Abstract
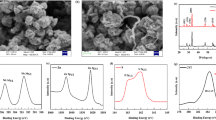
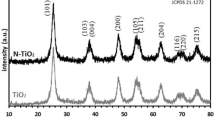
For energy storage system, it is still a huge challenge to achieve high energy density and high power density simultaneously. One potential solution is to fabricate electrochemical capacitors (ECs), which store electric energy through surface ion adsorption or redox reactions. Here we report a new electrode material, heavy nitrogen-doped (9.29 at.%) black titania (TiO2−x:N). This unique hybrid material, consisting of conductive amorphous shells supported on nanocrystalline cores, has rapid N-mediated redox reaction (TiO2−xNy + zH+ + ze− ↔ TiO2−xNyHz), especially in acidic solutions, providing a specific capacitance of 750 F g−1 at 2 mV s−1 (707 F g−1 at 1 A g−1), great rate capability (503 F g−1 at 20 A g−1), and maintain stable after initial fading. Being a new developed supercapacitor material, nitrogen-doped black titania may revive the oxide-based supercapacitors.
摘要
对于储能系统, 同时实现高能量密度和高功率密度仍是一个 巨大的挑战. 电化学超级电容器通过表面吸附或表面氧化还原反 应实现储能, 是解决上述问题的潜在方法之一. 本论文报道了一种 新型高氮掺杂(9.29 at.%)黑色二氧化钛(TiO2−x:N)超级电容器电极 材料. 该材料具有独特的微观结构, 由高导电的非晶壳层和一个纳 米晶核组成. 在酸性电解液中, 该材料可以通过氮参与的氧化还原 反应(TiO2−xNy + zH+ + ze− ↔ TiO2−xNyHz)可逆地与质子结合实现 能量的高效快速储存, 实现极高的比电容(2 mV s−1扫速下容量高 达750 F g−1, 1 A g−1电流密度下容量可达707 F g−1)、高倍率特性 (极高电流密度20 A g−1时容量仍可达503 F g−1)和长时间循环下的 高稳定性. 作为一种新型超级电容器电极材料, 氮掺杂黑色二氧化 钛或将引领金属氧化物型超级电容器的复兴.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller JR, Simon P. Materials science: Electrochemical capacitors for energy management. Science, 2008, 321: 651–652
Yu G, Xie X, Pan L, et al. Hybrid nanostructured materials for high-performance electrochemical capacitors. Nano Energy, 2013, 2: 213–234
Lin T, Chen IW, Liu F, et al. Nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon of extraordinary capacitance for electrochemical energy storage. Science, 2015, 350: 1508–1513
Chiang YM. Building a better battery. Science, 2010, 330: 1485–1486
Lu X, Yu M, Wang G, et al. H-TiO2@MnO2//H-TiO2@C core-shell nanowires for high performance and flexible asymmetric supercapacitors. Adv Mater, 2013, 25: 267–272
Fan Z, Yan J, Wei T, et al. Asymmetric supercapacitors based on graphene/MnO2 and activated carbon nanofiber electrodes with high power and energy density. Adv Funct Mater, 2011, 21: 2366–2375
Chen PC, Shen G, Shi Y, et al. Preparation and characterization of flexible asymmetric supercapacitors based on transition-metaloxide nanowire/single-walled carbon nanotube hybrid thin-film electrodes. ACS Nano, 2010, 4: 4403–4411
Wang DW, Li F, Liu M, et al. 3D aperiodic hierarchical porous graphitic carbon material for high-rate electrochemical capacitive energy storage. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2008, 47: 373–376
Ji J, Zhang LL, Ji H, et al. Nanoporous Ni(OH)2 thin film on 3D ultrathin-graphite foam for asymmetric supercapacitor. ACS Nano, 2013, 7: 6237–6243
Zhao X, Zhang L, Murali S, et al. Incorporation of manganese dioxide within ultraporous activated graphene for high-performance electrochemical capacitors. ACS Nano, 2012, 6: 5404–5412
Lu Q, Lattanzi MW, Chen Y, et al. Supercapacitor electrodes with high-energy and power densities prepared from monolithic NiO/Ni nanocomposites. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2011, 50: 6847–6850
Wu ZS, Wang DW, Ren W, et al. Anchoring hydrous RuO2 on graphene sheets for high-performance electrochemical capacitors. Adv Funct Mater, 2010, 20: 3595–3602
Augustyn V, Come J, Lowe MA, et al. High-rate electrochemical energy storage through Li+ intercalation pseudocapacitance. Nat Mater, 2013, 12: 518–522
Chmiola J, Yushin G, Gogotsi Y, et al. Anomalous increase in carbon capacitance at pore sizes less than 1 nanometer. Science, 2006, 313: 1760–1763
Pech D, Brunet M, Durou H, et al. Ultrahigh-power micrometresized supercapacitors based on onion-like carbon. Nat Nanotech, 2010, 5: 651–654
Simon P, Gogotsi Y. Materials for electrochemical capacitors. Nat Mater, 2008, 7, 845–854
Fujishima A, Honda K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature, 1972, 238: 37–38
Bach U, Lupo D, Comte P, et al. Solid-state dye-sensitized mesoporous TiO2 solar cells with high photon-to-electron conversion efficiencies. Nature, 1998, 395: 583–585
Wang Z, Yang C, Lin T, et al. Visible-light photocatalytic, solar thermal and photoelectrochemical properties of aluminium-reduced black titania. Energy Environ Sci, 2013, 6: 3007–3014
Wang Z, Yang C, Lin T, et al. H-doped black titania with very high solar absorption and excellent photocatalysis enhanced by localized surface plasmon resonance. Adv Funct Mater, 2013, 23: 5444–5450
Brezesinski T, Wang J, Polleux J, et al. Templated nanocrystal-based porous TiO2 films for next-generation electrochemical capacitors. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131: 1802–1809
Xia T, Zhang C, Oyler NA, et al. Hydrogenated TiO2 nanocrystals: A novel microwave absorbing material. Adv Mater, 2013, 25: 6905–6910
Green MA, Xu J, Liu H, et al. Terahertz absorption of hydrogenated TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater Today Phys, 2018, 4: 64–69
Green M, Van Tran AT, Smedley R, et al. Microwave absorption of magnesium/hydrogen-treated titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Nano Mater Sci, 2019, 1: 48–59
Green M, Xiang P, Liu Z, et al. Microwave absorption of aluminum/hydrogen treated titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Materiomics, 2019, 5: 133–146
Lu X, Wang G, Zhai T, et al. Hydrogenated TiO2 nanotube arrays for supercapacitors. Nano Lett, 2012, 12: 1690–1696
Lin T, Yang C, Wang Z, et al. Effective nonmetal incorporation in black titania with enhanced solar energy utilization. Energy Environ Sci, 2014, 7: 967–972
Bi H, Huang F, Liang J, et al. Large-scale preparation of highly conductive three dimensional graphene and its applications in CdTe solar cells. J Mater Chem, 2011, 21: 17366–17370
Gao Q, Demarconnay L, Raymundo-Piñero E, et al. Exploring the large voltage range of carbon/carbon supercapacitors in aqueous lithium sulfate electrolyte. Energy Environ Sci, 2012, 5: 9611–9617
Xie Y, Fu D. Photochemical performance and electrochemical capacitance of titania nanocomplexes. Mater Res Bull, 2010, 45: 628–635
Salari M, Aboutalebi SH, Konstantinov K, et al. A highly ordered titania nanotube array as a supercapacitor electrode. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2011, 13: 5038–5041
Salari M, Konstantinov K, Liu HK. Enhancement of the capacitance in TiO2 nanotubes through controlled introduction of oxygen vacancies. J Mater Chem, 2011, 21: 5128–5133
Zhou H, Zhang Y. Electrochemically self-doped TiO2 nanotube arrays for supercapacitors. J Phys Chem C, 2014, 118: 5626–5636
Ozkan S, Nguyen NT, Hwang I, et al. Highly conducting spaced TiO2 nanotubes enable defined conformal coating with nanocrystalline Nb2O5 and high performance supercapacitor applications. Small, 2017, 13: 1603821
Heng I, Lai CW, Juan JC, et al. Low-temperature synthesis of TiO2 nanocrystals for high performance electrochemical supercapacitors. Ceramics Int, 2019, 45: 4990–5000
Qorbani M, Khajehdehi O, Sabbah A, et al. Ti-rich TiO2 tubular nanolettuces by electrochemical anodization for all-solid-state high-rate supercapacitor devices. ChemSusChem, 2019, 12: 4064–4073
Wang Q, Li M, Wang Z. Supercapacitive performance of TiO2 boosted by a unique porous TiO2/Ti network and activated Ti3+. RSC Adv, 2019, 9: 7811–7817
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National key R&D Program of China (2016YFB0901600), and the Key Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (QYZDJ-SSWJSC013). Chen IW was supported by U.S. Department of Energy BES grant DE-FG02-11ER46814 and used the facilities (Laboratory for Research on the Structure of Matter) supported by NSF grant DMR-11-20901.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yang C, Huang F, and Chen IW designed the experiment; Yang C, Wang X, Xu J, and Wang Z engineered the samples and the tests; Gu H performed the SEM and TEM tests. Yang C, Wang X, and Dong W analyzed the data. Yang C and Dong W wrote the paper with support from Huang F. All authors contributed to the general discussion.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary information
Supporting data are available in the online version of the paper.
Chongyin Yang obtained his PhD under the supervision of Prof. Fuqiang Huang at Shanghai Institute of Ceramics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (SICCAS). He is now an assistant research scientist at the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Maryland. His research interests include the design, synthesis and application of supercapacitors and lithiumion batteries.
Fuqiang Huang obtained his PhD in science from Beijing Normal University in 1996. Then he joined the State Key Lab of High Performance Ceramics & Superfine Microstructure at SICCAS, and became a full professor in 2003. His research interests focus on the new energy materials and devices. He put forward the concept of multiple physical quantities synergy in structure function region for energy conversion materials and the theoretical model of accumulation factor.
Supporting Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Wang, X., Dong, W. et al. Nitrogen-doped black titania for high performance supercapacitors. Sci. China Mater. 63, 1227–1234 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-020-1303-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-020-1303-4