Abstract
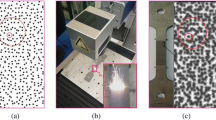
Digital image correlation (DIC) measurements were obtained using speckle patterns produced using two different methods. In the first case, speckles were produced on the surface of a test specimen using white and black spray paint, which is probably the most common approach. In the second case, a computer code was written that creates a random-speckle pattern digitally. The digital-speckle pattern was then printed on white paper using a standard laser printer. The speckled paper was subsequently bonded to the surface of a test specimen using a commercial strain gage adhesive. Strains were measured using both types of speckle patterns for a thin plate with hole and for a U-shaped beam loaded in tension. Strain fields measured using the painted and digital-speckle patterns are essentially identical and are well predicted by the corresponding elasticity solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sutton, M.A., Orteu, J.J., and Schreier, H.W., Image Correlation for Shape, Motion and Deformation Measurements: Basic Concepts, Theory and Applications, Springer London, Limited, London, UK (2009).
Pan, B., Qian, K., Xie, H., and Asundi, A., “Two-Dimensional Digital Image Correlation for In-Plane Displacement and Strain Measurement: A Review,” Measurement Science and Technology 20: 1–17 (2009).
Digital Image Correlation: Overview of Principles and Software. SEM Workshop, Correlated Solutions, Society of Experimental Mechanics, Bethel, CT (2009).
Zhou, P., and Goodson, K.E., “Subpixel Displacement and Deformation Gradient Measurement Using Digital Image/Speckle Correlation (Disc),” Optical Engineering 40: 1613–1620 (2001).
Wang, Y.H., Jiang, J.H., Wanintrudal, C., et al., “Whole Field Sheet-Metal Tensile Test Using Digital Image Correlation,” Experimental Techniques 34: 54–59 (2010).
Lava, P., Coppieters, S., Van Hecke, R., Van Houtte, P., and Debruyne, D., “Digital Image Correlation in the Classroom: Determining Stress Concentration Factors with Webcams,” Experimental Techniques 38(4): 1–9 (2012).
Wang, Y.Q., Sutton, M.A., Bruck, H.A., and Schreier, H.W., “Quantitative Error Assessment in Pattern Matching: Effects of Intensity Pattern Noise, Interpolation, Strain and Image Contrast on Motion Measurements,” Strain 45: 160–178 (2009).
Vic-3D 2010: Testing Guide, Correlated Solutions, Irmo, SC (2011).
Ashrafi, M., and Tuttle, M.E. (eds), “High Strain Gradient Measurements in Notched Laminated Composite Panels by Digital Image Correlation,” Composite, Hybrid, and Multifunctional Materials, Springer International Publishing, pp. 75–81 (2014).
Stoilov, G., Kavardzhikov, V., and Pashkouleva, D., “A Comparative Study of Random Patterns for Digital Image Correlation,” Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics 42: 3–92 (2012).
Dufour, J.-E., Hild, F., and Roux, S., “Integrated Digital Image Correlation for the Evaluation and Correction of Optical Distortions,” Optics and Lasers in Engineering 56: 121–133 (2014).
Guery, A., Latourte, F., Hild, F., and Roux, S., “Characterization of SEM Speckle Pattern Marking and Imaging Distortion by Digital Image Correlation,” Measurement Science and Technology 25: 015401–015413 (2014).
Gualtieri S., Novel Technique for DIC Speckle Pattern Optimization and Generation, Politesi Digital Archive of PhD and Post Graduate Theses, Mechanical Engineering, Politecnico di Milano, Italy (2012).
Shukla, A., and Dally, J.W., Experimental Solid Mechanics, College House Enterprises, LLC, Knoxville, TN (2010).
Omega. Pressure-Strain-Force, Force-Related Measurements, URL http://www.omega.com/literature/transactions/transactions_vol_iii.pdf/[accessed on 12 October 2014].
Liu, A.F., Mechanics and Mechanisms of Fracture: An Introduction, ASM International, Novelty, OH (2005).
Tuttle, M., “Illustrating Essentials of Experimental Stress Analysis Using a U-Shaped Beam,” Proulx, T., (ed), Experimental and Applied Mechanics, Volume 6, Springer, New York, NY, pp. 711–719 (2011).
Hild, F., and Roux, S., “Digital Image Correlation: From Displacement Measurement to Identification of Elastic Properties—A Review,” Strain 42: 69–80 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashrafi, M., Tuttle, M.E. Measurement of Strain Gradients Using Digital Image Correlation by Applying Printed-Speckle Patterns. Exp Tech 40, 891–897 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-016-0090-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-016-0090-0