Abstract
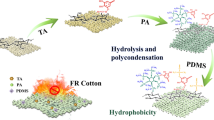
Intumescent flame retardant and hydrophobic coatings, consisting of sodium montmorillonite (MMT), ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP), and methyltrimethoxysilane (MTMS), were prepared via in situ sol-gel and self-assembly techniques to acquire multifunctional cotton fabrics. The impact of MTMS concentration on hydrophobicity, fire resistance, thermal stability, and heat release behavior of the coated fabrics was investigated. A Si-O-Si network structure was generated via the hydrolysis-condensation reaction of MTMS, induced by the catalysis of ADP. After treated by the coating with 2.0 wt.% of MTMS, the cotton fabric with a total uptake of 22.7 wt.% achieved appreciable flame retardancy and hydrophobicity, as well as satisfactory thermal stability and heat release behaviors. Overall, this research provides a facile and effective approach to prepare flame retardant and hydrophobic cotton fabrics.

Intumescent flame retardant and hydrophobic coatings, consisting of sodium montmorillonite, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, and methyltrimethoxysilane, were prepared via in situ sol-gel and self-assembly techniques to acquire multifunctional cotton fabrics.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens M (2017) Trends and patterns of U.S. fire loss. National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) report
Horrocks AR (2011) Flame retardant challenges for textiles and fibres: new chemistry versus innovatory solutions. Polym Degrad Stab 96:377–392
Horrocks AR, Kandola BK, Davies PJ, Zhang S, Padbury SA (2005) Developments in flame retardant textiles—a review. Polym Degrad Stab 88:3–12
Xing W, Jie G, Song L, Hu S, Lv X, Wang X, Hu Y (2011) Flame retardancy and thermal degradation of cotton textiles based on UV-curable flame retardant coatings. Thermochim Acta 513:75–82
Laufer G, Kirkland C, Morgan AB, Grunlan JC (2012) Intumescent multilayer nanocoating, made with renewable polyelectrolytes, for flame-retardant cotton. Biomacromolecules 13:2843–2848
Hu X-P, Li W-Y, Wang Y-Z (2004) Synthesis and characterization of a novel nitrogen-containing flame retardant. J Appl Polym Sci 94:1556–1561
Jiang D, Sun C, Zhou Y, Wang H, Yan X, He Q, Guo J, Guo Z (2015) Enhanced flame retardancy of cotton fabrics with a novel intumescent flame-retardant finishing system. Fibers Polym 16:388–396
Wang C, Wu Y, Li Y, Shao Q, Yan X, Han C, Wang Z, Liu Z, Guo Z Flame-retardant rigid polyurethane foam with a phosphorus-nitrogen single intumescent flame retardant. Polym Adv Technol
Gu H, Guo J, He Q, Tadakamalla S, Zhang X, Yan X, Huang Y, Colorado HA, Wei S, Guo Z (2013) Flame-retardant epoxy resin nanocomposites reinforced with polyaniline-stabilized silica nanoparticles. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:7718–7728
Yuan H, Xing W, Zhang P, Song L, Hu Y (2012) Functionalization of cotton with UV-cured flame retardant coatings. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:5394–5401
Bourbigot S, Jama C, Le Bras M, Delobel R, Dessaux O, Goudmand P (1999) New approach to flame retardancy using plasma assisted surface polymerisation techniques. Polym Degrad Stab 66:153–155
Vargas Garcia JR, Goto T (2003) Thermal barrier coatings produced by chemical vapor deposition. Sci Technol Adv Mater 4:397–402
Chun S-Y, Mizutani N (2001) The transport mechanism of YSZ thin films prepared by MOCVD. Appl Surf Sci 171:82–88
Cai Y, Wu N, Wei Q, Zhang K, Xu Q, Gao W, Song L, Hu Y (2008) Structure, surface morphology, thermal and flammability characterizations of polyamide6/organic-modified Fe-montmorillonite nanocomposite fibers functionalized by sputter coating of silicon. Surf Coat Technol 203:264–270
Alongi J, Malucelli G (2012) State of the art and perspectives on sol-gel derived hybrid architectures for flame retardancy of textiles. J Mater Chem 22:21805–21809
Alongi J, Colleoni C, Malucelli G, Rosace G (2012) Hybrid phosphorus-doped silica architectures derived from a multistep sol–gel process for improving thermal stability and flame retardancy of cotton fabrics. Polym Degrad Stab 97:1334–1344
Li Y-C, Schulz J, Grunlan JC (2009) Polyelectrolyte/nanosilicate thin-film assemblies: influence of pH on growth, mechanical behavior, and flammability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1:2338–2347
Li Y-C, Schulz J, Mannen S, Delhom C, Condon B, Chang S, Zammarano M, Grunlan JC (2010) Flame retardant behavior of polyelectrolyteb clay thin film assemblies on cotton fabric. ACS Nano 4:3325–3337
Carosio F, Alongi J, Malucelli G (2011) α-Zirconium phosphate-based nanoarchitectures on polyester fabrics through layer-by-layer assembly. J Mater Chem 21:10370–10376
Li Y-C, Mannen S, Schulz J, Grunlan JC (2011) Growth and fire protection behavior of POSS-based multilayer thin films. J Mater Chem 21:3060–3069
Alongi J, Carosio F, Malucelli G (2012) Influence of ammonium polyphosphate-/poly(acrylic acid)-based layer by layer architectures on the char formation in cotton, polyester and their blends. Polym Degrad Stab 97:1644–1653
Laufer G, Kirkland C, Cain AA, Grunlan JC (2012) Clay–chitosan nanobrick walls: completely renewable gas barrier and flame-retardant nanocoatings. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:1643–1649
Li X-M, Reinhoudt D, Crego-Calama M (2007) What do we need for a superhydrophobic surface? A review on the recent progress in the preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces. Chem Soc Rev 36:1350–1368
Bae GY, Jang J, Jeong YG, Lyoo WS, Min BG (2010) Superhydrophobic PLA fabrics prepared by UV photo-grafting of hydrophobic silica particles possessing vinyl groups. J Colloid Interface Sci 344:584–587
Hsieh C-T, Wu F-L, Chen W-Y (2009) Super water- and oil-repellencies from silica-based nanocoatings. Surf Coat Technol 203:3377–3384
Xue L, Li J, Fu J, Han Y (2009) Super-hydrophobicity of silica nanoparticles modified with vinyl groups. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 338:15–19
Ma W, Zhang D, Duan Y, Wang H (2013) Highly monodisperse polysilsesquioxane spheres: synthesis and application in cotton fabrics. J Colloid Interface Sci 392:194–200
Zhou H, Wang H, Niu H, Gestos A, Wang X, Lin T (2012) Fluoroalkyl silane modified silicone rubber/nanoparticle composite: a super durable, robust superhydrophobic fabric coating. Adv Mater 24:2409–2412
Bae GY, Min BG, Jeong YG, Lee SC, Jang JH, Koo GH (2009) Superhydrophobicity of cotton fabrics treated with silica nanoparticles and water-repellent agent. J Colloid Interface Sci 337:170–175
Xue C-H, Jia S-T, Chen H-Z, Wang M (2008) Superhydrophobic cotton fabrics prepared by sol–gel coating of TiO2 and surface hydrophobization. Sci Technol Adv Mater 9:035001
Vince J, Orel B, Vilčnik A, Fir M, Šurca Vuk A, Jovanovski V, Simončič B (2006) Structural and water-repellent properties of a urea/poly(dimethylsiloxane) sol−gel hybrid and its bonding to cotton fabric. Langmuir 22:6489–6497
Vilčnik A, Jerman I, Šurca Vuk A, Koželj M, Orel B, Tomšič B, Simončič B, Kovač J (2009) Structural properties and antibacterial effects of hydrophobic and oleophobic sol−gel coatings for cotton fabrics. Langmuir 25:5869–5880
Ding F, Liu J, Zeng S, Xia Y, Wells KM, Nieh M-P, Sun L (2017) Biomimetic nanocoatings with exceptional mechanical, barrier, and flame-retardant properties from large-scale one-step coassembly. Sci Adv 3:e1701212
Xiu Y, Hess DW, Wong CP (2008) UV and thermally stable superhydrophobic coatings from sol–gel processing. J Colloid Interface Sci 326:465–470
Iacono ST, Vij A, Grabow W, Smith JDW, Mabry JM (2007) Facile synthesis of hydrophobic fluoroalkyl functionalized silsesquioxane nanostructures. Chem Commun 4992–4994
Dong F, Guo W, Park S-S, Ha C-S (2011) Uniform and monodisperse polysilsesquioxane hollow spheres: synthesis from aqueous solution and use in pollutant removal. J Mater Chem 21:10744–10749
Romeo HE, Fanovich MA, Williams RJJ, Matějka L, Pleštil J, Brus J (2007) Self-assembly of a bridged silsesquioxane containing a pendant hydrophobic chain in the organic bridge. Macromolecules 40:1435–1443
Lee Y-G, Park J-H, Oh C, Oh S-G, Kim YC (2007) Preparation of highly monodispersed hybrid silica spheres using a one-step sol−gel reaction in aqueous solution. Langmuir 23:10875–10878
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E (1968) Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci 26:62–69
Guin T, Krecker M, Milhorn A, Hagen DA, Stevens B, Grunlan JC (2015) Exceptional flame resistance and gas barrier with thick multilayer nanobrick wall thin films. Adv Mater Interfaces 2:1500214
Liu G, Liu X, Yu J (2010) Ammonium polyphosphate with crystalline form V by ammonium dihydrogen phosphate process. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:5523–5529
Abdel-Kader A (1991) Electrical conductivity of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate crystals with regard to crystal structure and thermal analysis. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 2:7–10
Li J, Li B, Zhang X, Su R (2001) The study of flame retardants on thermal degradation and charring process of manchurian ash lignin in the condensed phase. Polym Degrad Stab 72:493–498
Giraud S, Bourbigot S, Rochery M, Vroman I, Tighzert L, Delobel R, Poutch F (2005) Flame retarded polyurea with microencapsulated ammonium phosphate for textile coating. Polym Degrad Stab 88:106–113
Acknowledgements
This research is sponsored by the National Science Foundation (CMMI-1562907). D.Z. acknowledges the China Scholarship Council for offering him a scholarship (no. 1412080020) to conduct research at University of Connecticut. B.L.W. acknowledges the Giolas-Harriott Fellowship and the National Science Foundation Louis Stokes Alliance for Minority Participation (LSAMP) Bridge to the Doctorate Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Williams, B.L., Becher, E.M. et al. Flame retardant and hydrophobic cotton fabrics from intumescent coatings. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 1, 177–184 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-017-0006-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-017-0006-1