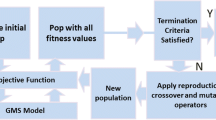
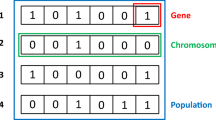
Abstract
Pollution source identification in groundwater resources is a challenging task due to existing uncertainties in both pollutant source characteristics and mass transport in porous media. To obtain a robust and cost-effective groundwater monitoring configuration, this paper presents a new regret-based optimization model which minimizes the number of monitoring wells and average regret in estimating undetected polluted area. A Monte Carlo analysis is used to consider existing uncertainties in both pollution source characteristics and parameters of groundwater quality simulation model. MODFLOW and MT3D, groundwater quantity and quality simulation models, are used to simulate the spatial and temporal variations of a water quality indicator in groundwater. For each non-dominated solution provided by a bi-objective optimization model, the optimal positions of monitoring wells are also determined by minimizing the corresponding regret in undetected polluted area. Furthermore, a Bayesian network (BN) is trained and validated based on results of the Monte Carlo analysis. The trained BN is capable of accurately determining an unknown pollution source using monitoring data in real-time operation of monitoring system. To demonstrate the efficiency and applicability of the proposed methodology, it is applied to the Tehran Aquifer in the Tehran refinery region, which is highly polluted due to leakage from several tanks of petroleum products.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afshar A, Najafi E (2014) Consequence management of chemical intrusion in water distribution networks under inexact scenarios. J Hydroinform 16(1):178–188
Akbari A, Ardestani M, Shayegan J (2012) Distribution and mobility of petroleum hydrocarbons in soils: case study of South Pars gas complex, southern Iran. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civil Eng 36(C2):265–275
American Society of Civil Engineers Task Committee on Long-Term Groundwater Monitoring Design (2003) Long-term groundwater monitoring: the state of the art. Reston, VA
Atmadja J, Bagtzoglou AC (2001) State of the art report on mathematical methods to reliable of groundwater pollution source identification. Environ Forensics 2(3):205–214
Bashi-Azghadi SN, Kerachian R (2010) Locating monitoring wells in groundwater systems using embedded optimization and simulation models. Sci Total Environ 408(10):2189–2198
Bashi-Azghadi SN, Kerachian R, Bazargan-Lari MR, Solouki K (2010) Characterizing an unknown pollution source in groundwater resources systems using PSVM and PNN. Expert Syst Appl 37:7154–7161
Bazargan-Lari MR (2014) An evidential reasoning approach to optimal monitoring of drinking water distribution systems for detecting deliberate contamination events. J Clean Prod 78:1–14
Bazargan-Lari MR, Kerachian R, Afshar H, Bashi-Azghadi SN (2013) Developing an optimal valve closing rule curve for real-time pressure control in pipes. J Mech Sci Technol 27(1):215–225
Biedermann A, Taroni F (2012) Bayesian networks for evaluating forensic DNA profiling evidence: a review and guide to literature. Forensic Sci Int (Genetics) 6:147–157
Burn DH (1989) Water-quality management through combined simulation-optimization approach. J Environ Eng 115(5):1011–1024
Chang NB, Davila E (2007) Minimax regret optimization analysis for a regional solid waste management system. Waste Manag 27(6):820–832
Cui L, Chen LR, Li YP, Huang GH, Li W, Xie YL (2011) An interval-based regret-analysis method for identifying long-term municipal solid waste management policy under uncertainty. J Environ Manag 92(6):1484–1494
Datta B, Chakrabarty D, Dhar A (2009) Simultaneous identification of unknown groundwater pollution sources and estimation of aquifer parameters. J Hydrol 376:48–57
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6(2):182–197
Dhar A, Datta B (2010) Logic-based design of groundwater monitoring network for redundancy reduction. J Water Resour Plan Manag 136(1):88–94
Du P, Li Y, Huang G (2012) Agricultural water management under uncertainty using minimax relative-regret analysis method. J Irrig Drain Eng 138(12):1033–1045
Ellis JH (1988) Acid rain control strategies. Environ Sci Technol 22(11):1248–1255
Hasheminejad H, Karimi-Jashni A, Talebbeydokhti N, Monajemi P (2013) Remediation of petroleum contaminated groundwater using sawdust as an adsorbent. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civil Eng 36(C2):265–275
He L, Huang GH, Lu HW (2008) A simulation-based fuzzy chance-constrained programming model for optimal groundwater remediation under uncertainty. Adv Water Resour 31(12):1622–1635
Kerachian R, Fallahnia M, Bazargan-Lari MR, Mansoori A, Sedghi H (2010) A fuzzy game theoretic approach for groundwater resources management: Application of Rubinstein bargaining theory. Resourc Conserv and Recycl 54(10):673–682. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2009.11.008
Li YP, Huang GH, Nie SL (2009) A robust interval-based minimax-regret analysis approach for identification of optimal water-resources-allocation strategies under uncertainty. Resour Conserv Recycl 54:86–96
Loaiciga HA, Charbeneau RJ, Everett LG, Fogg GE, Hobbs BF, Rouhani S (1992) Review of ground-water quality monitoring network design. J Hydraul Eng 118(1):11–37
Loulou R, Kanudia A (1999) Minimax regret strategies for greenhouse gas abatement: methodology and application. Oper Res Lett 25:219–230
Mahar PS, Datta B (1997) Optimal monitoring network and ground-water-pollution source identification. J Water Resour Plan Manag 123(4):199–207
Mahjouri N, Shamsoddinpour M (2016) Developing a methodology for early leakage detection in landfills: application of the fuzzy transformation technique and probabilistic artificial neural networks. Environ Earth Sci 75:1000. doi:10.1007/s12665-016-5757-4
Malekmohammadi B, Kerachian R, Zahraie B (2009) Developing monthly operating rules for a cascade system of reservoirs: application of Bayesian networks. Environ Model Softw 24(12):1420–1432
Mesbah SM, Kerachian R, Nikoo MR (2009) Developing real time operating rules for trading discharge permits in rivers: application of Bayesian networks. Environ Model Softw 24(2):238–246
Michalak AM, Kitanidis PK (2004) Estimation of historical groundwater contaminant distribution using the adjoint state method applied to geostatistical inverse modeling. Water Resour Res 40(8):W08302
Nikoo MR, Kerachian R, Niksokhan MH (2012) Equitable waste load allocation in rivers using fuzzy Bi-matrix games. Water Resour Manag 26(15):4539–4552
Niksokhan MH, Kerachian R, Amin P (2009) A stochastic conflict resolution model for trading pollutant discharge permits in river systems. Environ Monit Assess 154(1–4):219–232
Poorsepahy-Samian H, Kerachian R, Nikoo MR (2012) Water and pollution discharge permit allocation to agricultural zones: application of game theory and min-max regret analysis. Water Resour Manag 26(14):4241–4257
Prakash O, Datta B (2013) Sequential optimal monitoring network design and iterative spatial estimation of pollutant concentration for identification of unknown groundwater pollution source locations. Environ Monit Assess 185(7):5611–5626
Rafipour-Langeroudi M, Kerachian R, Bazargan-Lari MR (2014) Developing operating rules for conjunctive use of surface and groundwater considering the water quality issues. KSCE J Civ Eng 18(2):454–461
Sun AY, Painter SL, Wittmeyer GW (2006) A constrained robust least squares approach for contaminant source release history identification. Water Resour Res 42(4):W04414
Zekri S, Triki C, Al-Maktoumi A, Bazargan-Lari MR (2015) An optimization-simulation approach for groundwater abstraction under recharge uncertainty. Water Resour Manag 29(10):3681–3695
Zheng C (1990) MT3D, A modular three-dimensional transport model for simulation of advection, dispersion and chemical reactions of contaminants in groundwater systems. Report to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, p 170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bashi-Azghadi, S.N., Kerachian, R., Bazargan-Lari, M.R. et al. Pollution Source Identification in Groundwater Systems: Application of Regret Theory and Bayesian Networks. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 40, 241–249 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-016-0022-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-016-0022-3