Abstract
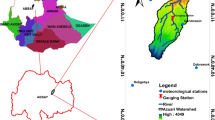
Water erosion is one of the most serious problems of soil degradation in the world, the north of Africa region is particularly exposed to this phenomenon. In fact, the phenomenon gets worse with the climate changes and the adverse anthropogenic environmental interventions. In recent decades, the estimation of soil erosion using empirical models has been a promising research topic. Nevertheless, their application over a large and ungauged areas remains a real challenge due to the availability and quality of the required data. Using the GIS environment, this study aims to estimate and compare the water erosion rates by the three models of Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE), Modified Universal Soil Loss Equation (MUSLE) and Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) in Wadi Gazouana North-West of Algeria. The estimated specific erosion in the entire wadi Ghazouana watershed surface is 9.65, (t/ha/year), 9.90 (t/ha/year) and 11.33 (t/ha/year) by USLE, RUSLE and MUSLE models, respectively. We can also conclude that USLE, RUSLE and MUSLE soil erosion models produced relatively similar results, however, the MUSLE model showed a higher spatial dispersion of the erosion risk compared to the others. The rain factor in this model was more effective; which explain its higher erosion rate.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
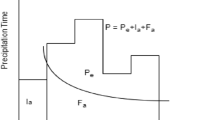
The computed average soil loss (t/ha/year)
- Q:
-
Volume of runoff in (m3)
- qp :
-
Peak flow rate in (m3/s)
- R:
-
Rainfall erosivity in (MJ/ha mm/h)
- Pi:
-
The monthly precipitation (mm)
- P:
-
The annual precipitation (mm)
- S:
-
Surface (km2)
References
Abdo H, Salloum J (2017) Spatial assessment of soil erosion in Alqerdaha basin (Syria). Model Earth Syst Environ 3:26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0294-z
Bangash RF, Passuello A, Sanchez-Canales M et al (2013) Ecosystem services in Mediterranean river basin: climate change impact on water provisioning and erosion control. Sci Total Environ 458–460:246–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.04.025
Beasley DB, Huggins LF, Monke EJ (1980) ANSWERS: a model for watershed planning. Trans ASAE 23:0938–0944. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.34692
Benchettouh A, Kouri L, Jebari S (2017) Spatial estimation of soil erosion risk using RUSLE/GIS techniques and practices conservation suggested for reducing soil erosion in Wadi Mina watershed (northwest, Algeria). Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2875-6
Bera A (2017) Assessment of soil loss by universal soil loss equation (USLE) model using GIS techniques: a case study of Gumti River Basin, Tripura, India. Model Earth Syst Environ 3:29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0289-9
Bouguerra H, Bouanani A, Khanchoul K et al (2017) Mapping erosion prone areas in the Bouhamdane watershed (Algeria) using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation through GIS. J Water Land Dev 32:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1515/jwld-2017-0002
Bryan K, Albritton CC (1943) Soil phenomena as evidence of climatic changes. Am J Sci 241:469–490
Chiew FHS, Whetton PH, McMahon TA, Pittock AB (1995) Simulation of the impacts of climate change on runoff and soil moisture in Australian catchments. J Hydrol 167:121–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(94)02649-V
Cormary Y, Masson J (1964) Etude de conservation des eaux et du sol au Centre de Recherches du Génie Rural de Tunisie: application à un projet-type de la formule de perte de sols de Wischmeier. Cahiers ORSTOM, série pédologie 2.3:3–26
da Cunha ER, Bacani VM, Panachuki E (2017) Modeling soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS in a watershed occupied by rural settlement in the Brazilian Cerrado. Nat Hazards 85:851–868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2607-3
Davis FM, Leonard RA, Knisel WG (1990) Groundwater loading effects of agricultural management systems (GLEAMS) user manual. USDA-ARS Southeast Watershed Res Lab Univ Georg Tifton, Tifton
Demmak A (1982) Contribution à l’étude de l’érosion et des transports solides en Algérie septentrionale [Contribution to the study of erosion and sediment transport in northern Algeria]. PhD Thesis, Manuscript, Université de Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris
Djoukbala O, Mazour M, Hasbaia M, Benselama O (2018) Estimating of water erosion in semiarid regions using RUSLE equation under GIS environment. Environ Earth Sci 77:345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7532-1
Elaloui A, Marrakchi C, Fekri A et al (2017) USLE-based assessment of soil erosion by water in the watershed upstream Tessaoute (Central High Atlas, Morocco). Model Earth Syst Environ 3:873–885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0340-x
Elwell HA (1978) (1978) Modelling soil losses in Southern Africa. J Agric Eng Res 23:117–127
FAO and ISRIC (2012) Harmonized world soil database. FAO, Rome, Italy and IIASA, Laxenburg, Austria
Fernández C, Vega JA (2016) Evaluation of RUSLE and PESERA models for predicting soil erosion losses in the first year after wildfire in NW Spain. Geoderma 273:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.03.016
Ghadiri H, Rose CW (1993) Water erosion processes and the enrichment of sorbed pesticides. Part 2. Enrichment under rainfall dominated erosion process. J Environ Manag 37:37–50
Harmon RS, Doe WW (2001) Landscape erosion and evolution modeling. Springer Science & Business Media, New York
Hudson N (1993) Field measurement of soil erosion and runoff. Food & Agriculture Org, Rome
Imamoglu A, Dengiz O (2017) Determination of soil erosion risk using RUSLE model and soil organic carbon loss in Alaca catchment (Central Black Sea region, Turkey). Rend Lincei 28:11–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-016-0556-0
Jiang L, Yao Z, Liu Z et al (2015) Estimation of soil erosion in some sections of Lower Jinsha River based on RUSLE. Nat Hazards 76:1831–1847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1569-6
Kalman R (1967) Essai d’évaluation pour le pré-Rif du facteur couverture végétale de la formule de Wischmeier de calcul de l’érosion. Rapport Rabat 1–12
Kinnell P (2001) Slope length factor for applying the USLE-M to erosion in grid cells. Soil Tillage Res 58:11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-1987(00)00179-3
Knisel WG (1980) CREAMS: a field scale model for Chemicals, Runoff, and Erosion from Agricultural Management Systems (USA). United States Dept Agric Conserv Res Rep
Lal R, Ahmadi M, Bajracharya RM (2000) Erosional impacts on soil properties and and corn yield on alfisols in central Ohio. Land Degrad Dev 11:575–585. https://doi.org/10.1002/1099-145X(200011/12)11:6%3C575::AID-LDR410%3E3.0.CO;2-N
Leopold LB (1951) Rainfall frequency: an aspect of climatic variation. Eos Trans Am Geophys Union 32:347–357
Lin CY, Lin WT, Chou WC (2002) Soil erosion prediction and sediment yield estimation: the Taiwan experience. Soil Tillage Res 68:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-1987(02)00114-9
Maeda EE, Pellikka PKE, Siljander M, Clark BJF (2010) Potential impacts of agricultural expansion and climate change on soil erosion in the Eastern Arc Mountains of Kenya. Geomorphology 123:279–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2010.07.019
Markose VJ, Jayappa KS (2016) Soil loss estimation and prioritization of sub-watersheds of Kali River basin, Karnataka, India, using RUSLE and GIS. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5218-2
Moore ID, Burch GJ (1986) Modelling erosion and deposition: topographic effects. Trans ASAE 29:1624 – 1630
Nearing M, Foster G, Lane L, Finkner S (1989) A process-based soil erosion model for USDA-Water Erosion Prediction Project technology. Trans ASAE 32:1587–1593
Neitsch S, Arnold J, Kiniry J, Williams J (2011) Soil & water assessment tool theoretical documentation version 2009. Texas Water Resources Institute, pp 1–647
Pham TG, Degener J, Kappas M (2018) Integrated universal soil loss equation (USLE) and geographical information system (GIS) for soil erosion estimation in A Sap basin: Central Vietnam. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 6:99–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2018.01.001
Planning Ministry of the Environment and Spatial (2000) National report on the state of the environment
Remini B (2000) L’envasement des barrages. Bull Réseau Eros 20:165–171
Renard K, Foster G, Weesies G et al (1997) Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). In: Agriculture handbook, No. 70. US Government Printing Office, Washington, pp 404
Roose É, Noni G De (2004) Recherches sur l ‘érosion hydrique en Afrique: revue et perspectives. Sci Chang planétaires/Sécheresse 15:121–129
Ruhe RV, Scholtes WH (1956) Ages and development of soil landscapes in relation to climatic and vegetational changes in Iowa 1. Soil Sci Soc Am J 20:264–273
Souidi Z, Hamimed A, Donze F (2014) Cartographie du risque de dégradation des terres en région semi-aride: Cas des Monts de Beni Chougrane dans le Tell Occidental Algérien. Geo Eco Trop 38:85–102
Tang J, Cheng XQ, Zhu B et al (2015a) Rainfall and tillage impacts on soil erosion of sloping cropland with subtropical monsoon climate—a case study in hilly purple soil area, China. J Mt Sci 12:134–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-014-3241-8
Tang Q, Xu Y, Bennett SJ, Li Y (2015b) Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS: a case study of the Yangou watershed in the Loess Plateau, China. Environ Earth Sci 73:1715–1724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3523-z
Tetford PE, Desloges JR, Nakassis D (2017) Modelling surface geomorphic processes using the RUSLE and specific stream power in a GIS framework, NE Peloponnese, Greece. Model Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0391-z
Thomas J, Joseph S, Thrivikramji KP (2018) Estimation of soil erosion in a rain shadow river basin in the southern Western Ghats, India using RUSLE and transport limited sediment delivery function. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 6:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2017.12.001
Toubal AK, Achite M, Ouillon S, Dehni A (2018) Soil erodibility mapping using the RUSLE model to prioritize erosion control in the Wadi Sahouat basin, North-West of Algeria. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6580-z
Toumi S, Meddi M, Mahé G, Brou YT (2013) Cartographie de l’érosion dans le bassin versant de l’Oued Mina en Algérie par télédétection et SIG. Hydrol Sci J 58:1542–1558. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2013.824088
Wang G, Wente S, Gertner GZ, Anderson A (2002) Improvement in mapping vegetation cover factor for the universal soil loss equation by geostatistical methods with Landsat Thematic Mapper images. Int J Remote Sens 23:3649–3667. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160110114538
Wijesundara NC, Abeysingha NS, Dissanayake DMSLB (2018) GIS-based soil loss estimation using RUSLE model: a case of Kirindi Oya river basin, Sri Lanka. Model Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0419-z
Williams JR (1975) Sediment routing for agricultural watersheds. JAWRA J Am Water Resour Assoc 11:965–974
Williams JR, Berndt HD (1977) Sediment yield prediction based on watershed hydrology. Trans ASAE 20:1100–1104
Williams JR, Nicks AD, Arnold JG (1985) Simulator for water resources in rural basins. J Hydraul Eng 111:970–986
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1965) Predicting rainfall erosion losses from cropland east of the Rocky Mountains [online]. In: Agricultural Handbook, No. 282. US Department of Agriculture - Agricultural Research Service, Brooksville, pp 47
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses - a guide to conservation planning. In: Agriculture Handbook No 537. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC
Zhang X-C (2012) Cropping and tillage systems effects on soil erosion under climate change in Oklahoma. Soil Sci Soc Am J 76:1789. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2012.0085
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Djoukbala, O., Hasbaia, M., Benselama, O. et al. Comparison of the erosion prediction models from USLE, MUSLE and RUSLE in a Mediterranean watershed, case of Wadi Gazouana (N-W of Algeria). Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 5, 725–743 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0562-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0562-6