Abstract
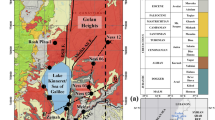
Carbonate aquifers provide large parts of the water supply for more than a quarter of the world’s population. The geochemical assessment of these heterogeneous aquifers is a valuable endeavor to ensure a rational management and protection of groundwater resources. To secure its durability, regard to increasing water demands and climate challenges make the problem of prevalence of water scarcity, vulnerability, and drought conditions extremely complicated. In Tebessa–Kasserine basin (Tuniso-Algerian international border), karst aquifers are receiving increasing interest, as the area has typical karst landscape and the hydrogeological system mostly consists of carbonates formation. Thus, a thorough understanding of aquifer behavior and water mineralization origin using geochemical and statistical tools can lead to relevant information regarding karst processes, groundwater chemistry, and protection. Subsequently, this study represents a pioneer baseline of the hydrogeochemical characterization of karst features in this international border area and it aims to identify the origin of karst water mineralization, its spatial distribution, and factors influencing water composition. The hydrogeochemical assessment of the sampled waters shifts from low mineralized Ca-HCO3 waters to Ca-SO4 and Na–Cl water types. TDS values range from 10 to 490.66 mg/l. A Gibbs diagram indicates that karst waters have been recently recharged by direct rainfall infiltration. Water quality gets modified along pathways and dissolution, formations weathering, and ion exchange processes seem to be the predominant geochemical factors influencing water mineralization. The PCA confirms the spatial variability of water types and indicates that it largely depends on aquifer lithology and on geographical position of water points.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addoum B (1995) L’Atlas Saharien Sud-oriental : Cinématique des plis-chevauchements et reconstitution du bassin du Sud-Est Constantinois (confins algéro-tunisiens). Thèse Doc. Ès Sci. Univ. Paris XI Orsay
Ahmadi R, Ouali J, Mercier E, Mansy JL (2006) The geomorphologic responses to hinge migration in the fault-related folds in the Southern Tunisian Atlas. J Struct Geol 28:721–728
Apaydin A, Aktas SD (2012) Assessment of groundwater quality of the Tatlicay aquifer and relation to the adjacent evaporitic formations (Cankiri, Turkey). Environ Monit Assess 184:2337–2357
Aquilina L, Ladouche B, Doerfliger N, Bakalowicz M (2003) Deep water circulation residence time and chemistry in a karst complex. Ground Water 41(6):790–805
Aquilina L, Ladouche B, Doerfliger N (2005) Recharge processes in karstic systems investigated through the correlation of chemical and isotopic composition of rain and spring-waters. Appl Geochem 20:2189–2206
Aquilina L, Ladouche B, Dorfliger N (2006) Water storage and transfer in the epikarst of karstic systems during high flow periods. J Hydrol 327:472–485
Barberá JA, Andreo B (2012) Functioning of a karst aquifer from Spain under highly variable climate conditions, deduced from hydrochemical records-Environ. Earth Sci 65:2337–2349
Barbieri M, Boschetti T, Petitta M, Tallini M (2005) Stable isotope (2H,18O and 87Sr/86Sr) and hydrochemistry monitoring for groundwater hydrodynamics analysis in a karst aquifer (Gran Sasso, central Italy). Appl Geochem 20:2063–2081
Barbieri M, Nigro A, Petitta M (2017) Groundwater mixing in the discharge area of San Vittorino Plain (Central Italy): geochemical characterization and implication for drinking uses. Environ Earth Sci 76:393
Besser H, Mokadem N, Redhaouania B, Rhimi N, Khelifi F, Ayadi Y, Omar Z, Bouajila A, Hamed Y (2017) GIS based model evaluation of groundwater quality and estimation of soil salinization and land degradation risks in arid Mediterranean site (SW Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 10:350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3148-0
Bicalho CC, Batiot-Guilhe C, Seidel JL, Van Exter S, Jourde H (2012) Geochemical evidence of water source characterization and hydrodynamic responses in a karst aquifer. J Hydrol 450–451:206–218
Calaforra JM, Pulido-Bosch A (1999) Gypsum karst features as evidence of diapiric processes in the Betic Cordillera, southern Spain. Geomorphology 29:251–264
Celle-Jeanton H, Travy Y, Blavoux B (2001) Isotopic typology of the precipitation in the Western Mediterranean region at three different time scales. Geophys Res Lett 28:1215–1218
Chiesi M, Waele JD, Paolo F (2010) Origin and evolution of a salty gypsum/anhydrite karst spring: the case of Poiano (Northern Apennines, Italy). Hydrogeol J 18:1111–1124
Cooper AH, Gutiérrez F (2013) Dealing with gypsum karst problems: hazards, environmental issues and planning. In: Shroder J (ed) Treatise on geomorphology, vol 6. Karst Geomorphology. Elsevier, New York, pp 451–462
Demdoum A, Hamed Y, Feki M, Hadji R, Djebbar M (2015) Multi-tracer investigation of groundwater in El Eulma Basin (northwestern Algeria), North Africa. Arab J Geosci 8(5):3321–3333
Emblanch C (1997) Les équilibres chimiques et isotopiques du carbone dans les aquiferes karstiques. Etude en région méditerranéenne de montagne sur le bassin expérimental de la Fontaine de Vaucluse (Doctoral dissertation)
Emblanch C, Puig JM, Zuppi GM, Mudry J, Blavoux B (1998) Comportement particulier lors des montées de crues dans les aquifères karstiques, mise en évidence d’une double fracturation et/ou de circulation profonde: Exemple de la Fontaine de Vaucluse. Eclogægeol. Helv 92:251–257
Emblanch C, Zuppi GM, Mudry J, Blavoux B, Batiot C (2003) Carbon 13 of TDIC to quantify the role of the unsaturated zone: the example of the Vaucluse karst systems (Southeastern France). J Hydrol 279(1):262–274
Farnham IM, Johannesson KH, Singh AK, Hodge VF, Stetzenbach KJ (2003) Factor analytical approaches for evaluating groundwater trace element chemistry data. Anal Chim Acta 490(1):123–138
Fidelibus MD, Gutiérrez F, Spilotro G (2011) Human-induced hydrogeological changes and sinkholes in the coastal gypsum karst of Lesina Marina area (Foggia Province, Italy). Eng Geol 118:1–19
Ford DC, Williams PW (1989) Karst geomorphology and hydrology, vol 601. Unwin Hyman, London
Ford D, Williams PD (2013) Karst hydrogeology and geomorphology. Wiley, New York
Fournillon A (2012) Modélisation géologique 3D et hydrodynamique appliquées aux réservoirs carbonatés karstiques: caractérisation des ressources en eau souterraine de l’Unité du Beausset (SE France) (Doctoral dissertation, Aix-Marseille Université)
Günay G (2002) Gypsum karst, Sivas, Turkey. Environ Geol 42:387–398
Gutiérrez F, Guerrero J, Lucha P (2008) A genetic classification of sinkholes illustrated from evaporite paleokarst exposures in Spain. Environ Geol 53:993–1006
Hadji R, Limani Y, Boumazbeur A, Demdoum A, Zighmi K, Zahri F, Chouabi A (2014) Climate change and their influence on shrinkage–swelling clays susceptibility in a semi-arid zone: a case study of Souk Ahras municipality, NE-Algeria. Desalin Water Treat 52(10–12):2057–2072
Hamed Y, Awad S, Ben Sâad A (2013) Nitrate contamination in groundwater in the Sidi Aïch-Gafsa Oasis region, Southern Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci, Journal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2445-5
Hamed Y, Ahmadi R, Hadji R, Mokadem N, Dhia HB, Ali W (2014) Groundwater evolution of the Continental Intercalaire aquifer of Southern Tunisia and a part of Southern Algeria: use of geochemical and isotopic indicators. Desalin Water Treat 52(10–12):1990–1996
Hamed Y, Hadji R, Redhaounia B, Bâali F, El Gayar A (2017) Climate impact on surface and groundwater in North Africa-A Global Synthesis of Findings and Recommendations. The 1st International Symposium (WREIANA 2017) March 24-25-26, 2017 Gafsa-Tunisia
Hamed Y, Redhaounia B, Ben Sâad A, Hadji R, Zahri F, Zighmi K (2017b) Hydrothermal waters from karst aquifer: case study of the Trozza basin (Central Tunisia). J Tethys 5(1):033–044
Hartmann J, Jansen N, Dürr HH, Kempe S, Köhler P (2009) Global CO2-consumption by chemical weathering: What is the contribution of highly active weathering regions? Global Planet Change 69(4):185–194
Jiménez-Torrecilla N, Galve JP, Asta MP, Gómez L, Fuentes J (2004) Los humedales salinos del entrono de Zaragoza: una singularidad hidrogeomorfológica. GeoTemas 6:115–118
Johnson KS, Neal JT (2003) Evaporite karst and engineering/environmental problems in the United States. Oklahoma Geological Survey circular, 109
Kačaroğlu F (1999) Review of groundwater pollution and protection in karst areas. Water Air Soil Pollut 113(1):337–356
Kaçaroglu F, Degirmenci M, Cerit O (2001) Water quality problems of a gypsiferious watershed: upper Kizilirmak Basin, Sivas, Turkey. Water Air Soil Pollut 128:161–180
Kamgang KB, Ekodeck GE (1991) Altération et bilans géochimiques des biotites des gneiss de Nkolbisson (NW de Yaoundé, Cameroun). Géodynamique 6(2):191–199
Khaska M, La Salle CLG, Lancelot J, Mohamad A, Verdoux P, Noret A, Simler R (2013) Origin of groundwater salinity (current seawater vs. saline deep water) in a coastal karst aquifer based on Sr and Cl isotopes. Case study of the La Clape massif (southern France). Appl Geochem 37:212–227
Klimchouk A, Lowe D, Cooper A, Sauro U (1996) Gypsum karst of the World. Int J Speleol 25(3–4):12
Kowalski WM (1997) Les stades d’effondrement du graben de Tébessa (confins Algéro-Tunisien) et la tectonique plicative Plio-Quaternaire. Bull Soc His Nat, Pays de Montbéliard, France
Lamont-Black J, Baker A, Younger PL, Cooper AH (2005) Utilising seasonal variations in hydrogeochemistry and excitation-emission fluorescence to develop a conceptual groundwater flow model with implications for subsidence hazards: an example from Co., Durham (UK). Environ Geol 48:320–335
Land AL (2003) Evaporite karst and regional groundwater circulation in the Lower Pecos Valley of Southeastern New México. In: Johnson KH, Neal JT (eds) Evaporite karst and engineering/environmental problems in the United States, 109. Oklahoma Geological Survey Circular, Norman, pp 227–232
Lopez-Chicano A, Bouamama M, Vallejos A, Pulido-Bosch A (2001) Factors which determine the hydrogeochemical behaviour of karstic springs: a case study from the Betic Cordilleras, Spain. Appl Geochem 16:1179–1192
Lumsden DN, Chimahusky JS (1980) Relationship between dolomite nonstoichiometry and carbonate facies parameters. In: Zenger DH, Dunham JB, Ethington RL (eds) Concepts and Models of Dolomitization. SEPM Special Publication, 28, pp 123–137
Mokadem N, Demdoum A, Hamed Y, Bouri S, Hadji R, Boyce A, Laouar R, Sâad A (2016) Hydrogeochemical and stable isotope data of groundwater of a multi-aquifer system: Northern Gafsa basin–Central Tunisia. J Afr Earth Sci 114:174–191
Moore PJ, Martin JB, Screaton EJ (2009) Geochemical and statistical evidence of recharge, mixing, and controls on spring discharge in an eogenetic karst aquifer. J Hydrol 376(3):443–455
Moral F, Cruz-Sanjulián JJ, Olías M (2008) Geochemical evolution of groundwater in the carbonate aquifers of Sierra de Segura (Betic Cordillera, southern Spain). J Hydrol 360(1):281–296
Mudry J (1987) Apport du traçage physico-chimique naturel à la connaissance hydrocinématique des aquifères carbonatés (Doctoral dissertation, Université de Franche-Comté)
Nader FH, Swennen R, Ottenburgs R (2003) Karst-meteoric dedolomitization in Jurassic carbonates, Lebanon. Geologica Belgica 6:3–23
Nguyet VTM, Thanh VP, Hai VD, Roi ND, Tra DTT (2016) Hydrogeochemical characterization and groundwater quality of the Dong Giao karst aquifer in Tam Diep, Ninh Binh, Vietnam. Postojna Acta Carsolog 45(3):233
Nicolini E, Rogers K, Rakowski D (2016) Baseline geochemical characterisation of a vulnerable tropical karstic aquifer; Lifou, New Caledonia. J Hydrol Reg Stud 5:114–130
Omelon CR, Pollard WH, Andersen DT (2006) A geochemical evaluation of perennial spring activity and associated mineral precipitates at expedition Fjord, Axel Heiberg Island, Canadian High Arctic. Appl Geochem 21:1–15
Panagopoulos G, Lambrakis N, Katagas C, Papoulis D, Tsolis-Katagas P (2005) Water–rock interaction induced by contaminated groundwater in a karst aquifer, Greece. Environ Geol 49(2):300–313
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos, Trans Am Geophys Union 25(6):914–928
Quinif Y (1975) Contribution à l’étude morphologique des karsts algériens de type hautalpin. Rev Géogr Phys Géol Dyn 18:5–18
Raines MA, Dewers TA (1997) Dedolomitization as a driving mechanism for karst generation in Permian Blaine Formation, Southwestern Oklahoma, USA. Carbonates Evaporites 12(1):24–31
Sánchez D, Barberá JA, Mudarra M, Andreo B (2015) Hydrogeochemical tool applied to the study of carbonate aquifers: examples from some karst systems of Southern Spain. Environ Earth Sci 74:199–215
Saporta G (2006) Probabilités, analyses des données et statistiques, Technip, Paris. SAS
Sen Z (1995) Applied hydrogeology for scientists and engineers. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Tuccimei P, Salvati R, Capelli G, Delitala MC, Primavera P (2005) Groundwater fluxes into a submerged sinkhole area, Central Italy, using radon and water chemistry. Appl Geochem 20:1831–1847
Van der Weijden CH, Pacheco FA (2003) Hydrochemistry, weathering and weathering rates on Madeira island. J Hydrol 283(1):122–145
Vicat JP, Mvondo H, Willems L, Pouclet A (2002) Phénomènes karstiques fossiles et actuels au sein des formations métamorphiques silico-alumineuses de la nappe pan-africaine de Yaoundé (Sud-Cameroun). C R Geosci 334(8):545–550
Ward WC, Halley RB (1985) Pleistocene mixing - Zone Dolomite, Northeastern Yucatan Peninsula. J Sed. Pet. 55:407–442
White WB (1988) Geomorphology and hydrology of karst terrains (No. 551.447 W4)
White WB (2002) Karst hydrology: recent developments and open questions. Eng Geol 65(2):85–105
Williams PW (2008) The role of the epikarst in karst and cave hydrogeology: a review. Int J Speleol 37(1):1
Wold S, Esbensen K, Geladi P (1987) Principal component analysis. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 2(1–3):37–52
Woo KS, Moore CH (1996) Burial dolomitization and dedolomitization of the late Cambrian Wagok Formation, Yeongweol, Korea. Carbonates Evaporites 11(1):104–112
Worthington SRH, Davies GJ, Ford DC (2000) Matrix, fracture and channel components of storage and flow in a Paleozoic limestone aquifer. In: Groundwater flow and contaminant transport in carbonate aquifers. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 113–128
Wu P, Tang C, Zhu L, Liu C, Cha X, Tao X (2009) Hydrogeochemical characteristics of surface water and groundwater in the karst basin, southwest China. Hydrol Process 23(14):2012–2022
Yechieli Y, Abelson M, Bein A, Crouvi O, Shtivelman V (2006) Sinkhole “swarms” along the Dead Sea coast: reflection of disturbance of lake and adjacent groundwater systems. Geol Soc Am Bull 118(9–10):1075–1087
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their review. Their gratitude extends to the International Association of Water Resources in the Southern Mediterranean Basin is for the support without forgetting of course the staff of the symposium of WREIANA 2017-Gafsa-Tunisia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The present paper is an original work and all the authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamad, A., Baali, F., Hadji, R. et al. Hydrogeochemical characterization of water mineralization in Tebessa-Kasserine karst system (Tuniso-Algerian Transboundry basin). Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr 3, 7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-017-0045-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-017-0045-6