Abstract
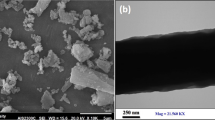
Bone tissue engineering has begun to draw attention in recent years. The interactive combination of biomaterials and cells is part of bone tissue engineering. Sodium alginate (SA) is a biologically compatible, degradable, non-toxic natural polymer accepted by the human body and is widely used in the field of tissue engineering. Polylactic acid (PLA) is another type of biodegradable thermoplastic polyester derived from renewable sources which are used in bone tissue engineering and biomedical owing to its biocompatibility and biodegradability. Hydroxyapatite (HA) and tricalcium phosphate (TCP) derived from natural sources such as marine species and bovine bone are biocompatible and non-toxic biomaterials which are used to reconstruct many parts of the skeleton. In this study, PLA, SA with different compositions, and nanofibers obtained by adding orange spiny oyster shell powders (Spondylus barbatus) to them by using electrospining technique. Cell culture study, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and physical analysis such as density, electrical conductivity, surface tension, viscosity measurement, and tensile strength measurement tests were carried out after the production process. Produced nanofibers showed smooth and beadless surface. The average diameters and distributions decreased with the addition of optimum PLA and TCP amount. The tensile strength of nanofibers was enhanced with the additional SA and TCP. The produced nanofibers are compatible with human bone tissue, which are not cytotoxic, and in addition, a high cell efficiency of SaOS-2 cells on the nanofibers was observed with SEM images.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balagangadharan, K., Dhivya, S., Selvamurugan, N.: Chitosan based nanofibers in bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 104, 1372–1382 (2017)
Ferrone, M.L., Raut, C.P.: Modern surgical therapy: limb salvage and the role of amputation for extremity soft-tissue sarcomas. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 21, 201–213 (2012)
Santoro, M., Shah, S.R., Walker, J.L., Mikos, A.G.: Poly (lactic acid) nano fibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering. Adv.Drug Deliv. Rev. 107, 206–212 (2016)
Liu, X., Holzwarth, J.M., Ma, P.X.: Functionalized synthetic biodegradable polymer scaffolds for tissue engineering. Macromol. Biosci. 12, 911–919 (2012)
Martinez, E., Engel, E., Planell, J.A., Samitier, J.: Effects of artificial micro- and nano-structured surfaces on cell behaviour. Ann. Anat. 191, 126–135 (2009)
Shelke, N., James, R., Laurencin, C., Kumbar, S.: Polysaccharide biomaterials for drug delivery and regenerative engineering. Polym. Adv. Technol. 25(5), 448–460 (2014)
Yang, J.M., Wang, N.C., Chiu, H.C.: Preparation and characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate blended membrane for alkaline solidpolymer electrolytes membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 457, 139–148 (2014)
Zhang, Y., Liu, J., Huang, L., Wang, Z., Wang, L.: Design and performance of a sericin-alginate interpenetrating network hydrogel for cell and drug delivery. Sci. Rep. 5, 12374 (2015)
Xua, W., Shenc, R., Yana, Y., Gao, J.: Preparation and characterization of electrospun alginate/PLA nanofibers as tissue engineering material by emulsion eletrospinning. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 65, 428–438 (2017)
Ginzberg, M.D., Bonshtein, I.G., Agbaria, R., Cohen, S.: Tissue Eng. 9, 757–763 (2003)
Paul, W., Sharma, C.P.: Trends. Biomater. Artif. Organ. 18, 18–23 (2004)
Nie, H., He, A., Zheng, J., Xu, S., Li, J., Han, C.: Effects of chain conformation and entanglement on the electrospinning of pure alginate. Biomacromolecules. 9(5), 1362–1365 (2008)
Safi, S., Morshed, M., Hosseini Ravandi, S.A., Ghiaci, M.: Study of electrospinning of sodium alginate, blended solutions of sodium alginate/poly (vinyl alcohol) and sodium alginate/poly (ethylene oxide). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 104, 3245–3255 (2007)
Rasal, R.M., Janorkar, A.V., Hirt, D.E.: Poly(lacticacid) modifications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 35, 338–356 (2010)
Montjovent, M.O., Mathieu, L., Hinz, B.: Biocompatibility of bioresorbable poly (L-lactic acid) composite scaffolds obtained by supercritical gas foaming with human fetal bone cells. Tissue Eng. 11, 1640–1649 (2005)
Zhou, C.J., Shi, Q.F., Guo, W.H., Terrell, L., Qureshi, A.T., Hayes, D.J., Wu, Q.L.: Electrospun bionano composites caffolds for bone tissue engineering by cellulose nano crystals reinforcing malei can hydride grafted PLA. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 5, 3847–3854 (2013)
Casasola, R., Thomas, N.L., Trybala, A., Georgiadou, S.: Electrospun polylacticacid (PLA) fibres: effect of different solvent systems on fibremorphology and diameter. Polymer. 55, 4728–4737 (2014)
Kikuchi, M., Koyama, Y., Takakuda, K., Miyairi, H., Shirahama, N., Tanaka, J.: In vitro change in mechanical strength of β-tricalcium phosphate/copolymerized poly-Llactide composites and their application for guided bone regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 62, 265–272 (2002)
Sionkowska, A.: Current research on the blends of natural and synthetic polymers as new biomaterials: review. Prog Polym Scı. 36, 1254–1276 (2011)
Macha, I.J., Ozyegin, L., Chou, J., Samur, R., Oktar, F., Ben- Nissan, B.: An alternative synthesis method for di calcium phosphate (monetite) powders from Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) shells. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 49(2), 122–128 (2013)
Kel, D., Gökçe, H., Bilgiç, D., Agaogulları, D., Duman, I., Öveçoğlu, M.L., Kayalı, E.S., Kıyıcı, I.A., Agathopoulos, S., Oktar, F.N.: Production of natural bioceramic from land snails. Key Eng. Mater. 493–494, 287–292 (2012). www.scientific.net/KEM.493-494.287
Macha, I.J., Ozyegin, L.S., Oktar, F.N., Ben-Nissan, B.: Conversion of ostrich eggshells (Struthio camelus) to calcium phosphates. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 51(1), 125–133 (2015)
Gunduz, O., Sahin, Y.M., Agathopoulos, S., Ben-Nissan, B., Oktar, F.N.: A new method for fabrication of nanohydroxyapatite and TCP from the sea snail Cerithium vulgatum. J. Nanomater. 6(2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/382861
Woo, K.M., Jun, J.H., Chen, V.J., Seo, J., Baek, J.H., Ryoo, H.M., Kim, G.S.: Nano-fibrous scaffolding promotes osteoblast differentiation and biomineralization. Biomaterials. 28, 335–343 (2007)
Desai, K., Kit, K., Li, J. J., Davidson, P. M., Zivanovic, S., & Meyer, HNanofibrous chitosan non-wovens for filtration applications. Polymer. 50, 3661–3669 (2009)
Sambaer, W., Zatloukal, M., Kimmer, D.: 3D modeling of filtration process via polyurethane nanofiber based nonwoven filters prepared by electrospinning process. Chem. Eng. Sci. 66, 613–623 (2011)
Zhu, Y.C., Bando, Y., Xue, D.F., Sekiguchi, T., Golberg, D., Xu, F.F., Liu, Q.L.: New boron nitride whiskers: showing strong ultraviolet and visible light luminescence. J. Phys. Chem. B. 108(20), 6193–6196 (2004)
Bhardwaj, N., Kundu, S.C.: Electrospinning: a fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 28, 325–347 (2010)
Mosmann, T.: Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods. 65(1–2), 55–63 (1983)
Kalkandelen, C., Suleymanoglu, M., Kuruca, S.E., Akan, A., Oktar, F.N., Gunduz, O.: Part 2: biocompatibility evaluation of hydroxyapatite-based clinoptilolite and Al2O3 composites. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 53(1), 217–223 (2017)
Demir, M.M., Yilgor, I., Yilgor, E., Erman, B.: Electrospinning of polyurethanefiber. Polymer. 43, 3303–3309 (2002)
Tana, S.H., Inaia, R., Kotakib, M., Ramakrishna, S.: Systematic parameter study for ultra-fine fiber fabrication via electrospinning process. Polymer. 46, 6128–6134 (2005)
Zong, X.H., Kim, K., Fang, D.F., Ran, S.F., Hsiao, B.S., Chu, B.: Structure and process relationship of electrospun bioabsorbable nanofiber membranes. Polymer. 43, 4403 (2002)
Kim, H.S., Kim, K., Jin, H.J., Chin, I.J.: Morphological characterization of electrospun nano-fibrous membranes of biodegradable poly(L-lactide) and poly (lactideco- glycolide). Macromol. Symp. 224, 145 (2005)
Haghi, A.K., Akbari, M.: Trends in electrospinning of natural nanofibers. Phys. Status Solidi (A) Appl. Mater. Sci. 204, 1830–1834 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa
Jiang, H.L., Fang, D.F., Hsiao, B.S., Chu, B., Chen, W.L.: Optimization and characterization of dextran membranes prepared by electrospinning. Biomacromolecules. 5, 326 (2004)
Huang, L., Nagapudi, K., Apkarian, R.P., Chaikof, E.L.: Engineered collagen-PEO nanofibers and fabrics. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 12, 979 (2001)
Shalumon, K.T., Anulekha, K.H., Nair, S.V., Nair, S.V., Chennazhi, K.P., Jayakumar, R.: Sodium alginate/poly (vinyl alcohol)/nano ZnO composite nanofibers for antibacterial wound dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 49, 247–254 (2011)
Zhang, C., Wang, L., Zhai, T., Wang, X., Dan, Y., Turng, L.S.: The surface grafting of graphene oxide with poly (ethylene glycol) as a reinforcement for poly(lactic acid) nanocomposite scaffolds for potential tissue engineering applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 53, 403–413 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2015.08.043
Zheng, J., Yu, X., Wang, C., Cao, Z., Yang, H., Ma, D., Xu, X.: Facile synthesis of three-dimensional reinforced Sn@polyaniline/sodium alginate nanofiber hydrogel network for high performance lithium-ion battery. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 4457–4464 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4317-8
Moreira, A.P.D., Sader, M.S., Soares, G.D.d.A., Leão, M.H.M.R.: Strontium incorporation on microspheres of alginate/β-tricalcium phosphate as delivery matrices. Mater. Res. 17(4), 967–973 (2014)
Pham, Q.P., Sharma, U., Mikos, A.G.: Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: a review. Tissue Eng. 12(5), 1197–1211 (2006)
Fan, H.S., Wen, X.T., Tan, Y.F., Wang, R., Cao, H.D., Zhang, X.D.: Compare of electrospinning PLA and PLA/β-TCP scaffold in vitro. Mater. Sci. Forum. 475-479, 2379–2382 (2005)
Karacan, I., Gunduz, O., Ozyegin, L.S., Gökce, H., Ben-Nissan, B., Akyol, S., Oktar, F.N.: The natural nano-bioceramic powder production from organ pipe red coral (Tubipora musica) by a simple chemical conversion method. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 54, 317–329 (2018)
Gunduz, O., Sahin, Y.M., Agathopoulos, S., Ağaoğulları, D., Gökçe, H., Kayali, E.S., Aktas, C., Ben-Nissan, B., Oktar, F.N.: Nano calcium phosphate powder production through chemical agitation from Atlantic deer cowrie shells (Cypraea cervus Linnaeus). Key Eng. Mater. 587, 80–85 (2014)
Munteanu, B.S., Aytac, Z., Pricope, G.M., Uyar, T.: Polylactic acid (PLA)/silver-NP/VitaminE bionanocomposite electrospun nanofibers with antibacterial and antioxidant activity. J. Nanopart. Res. 16(10), 2643 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2643-4
Venkatesan, J., Bhatnagar, I., Manivasagan, P., Kang, K.H., Kim, S.K.: Alginate composites for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 72, 269–281 (2015)
Hong, Z., Qiu, X., Sun, J., Deng, M., Chen, X., Jing, X.: Grafting polymerization of L-lactide on the surface of hydroxyapatite nanocrystals. Polymer. 45(19), 6699–6706 (2004)
Zhang, C.Y., Lu, H., Zhuang, Z., Wang, X.P., Fang, Q.F.: Nano-hydroxyapatite/poly (L-lactic acid) composite synthesized by a modified in situ precipitation: preparation and properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 21, 3077–3083 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-010-4161-y
Ma, H., Su, W., Tai, Z., Sun, D., Yan, X., Liu, B., Xue, Q.: Preparation and cytocompatibility of polylactic acid/hydroxyapatite/ graphene oxide nanocomposite fibrous membrane. 57(23), 3051–3058 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-012-5336-3
Venkatesan, J., Bhatnagar, I., Manivasagan, P., Kang, K.H., Kim, S.K.: Alginate composites for bone tissue engineering: a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 72, 269–281 (2015)
Tajbakhsh, S., Hajiali, F.: A comprehensive study on the fabrication and properties of biocomposites of poly (lactic acid)/ceramics for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. 70, 897–912 (2017)
Funding
This study has been funded by the Ministry of Development, Turkey; project no: 2016K121280.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cesur, S., Oktar, F.N., Ekren, N. et al. Preparation and characterization of electrospun polylactic acid/sodium alginate/orange oyster shell composite nanofiber for biomedical application. J Aust Ceram Soc 56, 533–543 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00363-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00363-1