Abstract
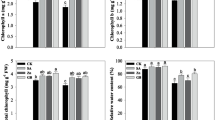
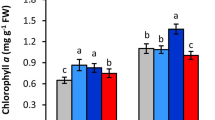
Drought stress limits the oilseed crops productivity in semi-arid areas. To alleviate drought stress effects during seed-filling stage, the effect of foliar application of different Zn concentration (0, 0.6 and 1.2 kg ha−1) on five safflower genotypes was investigated in a 2-year (2015–2016 and 2016–2017) field experiments. The results showed that supplemental Zn (1.2 kg ha−1) significantly increased drought resistance by enhancement in proline (20%) and carbohydrate accumulation (4.3%), relative water content (2.4%) and chlorophyll content (3.8%) in all studied safflower genotypes. The induced improve in safflower’s physiological traits achieved in the Zn supplemented treatment resulted in a significant increase in genotypes yield and its components. Moreover, Zn foliar application significantly reduced the drought adverse effect on oil yield and improved the unsaturated fatty acids content. Finally, Zn foliar application can represent an effective means to mitigate the adverse effects of drought stress on growth and the yield of safflower genotypes in water shortage condition.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Lattief, E. A. (2013). Safflower yields and water use efficiency as affected by irrigation at different soil moisture depletion levels and plant population density under arid conditions. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science,59, 1545–1557. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2012.735769.
Anosheh, H. P., Sadeghi, H., & Emam, Y. (2011). Chemical priming with urea and KNO3 enhances maize hybrids (Zea mays L.) seed viability under abiotic stress. Journal of Crop Science and Biotechnology,14, 289–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-011-0039-x.
Ashraf, M., Harris, P., & Harris, P. (2005). Use of genetic engineering and molecular biology approaches for crop improvement for stress environments. Abiotic Stress. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781482293609-11.
Ashrafi, E., & Razmjoo, K. (2010). Effect of irrigation regimes on oil content and composition of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) cultivars. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society,87, 499–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-009-1527-8.
Bates, L. S., Waldren, R. P., & Teare, I. D. (1973). Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant and Soil,39, 205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018060.
Cakmak, I. (2008). Enrichment of cereal grains with zinc: Agronomic or genetic biofortification? Plant and Soil,302, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9466-3.
Cakmak, I., Kalayci, M., Kaya, Y., Torun, A. A., Aydin, N., Wang, Y., et al. (2010). Biofortification and localization of zinc in wheat grain. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry,58, 9092–9102. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf101197h.
Coleman, J. E. (1998). Zinc enzymes. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology,2, 222–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1367-5931(98)80064-1.
Colnago, L. A., Azeredo, R. B. V., Marchi Netto, A., Andrade, F. D., & Venâncio, T. (2011). Rapid analyses of oil and fat content in agri-food products using continuous wave free precession time domain NMR. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry,49, S113–S120. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrc.2841.
Cornic, G. (1994). Drought stress and high light effects on leaf photosynthesis. Photoinhibition of Photosynthesis, 297–313. https://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10006109918/. Accessed 23 Nov 2018.
Errabii, T., Gandonou, C. B., Essalmani, H., Abrini, J., Idaomar, M., & Skali Senhaji, N. (2007). Effects of NaCl and mannitol induced stress on sugarcane (Saccharum sp.) callus cultures. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum,29, 95–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-006-0006-1.
Eslam, P. (2011). Evaluation of physiological indices for improving water deficit tolerance in spring safflower. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 13, 327–338. https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Evaluation+of+physiological+indices+for+improving+water+deficit+tolerance+in+spring+safflower.+J+Agric+Sci+Technol+&btnG. Accessed 23 Nov 2018.
Fernández, V., & Eichert, T. (2009). Uptake of hydrophilic solutes through plant leaves: Current state of knowledge and perspectives of foliar fertilization. CRC Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences,28, 36–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352680902743069.
Gandonou, C. B., Errabii, T., Abrini, J., Idaomar, M., & Senhaji, N. S. (2006). Selection of callus cultures of sugarcane (Saccharum sp.) tolerant to NaCl and their response to salt stress. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture,87, 9–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-006-9113-3.
Ghamarnia, H., Environ, S., & Sepehri, J. (2010). Different irrigation regimes affect water use, yield and other yield components of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) crop in a semi-arid region of Iran. Journal of Food, Agriculture and Environment, 8, 590–593. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Houshang_Ghamarnia/publication/234841399_Different_irrigation_regimes_affect_water_use_yield_and_other_yield_components_of_safflower_Carthamus_tinctorius_L_crop_in_a_semi-arid_region_of_Iran/links/56852df008ae19758394e. Accessed 23 Nov 2018.
Ghanaatiyan, K., & Sadeghi, H. (2017). Differential responses of chicory ecotypes exposed to drought stress in relation to enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants as well as ABA concentration. Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology,92, 404–410. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2017.1286235.
Guo, M. (2009). Soil sampling and methods of analysis. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2008.0018br.
Hänsch, R., & Mendel, R. R. (2009). Physiological functions of mineral micronutrients (Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Ni, Mo, B, Cl). Current Opinion in Plant Biology,12, 259–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PBI.2009.05.006.
Hassan, M. J., Zhang, G., Wu, F., Wei, K., & Chen, Z. (2005). Zinc alleviates growth inhibition and oxidative stress caused by cadmium in rice. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science,168, 255–261. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.200420403.
Hojati, M., Modarres-Sanavy, S. A., Karimi, M., & Ghanati, F. (2011a). Responses of growth and antioxidant systems in Carthamus tinctorius L. under water deficit stress. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum,33, 105–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0521-y.
Hojati, M., Modarres-Sanavy, S. A. M., Karimi, M., & Ghanati, F. (2011b). Responses of growth and antioxidant systems in Carthamus tinctorius L. under water deficit stress. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum,33, 105–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0521-y.
Hussain, S., Maqsood, M. A., Rengel, Z., & Aziz, T. (2012). Biofortification and estimated human bioavailability of zinc in wheat grains as influenced by methods of zinc application. Plant and Soil,361, 279–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1217-4.
Istanbulluoglu, A., Gocmen, E., Gezer, E., Pasa, C., & Konukcu, F. (2009). Effects of water stress at different development stages on yield and water productivity of winter and summer safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Agricultural Water Management,96, 1429–1434. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AGWAT.2009.04.004.
Kar, G., Kumar, A., & Martha, M. (2007). Water use efficiency and crop coefficients of dry season oilseed crops. Agricultural Water Management,87, 73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AGWAT.2006.06.002.
Karim, M. R., Zhang, Y.-Q., Zhao, R.-R., Chen, X.-P., Zhang, F.-S., & Zou, C.-Q. (2012). Alleviation of drought stress in winter wheat by late foliar application of zinc, boron, and manganese. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science,175, 142–151. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201100141.
Kauser, R., Athar, H. U. R., & Ashraf, M. (2006). Chlorophyll fluorescence: A potential indicator for rapid assessment of water stress tolerance in Canola (Brassica napus L.). Pakistan Journal of Botany, 38(5 Spec issue), 1501–1509. https://www.escholar.manchester.ac.uk/uk-ac-man-scw:158076. Accessed 10 Feb 2019.
Kaya, C., & Higgs, D. (2002). Response of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) cultivars to foliar application of zinc when grown in sand culture at low zinc. Scientia Horticulturae (Amsterdam),93, 53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4238(01)00310-7.
Khan, H. R., McDonald, G. K., & Rengel, Z. (2003). Zn fertilization improves water use efficiency, grain yield and seed Zn content in chickpea. Plant and Soil,249, 389–400. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022808323744.
Khan, H. R., McDonald, G. K., & Rengel, Z. (2004). Zinc fertilization and water stress affects plant water relations, stomatal conductance and osmotic adjustment in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Plant and Soil,267, 271–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-005-0120-7.
Li, D., & Mündel, H. H. (1996). Safflower. Carthamus tinctorius L. Promoting the conservation and use of underutilized and neglected crops. 7. Rome: Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research (p. 83).
Lobell, D. B., Burke, M. B., Tebaldi, C., Mastrandrea, M. D., Falcon, W. P., & Naylor, R. L. (2008). Prioritizing climate change adaptation needs for food security in 2030. Science,319, 607–610. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1152339.
Mousavi, S. (2011). Zinc in crop production and interaction with phosphorus. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5, 1503–1509. https://www.researchgate.net/file.PostFileLoader.html?id=589043c8dc332d7c8f1db4e5&assetKey=AS%3A456500230529029%401485849544613. Accessed 23 Nov 2018.
Movahhedy-Dehnavy, M., Modarres-Sanavy, S. A. M., & Mokhtassi-Bidgoli, A. (2009). Foliar application of zinc and manganese improves seed yield and quality of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) grown under water deficit stress. Industrial Crops and Products,30, 82–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INDCROP.2009.02.004.
Nazari, M., Mirlohi, A., & Majidi, M. M. (2017). Effects of drought stress on oil characteristics of Carthamus species. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society,94, 247–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-016-2938-y.
Pandey, R. (2015). Mineral nutrition of plants. In Plant biology and biotechnology (New Delhi: Springer India), pp. 499–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2286-6_20.
Patade, V. Y., Suprasanna, P., & Bapat, V. A. (2008). Effects of salt stress in relation to osmotic adjustment on sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) callus cultures. Plant Growth Regulation,55, 169–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-008-9270-y.
Pinheiro, C., & Chaves, M. M. (2011). Photosynthesis and drought: Can we make metabolic connections from available data? Journal of Experimental Botany,62, 869–882. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq340.
Pourdad, S. (2008). Study on drought resistance indices in spring safflower. Acta Agron. Hungarica,56, 203–212. https://doi.org/10.1556/AAgr.56.2008.2.9.
Rehman, H., Aziz, T., Farooq, M., Wakeel, A., & Rengel, Z. (2012). Zinc nutrition in rice production systems: A review. Plant and Soil,361, 203–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1346-9.
Reiahisamani, N., Esmaeili, M., Khoshkholgh Sima, N. A., Zaefarian, F., & Zeinalabedini, M. (2018). Assessment of the oil content of the seed produced by Salicornia L., along with its ability to produce forage in saline soils. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution,65, 1879–1891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-018-0661-2.
Sadeghi, H., & Delaviz, M. (2016). Response of three new Atriplex species (Atriplex spp.) to drought and its recovery. Acta Ecologica Sinica,36, 212–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chnaes.2016.04.010.
Sadeghi, H., & Robati, Z. (2015). Response of Cichorium intybus L. to eight seed priming methods under osmotic stress conditions. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology,4, 443–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2015.08.003.
Sadeghi, H., & Rostami, L. (2017). Changes in biochemical characteristics and Na and K content of caper (Capparis spinosa L.) seedlings under water and salt stress. J. Agric. Rural Dev. Trop. Subtrop.,118, 199–206.
Sadoogh, F., and Shariatmadari, H. (2014). Adjusted nutrition of tomato with potassium and zinc in drought stress conditions induced by polyethylene glycol 6000 in hydroponic culture. Journal of Science and Technology of Greenhouse Culture, 5. https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/20143245145. Accessed 29 Nov 2018.
Singh, S., Angadi, S. V., Grover, K., Begna, S., & Auld, D. (2016). Drought response and yield formation of spring safflower under different water regimes in the semiarid Southern High Plains. Agricultural Water Management,163, 354–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AGWAT.2015.10.010.
Tavallali, V., Rahemi, M., Eshghi, S., Kholdebarin, B., and Ramezanian, A. (2010). Zinc alleviates salt stress and increases antioxidant enzyme activity in the leaves of pistachio (Pistacia vera L.’Badami’) seedlings. Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry, 34, 349–359. http://journals.tubitak.gov.tr/agriculture/abstract.htm?id=11113. Accessed 30 Nov 2018.
Tsonev, T., Jose, F., & Lidon, C. (2012). Zinc in plants—An overview. http://ejfa.info/322. Accessed 23 Nov 2018.
Upadhyaya, H., Dutta, B. K., & Panda, S. K. (2013). Zinc modulates drought-induced biochemical damages in Tea [Camellia sinensis (L) O Kuntze]. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry,61, 6660–6670. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf304254z.
Valliyodan, B., & Nguyen, H. T. (2006). Understanding regulatory networks and engineering for enhanced drought tolerance in plants. Current Opinion in Plant Biology,9, 189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PBI.2006.01.019.
Wang, S., Li, M., Liu, K., Tian, X., Li, S., Chen, Y., et al. (2017). Effects of Zn, macronutrients, and their interactions through foliar applications on winter wheat grain nutritional quality. PLoS One,12, e0181276. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181276.
Wu, S., Hu, C., Tan, Q., Li, L., Shi, K., Zheng, Y., et al. (2015). Drought stress tolerance mediated by zinc-induced antioxidative defense and osmotic adjustment in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Acta Physiologiae Plantarum,37, 167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-015-1919-3.
Xu, J., Yin, H., & Li, X. (2009). Protective effects of proline against cadmium toxicity in micropropagated hyperaccumulator, Solanum nigrum L. Plant Cell Reports,28, 325–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0643-5.
Yang, X., Tian, X., Gale, W., Cao, Y., Lu, X., & Zhao, A. (2011). Effect of soil and foliar zinc application on zinc concentration and bioavailability in wheat grain grown on potentially zinc-deficient soil. Cereal Research Communications,39, 535–543. https://doi.org/10.1556/CRC.39.2011.4.8.
Yau, S. K. (2004). Yield, agronomic performance, and economics of safflower in comparison with other rainfed crops in a semi-arid, high-elevation Mediterranean environment. Experimental Agriculture, 40, 453–462. https://www.escholar.manchester.ac.uk/uk-ac-man-scw:158076. Accessed 10 Feb 2019.
Yavas, I., and Unay, A. (2016). Effects of zinc and salicylic acid on wheat under drought stress. Journal of Animal and Plant Sciences, 26, 1012–1018. http://www.thejaps.org.pk/docs/v-26-04/16.pdf. Accessed 29 Nov 2018.
Yeilaghi, H., Arzani, A., Ghaderian, M., Fotovat, R., Feizi, M., & Pourdad, S. S. (2012). Effect of salinity on seed oil content and fatty acid composition of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) genotypes. Food Chemistry,130, 618–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2011.07.085.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahmani, F., Sayfzadeh, S., Jabbari, H. et al. Alleviation of Drought Stress Effects on Safflower Yield by Foliar Application of Zinc. Int. J. Plant Prod. 13, 297–308 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-019-00055-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-019-00055-7