.com/psmp/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
SAMSUNG, “Mobile Pringt Control,” http://www.samsung.com/us/mobile-print-app/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
3D Systems, “Cube Print,” https://prod.cubify.com/support/cube/downloads (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
WOW 3D Printer Professional, “WOW 3D Printer Apps,” https://wow3dprinter.word press.com/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Octo Print, “3D Printer Control,” http://octoprint.org/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Ultimaker, “Ultimaker 3,” https://ultimaker.com/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Xiaoan, G. and Lina, W., “Networked Control and Monitoring System Based on Industrial Ethernet,” Proc. of the 6th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, pp. 1337–1341, 2011.
Stănciulescu, S., Berger, T., Walkingshaw, E., and Wąsowski, A., “Concepts, Operations, and Feasibility of a Projection-Based Variation Control System,” Proc. of IEEE International Conference on Software Maintenance and Evolution, pp. 323–333, 2016.
MAdekolu, A. M., Khan, H., and Neelam, M., “Network Monitoring,” Sc. Thesis, School of Information Science, Computer and Electrical Engineering, Halmstad University, 2014.
PaperCut, “PaperCutNG & PaperCutMF,” http://www.papercut.com/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Print Manager, “Print Manager Plus 9.0, http://www.printmanager.com/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Fitosoft, “Objectprint,” http://www.fitosoft.com/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Manage Engine, “Event Log Analyzer,” https://www.manageengine.com/products/eventlog/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
SoftPerfect, “Print Inspector,” https://www.softperfect.com/products/pinspector/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
4 Office Automation, “Print Monitoring Software Solutions,” http://www.4office.ca/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Xerox, “A.N.D. Pcounter,” http://www.office.xerox.com/softwaresolutions/a-n-d-pcounter/enus.html (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Shane Wall, “HP’s IoT Printing Services,” https://shanewallcto.com/2015/07/28/hp-iot-printing-services/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
Print Monitor, “Cloud Based Printer Monitoring Software,” http://www.printmonitoringonline.com/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
MPS Monitor Cloud, “Remote Printer Monitoring,” http://www.mpsmonitor.com/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
O&K Print Watch, “Print monitor and printing control software,” https://www.prnwatch.com/ (Accessed 22 JUN 2017)
PAESSLER, “PRTG Network Monitor,” https://www.paessler.com/prtg
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, S., Song, S.E. & Cho, Y.T. Effective software solutions for 4D printing: A review and proposal. Int. J. of Precis. Eng. and Manuf.-Green Tech. 4, 359–371 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-017-0041-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-017-0041-y