Abstract
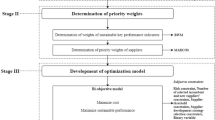
Sustainability has become a significant business issue, and efforts to achieve a sustainable supply chain have been intensely considered. In order to manage a sustainable supply chain, it is essential to choose the appropriate suppliers and assign the right amount of orders among them. Uncertainty about future demand makes these matters a substantial concern, and despite their importance, it has received much less attention from researchers in supplier selection and order allocation problems. In this regard, this paper presents a three-stage method for sustainable supplier selection and order allocation. In the first stage, fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS were used to weight the criteria and rank the sustainable suppliers, and suppliers with acceptable sustainability performance were selected. In the second stage, the future value of demand is forecasted by polynomial regression (PR). In the third stage, a mathematical programming model was formulated considering a novel quality standard policy. Efficient solutions were obtained by solving a novel multi-objective, multi-period stochastic mixed-integer model utilizing LP-metric. Also, a real-world case study for a small business is presented to validate the performance of the proposed method. A sensitivity analysis reveals the effect of changes in demand, suppliers’ capacity, purchasing costs, and quality policy.































Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Due to the nature of this research, data is available within the text.
References
Abbaspour S, Aghsami A, Jolai F, Yazdani M (2022) An integrated queueing-inventory-routing problem in a green dual-channel supply chain considering pricing and delivery period: A case study of construction material supplier. J Comput Des Eng 9(5):1917–1951
Ahmadi S, Amin SH (2019) An integrated chance-constrained stochastic model for a mobile phone closed-loop supply chain network with supplier selection. J Clean Prod 226:988–1003
Aktepe A, Yanık E, Ersöz S (2021) Demand forecasting application with regression and artificial intelligence methods in a construction machinery company. J Intell Manuf 32:1587–1604
Amin SH, Wu H, Karaphillis G (2018) A perspective on the reverse logistics of plastic pallets in Canada. J Remanufacturing 8(3):153–174
Amindoust A (2018) Supplier selection considering sustainability measures: an application of weight restriction fuzzy-DEA approach. RAIRO-Oper Res 52(3):981–1001
Amindoust A, Ahmed S, Saghafinia A, Bahreininejad A (2012) Sustainable supplier selection: a ranking model based on fuzzy inference system. Appl Soft Comput 12(6):1668–1677
Ayhan MB, Kilic HS (2015) A two stage approach for supplier selection problem in multi-item/multi-supplier environment with quantity discounts. Comput Ind Eng 85:1–12
Azani M, Shaerpour M, Yazdani MA, Aghsami A, Jolai F (2022) A novel scenario-based Bi-objective optimization model for sustainable food supply chain during the COVID-19: a case study. Process Integr Optim Sustain (6):1–21
Baltputnis K, Petrichenko R, Sobolevsky D (2018) Heating demand forecasting with multiple regression: model setup and case study. In: 2018 IEEE 6th Workshop on Advances in Information, Electronic and Electrical Engineering (AIEEE). Vilnius Lithuania, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/AIEEE.2018.8592144
Beiki H, Mohammad Seyedhosseini S, Ponkratov V, Olegovna Zekiy A, Ivanov SA (2021) Addressing a sustainable supplier selection and order allocation problem by an integrated approach: a case of automobile manufacturing. J Ind Prod Eng 38(4):239–253
Benyoucef M, Canbolat M (2007) Fuzzy AHP-based supplier selection in e-procurement. Int J Serv Oper Manag 3(2):172–192
Bera D, Chatterjee ND, Bera S (2021) Comparative performance of linear regression, polynomial regression and generalized additive model for canopy cover estimation in the dry deciduous forest of West Bengal. Remote Sens Appl: Soc Environ 22:100502
Branke J (2008) Consideration of partial user preferences in evolutionary multiobjective optimization. Multiobjective Optim 5252:157–178
Bruno DE, Barca E, Goncalves RM, de Araujo Queiroz HA, Berardi L, Passarella G (2018) Linear and evolutionary polynomial regression models to forecast coastal dynamics: comparison and reliability assessment. Geomorphology 300:128–140
Buckley JJ (1985) Fuzzy hierarchical analysis. Fuzzy Sets Syst 17(3):233–247
Dai Z, Aqlan F, Gao K, Zhou Y (2019) A two-phase method for multi-echelon location-routing problems in supply chains. Expert Syst Appl 115:618–634
Deb K (2011) Multi-objective optimisation using evolutionary algorithms: an introduction. In: Multi-objective evolutionary optimisation for product design and manufacturing. Springer, pp 3–34
Dobos I, Vörösmarty G (2021) Green supplier selection using a common weights analysis of DEA and EOQ types of order allocation. Manag Decis Econ 42(3):612–621
Duan C-Y, Liu H-C, Zhang L-J, Shi H (2019) An extended alternative queuing method with linguistic Z-numbers and its application for green supplier selection and order allocation. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21(8):2510–2523
Duan L, Ventura JA (2019) A dynamic supplier selection and inventory management model for a serial supply chain with a novel supplier price break scheme and flexible time periods. Eur J Oper Res 272(3):979–998
Firouzi F, Jadidi O (2021) Multi-objective model for supplier selection and order allocation problem with fuzzy parameters. Expert Syst Appl 180:115129
Franek J, Kresta A (2014) Judgment scales and consistency measure in AHP. Procedia Econ Financ 12:164–173
Gandomi A, Haider M (2015) Beyond the hype: big data concepts, methods, and analytics. Int J Inf Manag 35(2):137–144
Ghadimi P, Toosi FG, Heavey C (2018) A multi-agent systems approach for sustainable supplier selection and order allocation in a partnership supply chain. Eur J Oper Res 269(1):286–301
Ghoushchi SJ, Milan MD, Rezaee MJ (2018) Evaluation and selection of sustainable suppliers in supply chain using new GP-DEA model with imprecise data. J Ind Eng Int 14(3):613–625
Gören HG (2018) A decision framework for sustainable supplier selection and order allocation with lost sales. J Clean Prod 183:1156–1169
Govindan K, Mina H, Esmaeili A, Gholami-Zanjani SM (2020) An integrated hybrid approach for circular supplier selection and closed loop supply chain network design under uncertainty. J Clean Prod 242:118317
Gumus AT (2009) Evaluation of hazardous waste transportation firms by using a two step fuzzy-AHP and TOPSIS methodology. Expert Syst Appl 36(2, Part 2):4067–4074
Hamdan S, Cheaitou A (2017) Supplier selection and order allocation with green criteria: an MCDM and multi-objective optimization approach. Comput Oper Res 81:282–304
Harker PT, Vargas LG (1987) The theory of ratio scale estimation: Saaty’s analytic hierarchy process. Manag Sci 33(11):1383–1403
Hashemzahi P, Azadnia A, Galankashi MR, Helmi SA, Rafiei FM (2020) Green supplier selection and order allocation: a nonlinear stochastic model. Int J Value Chain Manag 11(2):111–138
Ho W, Xu X, Dey PK (2010) Multi-criteria decision making approaches for supplier evaluation and selection: a literature review. Eur J Oper Res 202(1):16–24
Hwang C-L, Yoon K (1981) Methods for multiple attribute decision making. In: Multiple attribute decision making. Springer, pp 58–191
Islam S, Amin SH, Wardley LJ (2021) Machine learning and optimization models for supplier selection and order allocation planning. Int J Prod Econ 242:108315
Jia R, Liu Y, Bai X (2020) Sustainable supplier selection and order allocation: distributionally robust goal programming model and tractable approximation. Comput Ind Eng 140:106267
Kaur H, Singh SP (2021) Multi-stage hybrid model for supplier selection and order allocation considering disruption risks and disruptive technologies. Int J Prod Econ 231:107830
Kaviani MA, Peykam A, Khan SA, Brahimi N, Niknam R (2020) A new weighted fuzzy programming model for supplier selection and order allocation in the food industry. J Model Manag 15
Koprulu A, Albayrakoglu MM (2007) Supply chain management in the textile industry: a supplier selection model with the analytical hierarchy process. Proceeding of the International Symposium on the Analytic Hierarchy Process, Via Del Mar, Chile
Li F, Wu C-H, Zhou L, Xu G, Liu Y, Tsai S-B (2021) A model integrating environmental concerns and supply risks for dynamic sustainable supplier selection and order allocation. Soft Comput 25(1):535–549
Liaqait RA, Warsi SS, Agha MH, Zahid T, Becker T (2021) A multi-criteria decision framework for sustainable supplier selection and order allocation using multi-objective optimization and fuzzy approach. Eng Optim 54:1–22
Liu Y, Eckert CM, Earl C (2020) A review of fuzzy AHP methods for decision-making with subjective judgements. Expert Syst Appl 113738
Lo H-W, Liou JJ, Wang H-S, Tsai Y-S (2018) An integrated model for solving problems in green supplier selection and order allocation. J Clean Prod 190:339–352
Masoumi M, Aghsami A, Alipour-Vaezi M, Jolai F, Esmailifar B (2022) An M/M/C/K queueing system in an inventory routing problem considering congestion and response time for post-disaster humanitarian relief: a case study. J Humanit Logist Supply Chain Manag 12(2):182–219
Mavi RK, Goh M, Mavi NK (2016) Supplier selection with Shannon entropy and fuzzy TOPSIS in the context of supply chain risk management. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 235:216–225
Mirzapour Al-E-Hashem S, Malekly H, Aryanezhad MB (2011) A multi-objective robust optimization model for multi-product multi-site aggregate production planning in a supply chain under uncertainty. Int J Prod Econ 134(1):28–42
Mohammadnazari Z, Mousapour Mamoudan M, Alipour-Vaezi M, Aghsami A, Jolai F, Yazdani M (2022) Prioritizing post-disaster reconstruction projects using an integrated multi-criteria decision-making approach: a case study. Buildings 12(2):136
Mohammed A, Harris I, Govindan K (2019) A hybrid MCDM-FMOO approach for sustainable supplier selection and order allocation. Int J Prod Econ 217:171–184
Mohammed A, Setchi R, Filip M, Harris I, Li X (2018) An integrated methodology for a sustainable two-stage supplier selection and order allocation problem. J Clean Prod 192:99–114
Moheb-Alizadeh H, Handfield R (2019) Sustainable supplier selection and order allocation: a novel multi-objective programming model with a hybrid solution approach. Comput Ind Eng 129:192–209
Montgomery DC (2013) Statistical quality control: a modern introduction. J. Wiley
Mousakhani S, Nazari-Shirkouhi S, Bozorgi-Amiri A (2017) A novel interval type-2 fuzzy evaluation model based group decision analysis for green supplier selection problems: a case study of battery industry. J Clean Prod 168:205–218
Naqvi MA, Amin SH (2021) Supplier selection and order allocation: a literature review. Journal of Data. Inf Manag 3:1–15
Nasr AK, Tavana M, Alavi B, Mina H (2021) A novel fuzzy multi-objective circular supplier selection and order allocation model for sustainable closed-loop supply chains. J Clean Prod 287:124994
Nourmohamadi Shalke P, Paydar MM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M (2018) Sustainable supplier selection and order allocation through quantity discounts. Int J Manag Sci Eng Manag 13(1):20–32
Park K, Kremer GEO, Ma J (2018) A regional information-based multi-attribute and multi-objective decision-making approach for sustainable supplier selection and order allocation. J Clean Prod 187:590–604
Paydar MM, Arabsheybani A, Safaei AS (2017) A new approach for sustainable supplier selection. Int J Ind Eng Prod Res 28(1):47–59
Rahmani Mokarrari K, Shirazian S, Aghsami A, Jolai F (2022) A stochastic-fuzzy multi-objective model for the last-mile delivery problem using drones and ground vehicles, a case study. Scientia Iranica
Rezaei A, Aghsami A, Rabbani M (2021) Supplier selection and order allocation model with disruption and environmental risks in centralized supply chain. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 12:1–37
Rezaei A, Rahiminezhad Galankashi M, Mansoorzadeh S, Mokhatab Rafiei F (2020) Supplier selection and order allocation with lean manufacturing criteria: an integrated MCDM and bi-objective modelling approach. Eng Manag J 32(4):253–271
Saaty TL (1988) What is the analytic hierarchy process? In: Mathematical models for decision support. Springer, pp 109–121
Safa M, Shahi A, Haas CT, Hipel KW (2014) Supplier selection process in an integrated construction materials management model. Autom Constr 48:64–73
Safaeian M, Fathollahi-Fard AM, Tian G, Li Z, Ke H (2019) A multi-objective supplier selection and order allocation through incremental discount in a fuzzy environment. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 37(1):1435–1455
Scott J, Ho W, Dey PK, Talluri S (2015) A decision support system for supplier selection and order allocation in stochastic, multi-stakeholder and multi-criteria environments. Int J Prod Econ 166:226–237
Sen DK, Datta S, Mahapatra S (2018) Sustainable supplier selection in intuitionistic fuzzy environment: a decision-making perspective. Benchmarking: An International Journal
Shah I, Iftikhar H, Ali S, Wang D (2019) Short-term electricity demand forecasting using components estimation technique. Energies 12(13):2532
Shakibaei H, Farhadi-Ramin MR, Alipour-Vaezi M, Aghsami A, Rabbani M (2023) Designing a post-disaster humanitarian supply chain using machine learning and multi-criteria decision-making techniques. Kybernetes
Son N, Hop N (2021) A hybrid meta-heuristics approach for supplier selection and order allocation problem for supplying risks of recyclable raw materials. Int J Ind Eng Comput 12(2):177–190
Sontake A, Jain N, Singh A (2021) Sustainable supplier selection and order allocation considering discount schemes and disruptions in supply chain. In: Operations Management and Systems Engineering. Springer, pp 61–94
Stević Ž, Pamučar D, Puška A, Chatterjee P (2020) Sustainable supplier selection in healthcare industries using a new MCDM method: measurement of alternatives and ranking according to COmpromise solution (MARCOS). Comput Ind Eng 140:106231
Sun C-C (2010) A performance evaluation model by integrating fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS methods. Expert Syst Appl 37(12):7745–7754
Tavana M, Fallahpour A, Di Caprio D, Santos-Arteaga FJ (2016) A hybrid intelligent fuzzy predictive model with simulation for supplier evaluation and selection. Expert Syst Appl 61:129–144
Vahidi F, Torabi SA, Ramezankhani M (2018) Sustainable supplier selection and order allocation under operational and disruption risks. J Clean Prod 174:1351–1365
Vasiljević M, Fazlollahtabar H, Stević Ž, Vesković S (2018) A rough multicriteria approach for evaluation of the supplier criteria in automotive industry. Decis Mak: Appl Manag Eng 1(1):82–96
Ventura JA, Bunn KA, Venegas BB, Duan L (2021) A coordination mechanism for supplier selection and order quantity allocation with price-sensitive demand and finite production rates. Int J Prod Econ 233:108007
Wilson VH, NS AP, Shankharan A, Kapoor S, Rajan AJ (2020) Ranking of supplier performance using machine learning algorithm of random forest. Int J Adv Res Eng Technol (IJARET) 11(5)
Zadeh LA (1996) Fuzzy sets. In Fuzzy sets, fuzzy logic, and fuzzy systems: selected papers by Lotfi A Zadeh. World Scientific, pp 394–432
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. Alireza Jafari for his cooperation in the review and insightful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by the author.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors agree with publishing in this journal.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
The undersigned authors declare that this manuscript is original, has not been published before, and is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jafari-Raddani, M., Asgarabad, H.C., Aghsami, A. et al. A Hybrid Approach to Sustainable Supplier Selection and Order Allocation Considering Quality Policies and Demand Forecasting: A Real-Life Case Study. Process Integr Optim Sustain 8, 39–69 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41660-023-00350-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41660-023-00350-x