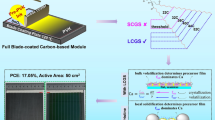
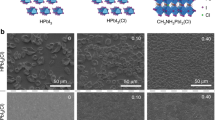
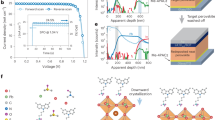
Abstract
A fire-new spray method was employed to fabricate hole-conductor-free carbon-based perovskite solar cells. With the use of superfine airbrushes, low-temperature commercial carbon paste, and their ester dispersants, this work proposes a low-cost, time-saving, skillful gas-driven ink spray (GDIS) deposition strategy to stable perovskite solar cells. Under optimized conditions, a champion photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE) value of 8.70% and a stabilized PCE value of 7.03% were achieved. More importantly, the hole-conductor-free carbon-based perovskite solar cells exhibit excellent stability after 60 days of storage in the dark with an RH of 30%.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Best research-cell efficiencies (Updated to 27th April, 2019), https://www.nrel.gov/pv/assets/pdfs/best-Research-Cell-Efficiencies-190416.pdf. (n.d.).
B. wook Park, S. Il Seok, Intrinsic instability of inorganic–organic hybrid halide perovskite materials, advanced materials. 1805337 (2019) 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201805337.
M. Jung, S.G. Ji, G. Kim, S. Il Seok, Perovskite precursor solution chemistry: from fundamentals to photovoltaic applications. Chemical Society Reviews. 48(2011), 2038 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cs00656c
F. Meng, A. Liu, L. Gao, J. Cao, Y. Yan, N. Wang, M. Fan, G. Wei, T. Ma, Current progress in interfacial engineering of carbon-based perovskite solar cells. Journal of Materials Chemistry A. 7, 8690–8699 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta01364d
H.S. Kim, J.Y. Seo, N.G. Park, Material and device stability in perovskite solar cells. Chemsuschem 9, 2528–2540 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201600915
R.G. Wilks, M. Bär, Perovskite solar cells: Danger from within. Nat. Energy 2, 16204 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nenergy.2016.204
M. Grätzel, The light and shade of perovskite solar cells. Nat. Mater. 13, 838–842 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4065
P. Gao, M. Grätzel, M.K. Nazeeruddin, Organohalide lead perovskites for photovoltaic applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 2448–2463 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ee00942h
J.-P. Correa-Baena, A. Abate, M. Saliba, W. Tress, T. JesperJacobsson, M. Grätzel, A. Hagfeldt, The rapid evolution of highly efficient perovskite solar cells. Energy & Environmental Science 10(710), 727 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EE03397K
Y. Cai, L. Liang, P. Gao, Promise of commercialization: carbon materials for low-cost perovskite solar cells. Chin. Phys. B 27, 18805 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/27/1/018805
W. Zhou, Z. Wen, P. Gao, Less is more: dopant-free hole transporting materials for high-efficiency perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1702512 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201702512
L. Calió, S. Kazim, M. Grätzel, S. Ahmad, Hole-transport materials for perovskite solar cells. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition. 55, 14522–14545 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201601757
H. Chen, S. Yang, Carbon-based perovskite solar cells without hole transport materials: the front runner to the market?, Advanced Materials. 29 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201603994.
L. Etgar, P. Gao, Z. Xue, Q. Peng, A.K. Chandiran, B. Liu, Mesoscopic CH 3 NH 3 PbI 3 /TiO 2 heterojunction solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 17396–17399 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja307789s
T. Leijtens, Overcoming ultraviolet light instability of Overcoming ultraviolet light instability of sensitized TiO 2 with meso-superstructured organometal tri-halide perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 4, 1–8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3885
K. Domanski, J.-P. Correa-Baena, N. Mine, M.K. Nazeeruddin, A. Abate, M. Saliba, W. Tress, A. Hagfeldt, M. Grätzel, Not all that glitters is gold: metal-migration-induced degradation in perovskite solar cells. ACS Nano 10, 6306–6314 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.6b02613
L. Liang, Y. Cai, X. Li, M.K. Nazeeruddin, P. Gao, All that glitters is not gold: Recent progress of alternative counter electrodes for perovskite solar cells. Nano Energy 52, 211–238 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.07.049
J. Ryu, K. Lee, J. Yun, H. Yu, J. Lee, J. Jang, Paintable carbon-based perovskite solar cells with engineered perovskite / carbon interface using carbon nanotubes dripping method, (2017) 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201701225.
K. Aitola, K. Sveinbjörnsson, J.-P. Correa-Baena, A. Kaskela, A. Abate, Y. Tian, E.M.J. Johansson, M. Grätzel, E.I. Kauppinen, A. Hagfeldt, G. Boschloo, Carbon nanotube-based hybrid hole-transporting material and selective contact for high efficiency perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ Sci. 9, 461–466 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EE03394B
X. Zheng, H. Chen, Q. Li, Y. Yang, Z. Wei, Y. Bai, Y. Qiu, D. Zhou, K.S. Wong, S. Yang, Boron doping of multiwalled carbon nanotubes significantly enhances hole extraction in carbon-based perovskite solar cells. Nano Lett. 17, 2496–2505 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b00200
Z. Wei, H. Chen, K. Yan, X. Zheng, S. Yang, Hysteresis-free multi-walled carbon nanotube-based perovskite solar cells with a high fill factor. Journal of Materials Chemistry A. 3, 24226–24231 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA07714A
Z. Li, P.P. Boix, G. Xing, K. Fu, S.A. Kulkarni, S.K. Batabyal, W. Xu, A. Cao, T.C. Sum, N. Mathews, L.H. Wong, Carbon nanotubes as an efficient hole collector for high voltage methylammonium lead bromide perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale 3, 6352–6360 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr06177f
M. Bag, L.A. Renna, S.P. Jeong, X. Han, C.L. Cutting, D. Maroudas, D. Venkataraman, Evidence for reduced charge recombination in carbon nanotube/perovskite-based active layers. Chem. Phys. Lett. 662, 35–41 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2016.09.004
J. Lee, M.M. Menamparambath, J.-Y. Hwang, S. Baik, Hierarchically structured hole transport layers of Spiro-OMeTAD and multiwalled carbon nanotubes for perovskite solar cells. Chemsuschem 8, 2358–2362 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201403462
K. Aitola, K. Domanski, J.-P. Correa-Baena, K. Sveinbjörnsson, M. Saliba, A. Abate, M. Grätzel, E. Kauppinen, E.M.J. Johansson, W. Tress, A. Hagfeldt, G. Boschloo, High temperature-stable perovskite solar cell based on low-cost carbon nanotube hole contact. Adv. Mater. 29, 1606398 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201606398
D.R. Barbero, S.D. Stranks, Functional single-walled carbon nanotubes and Nanoengineered networks for organic- and perovskite-solar-cell applications. Adv. Mater. 28, 9668–9685 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201600659
Q. Luo, H. Ma, Y. Zhang, X. Yin, Z. Yao, N. Wang, J. Li, S. Fan, K. Jiang, H. Lin, Cross-stacked superaligned carbon nanotube electrodes for efficient hole conductor-free perovskite solar cells. J Mater Chem A. 4, 5569–5577 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA01715K
X. Wang, Z. Li, W. Xu, S.A. Kulkarni, S.K. Batabyal, S. Zhang, A. Cao, L.H. Wong, TiO2 nanotube arrays based flexible perovskite solar cells with transparent carbon nanotube electrode. Nano Energy 11, 728–735 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2014.11.042
H. Li, K. Cao, J. Cui, S. Liu, X. Qiao, Y. Shen, M. Wang, 14.7% Efficient mesoscopic perovskite solar cells using single walled carbon nanotubes/carbon composite counter electrodes. Nanoscale 8(6379), 6385 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR07347B
Z. Li, S.A. Kulkarni, P.P. Boix, E. Shi, A. Cao, K. Fu, S.K. Batabyal, J. Zhang, Q. Xiong, L.H. Wong, N. Mathews, S.G. Mhaisalkar, Laminated carbon nanotube networks for metal electrode-free efficient perovskite solar cells. ACS Nano 8, 6797–6804 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn501096h
F. Lang, M.A. Gluba, S. Albrecht, J. Rappich, L. Korte, B. Rech, N.H. Nickel, Perovskite solar cells with large-area CVD-graphene for tandem solar cells. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 6(2745), 2750 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b01177
J. Yoon, H. Sung, G. Lee, W. Cho, N. Ahn, H.S. Jung, M. Choi, Superflexible, high-efficiency perovskite solar cells utilizing graphene electrodes: towards future foldable power sources. Energy Environ Sci. 10, 337–345 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EE02650H
P. You, Z. Liu, Q. Tai, S. Liu, F. Yan, Efficient semitransparent perovskite solar cells with graphene electrodes. Adv. Mater. 27, 3632–3638 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201501145
Z. Liu, P. You, C. Xie, G. Tang, F. Yan, Ultrathin and flexible perovskite solar cells with graphene transparent electrodes. Nano Energy 28, 151–157 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.08.038
H. Sung, N. Ahn, M.S. Jang, J.-K. Lee, H. Yoon, N.-G. Park, M. Choi, Transparent conductive oxide-free graphene-based perovskite solar cells with over 17% efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1501873 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201501873
S. Wang, P. Jiang, W. Shen, A. Mei, S. Xiong, X. Jiang, Y. Rong, Y. Tang, Y. Hu, H. Han, A low-temperature carbon electrode with good perovskite compatibility and high flexibility in carbon based perovskite solar cells. Chem. Commun. 55, 2765–2768 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cc09905g
J. Duan, T. Hu, Y. Zhao, B. He, Q. Tang, Carbon-electrode-tailored all-inorganic perovskite solar cells to harvest solar and water-vapor energy. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition. 57, 5746–5749 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201801837
Z. Yu, B. Chen, P. Liu, C. Wang, C. Bu, N. Cheng, S. Bai, Y. Yan, X. Zhao, Stable organic-inorganic perovskite solar cells without hole-conductor layer achieved via cell structure design and contact engineering. Adv. Func. Mater. 26, 4866–4873 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201504564
Z. Liu, T. Shi, Z. Tang, B. Sun, G. Liao, Using a low-temperature carbon electrode for preparing hole-conductor-free perovskite heterojunction solar cells under high relative humidity. Nanoscale 8, 7017–7023 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR07091K
H.N. Chen, Z.H. Wei, H.X. He, X.L. Zheng, K.S. Wong, S.H. Yang, Solvent engineering boosts the efficiency of paintable carbon-based perovskite solar cells to beyond 14%. Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1502087 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201502087
C.-Y. Chan, Y. Wang, G.-W. Wu, E.W.-G. Diau, Solvent-extraction crystal growth for highly efficient carbon-based mesoscopic perovskite solar cells free of hole conductors. J Mater Chem A. 4, 3872–3878 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA00912C
S. Gholipour, J.-P. Correa-Baena, K. Domanski, T. Matsui, L. Steier, F. Giordano, F. Tajabadi, W. Tress, M. Saliba, A. Abate, A. Morteza Ali, N. Taghavinia, M. Grätzel, A. Hagfeldt, Highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells based on a low-cost carbon cloth. Advanced Energy Materials 6, 1601116 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201601116
A. Mei, X. Li, L. Liu, Z. Ku, T. Liu, Y. Rong, M.M. Xu, M. Hu, J. Chen, Y. Yang, M. Gratzel, H. Han, M. Grätzel, H. Han, M. Gratzel, H. Han, A hole-conductor-free, fully printable mesoscopic perovskite solar cell with high stability. Science 345, 295–298 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254763
K. Cao, Z. Zuo, J. Cui, Y. Shen, T. Moehl, S.M. Zakeeruddin, M. Grätzel, M. Wang, Efficient screen printed perovskite solar cells based on mesoscopic TiO2/Al2O3/NiO/carbon architecture. Nano Energy 17, 171–179 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2015.08.009
F. Zhang, X. Yang, H. Wang, M. Cheng, J. Zhao, L. Sun, Structure engineering of hole-conductor free perovskite-based solar cells with low-temperature-processed commercial carbon paste as cathode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 6, 16140–16146 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am504175x
H. Zhou, Y. Shi, Q. Dong, H. Zhang, Y. Xing, K. Wang, Y. Du, T. Ma, Hole-conductor-free, metal-electrode-free TiO2/CH3NH3PbI3 heterojunction solar cells based on a low-temperature carbon electrode. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 5, 3241–3246 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/jz5017069
H. Wei, J. Xiao, Y. Yang, S. Lv, J. Shi, X. Xu, J. Dong, Y. Luo, D. Li, Q. Meng, Free-standing flexible carbon electrode for highly efficient hole-conductor-free perovskite solar cells. Carbon 93, 861–868 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.05.042
J. Bouclé, N. Herlin-Boime, The benefits of graphene for hybrid perovskite solar cells. Synth. Met. 222, 3–16 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2016.03.030
M. Acik, S.B. Darling, Graphene in perovskite solar cells: device design, characterization and implementation. Journal of Materials Chemistry A. 4, 6185–6235 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA09911K
Z. Yin, J. Zhu, Q. He, X. Cao, C. Tan, H. Chen, Q. Yan, H. Zhang, Graphene-based materials for solar cell applications. Adv. Energy Mater. 4, 1300574 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201300574
M. Chang, S. Huang, Carbon-Based materials used for perovskite solar cell. ChemNanoMat. 83, 515–527 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12910
S.N. Habisreutinger, R.J. Nicholas, H.J. Snaith, Carbon nanotubes in perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1601839 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201601839
S. Collavini, J.L. Delgado, Carbon nanoforms in perovskite-based solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1601000 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201601000
H. Zhang, J. Xiao, J. Shi, H. Su, Y. Luo, D. Li, H. Wu, Y.-B. Cheng, Q. Meng, Self-adhesive macroporous carbon electrodes for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Adv. Func. Mater. 28, 1802985 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201802985
J. Yoon, U. Kim, Y. Yoo, J. Byeon, S. Lee, J. Nam, K. Kim, Q. Zhang, E.I. Kauppinen, S. Maruyama, P. Lee, I. Jeon, Foldable perovskite solar cells using carbon nanotube-embedded ultrathin polyimide conductor. Advanced Science. 8, 2004092 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202004092
G. Zhang, P. Xie, Z. Huang, Z. Yang, Z. Pan, Y. Fang, H. Rao, X. Zhong, Modification of energy level alignment for boosting carbon-based CsPbI 2 Br solar cells with 14% certified efficiency. Adv. Func. Mater. 31, 2011187 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202011187
D. Bogachuk, S. Zouhair, K. Wojciechowski, B. Yang, V. Babu, L. Wagner, B. Xu, J. Lim, S. Mastroianni, H. Pettersson, A. Hagfeldt, A. Hinsch, Low-temperature carbon-based electrodes in perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 13, 3880–3916 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ee02175j
X. Chen, Y. Xia, Q. Huang, Z. Li, A. Mei, Y. Hu, T. Wang, R. Cheacharoen, Y. Rong, H. Han, Tailoring the dimensionality of hybrid perovskites in mesoporous carbon electrodes for type-ii band alignment and enhanced performance of printable hole-conductor-free perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 11, 2100292 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202100292
Z. Liu, M. Zhang, X. Xu, L. Bu, W. Zhang, W. Li, Z. Zhao, M. Wang, Y.-B. Cheng, H. He, p-Type mesoscopic NiO as an active interfacial layer for carbon counter electrode based perovskite solar cells. Dalton Trans. 44, 3967–3973 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4DT02904F
X. Xu, Z. Liu, Z. Zuo, M. Zhang, Z. Zhao, Y. Shen, H. Zhou, Q. Chen, Y. Yang, M. Wang, Hole selective NiO contact for efficient perovskite solar cells with carbon electrode. Nano Lett. 15, 2402–2408 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl504701y
Z. Ku, Y. Rong, M. Xu, T. Liu, H. Han, Full printable processed mesoscopic CH3NH3PbI3/TiO2 heterojunction solar cells with carbon counter electrode. Sci. Rep. 3, 3132 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03132
S.G. Hashmi, D. Martineau, M.I. Dar, T.T.T. Myllymäki, T. Sarikka, V. Ulla, S.M. Zakeeruddin, M. Grätzel, High performance carbon-based printed perovskite solar cells with humidity assisted thermal treatment. Journal of Materials Chemistry A. 5, 12060–12067 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TA04132B
S.G. Hashmi, D. Martineau, X. Li, M. Ozkan, A. Tiihonen, M.I. Dar, T. Sarikka, S.M. Zakeeruddin, J. Paltakari, P.D. Lund, M. Grätzel, Air processed inkjet infiltrated carbon based printed perovskite solar cells with high stability and reproducibility. Advanced Materials Technologies. 2, 1600183 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.201600183
Y. Hu, S. Si, A. Mei, Y. Rong, H. Liu, X. Li, H. Han, Stable large-area (10 × 10 cm 2) printable mesoscopic perovskite module exceeding 10% efficiency. Solar RRL. 1, 1600019 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/solr.201600019
F. Zhang, X. Yang, M. Cheng, W. Wang, L. Sun, Boosting the efficiency and the stability of low cost perovskite solar cells by using CuPc nanorods as hole transport material and carbon as counter electrode. Nano Energy 20, 108–116 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2015.11.034
G. Yue, D. Chen, P. Wang, J. Zhang, Z. Hu, Y. Zhu, Low-temperature prepared carbon electrodes for hole-conductor-free mesoscopic perovskite solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 218, 84–90 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.09.112
C. Zhang, Y. Luo, X. Chen, Y. Chen, Z. Sun, S. Huang, Effective improvement of the photovoltaic performance of carbon-based perovskite solar cells by additional solvents. Nano-Micro Letters. 8, 347–357 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-016-0094-4
M. Chen, R.-H. Zha, Z.-Y. Yuan, Q.-S. Jing, Z.-Y. Huang, X.-K. Yang, S.-M. Yang, X.-H. Zhao, D.-L. Xu, G.-D. Zou, Boron and phosphorus co-doped carbon counter electrode for efficient hole-conductor-free perovskite solar cell. Chem. Eng. J. 313, 791–800 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.050
Z. Wei, H. Chen, K. Yan, S. Yang, Inkjet printing and instant chemical transformation of a CH3NH3PbI3/nanocarbon electrode and interface for planar perovskite solar cells. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition. 53, 13239–13243 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201408638
X. Chang, W. Li, L. Zhu, H. Liu, H. Geng, S. Xiang, J. Liu, H. Chen, Carbon-based CsPbBr 3 perovskite solar cells: all-ambient processes and high thermal stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8, 33649–33655 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b11393
X. Chang, W. Li, H. Chen, L. Zhu, H. Liu, H. Geng, S. Xiang, J. Liu, X. Zheng, Y. Yang, S. Yang, Colloidal precursor-induced growth of ultra-even CH3NH3PbI3 for high-performance paintable carbon-based perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8, 30184–30192 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b09925
Z. Wei, K. Yan, H. Chen, Y. Yi, T. Zhang, X. Long, J. Li, L. Zhang, J. Wang, S. Yang, Cost-efficient clamping solar cells using candle soot for hole extraction from ambipolar perovskites. Energy Environ Sci. 7, 3326–3333 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EE01983K
N. Zhang, Y. Guo, X. Yin, M. He, X. Zou, Spongy carbon film deposited on a separated substrate as counter electrode for perovskite-based solar cell. Mater. Lett. 182, 248–252 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.07.004
S.G. Hashmi, A. Tiihonen, D. Martineau, M. Ozkan, P. Vivo, K. Kaunisto, V. Ulla, S.M. Zakeeruddin, M. Grätzel, Long term stability of air processed inkjet infiltrated carbon-based printed perovskite solar cells under intense ultra-violet light soaking. Journal of Materials Chemistry A. 5, 4797–4802 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA10605F
Y. Yang, H. Chen, X. Zheng, X. Meng, T. Zhang, C. Hu, Nano Energy Ultrasound-spray deposition of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on NiO nanoparticles-embedded perovskite layers for high-performance carbon- based perovskite solar cells. Nano Energy 42, 322–333 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.11.003
T. Bu, L. Wu, X. Liu, X. Yang, P. Zhou, X. Yu, T. Qin, J. Shi, S. Wang, S. Li, Z. Ku, Y. Peng, F. Huang, Q. Meng, Y.-B. Cheng, J. Zhong, Synergic interface optimization with green solvent engineering in mixed perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1700576 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201700576
F. Yang, G. Kapil, P. Zhang, Z. Hu, M.A. Kamarudin, T. Ma, S. Hayase, Dependence of acetate-based antisolvents for high humidity fabrication of CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite devices in ambient atmosphere. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10, 16482–16489 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b02554
X. Zheng, Z. Wei, H. Chen, Q. Zhang, H. He, S. Xiao, Z. Fan, K.S. Wong, S. Yang, Designing nanobowl arrays of mesoporous TiO 2 as an alternative electron transporting layer for carbon cathode-based perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale 8, 6393–6402 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR06715D
H. Jiang, X. Liu, N. Chai, F. Huang, Y. Peng, J. Zhong, Q. Zhang, Z. Ku, Y. Cheng, Alleviate the J – V hysteresis of carbon-based perovskite solar cells via introducing additional methylammonium chloride into MAPbI 3 precursor. RSC Adv. 8, 35157–35161 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA04347G
Y. Shao, Z. Xiao, C. Bi, Y. Yuan, J. Huang, Origin and elimination of photocurrent hysteresis by fullerene passivation in CH3NH3PbI3 planar heterojunction solar cells. Nat. Commun. 5, 5784 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6784
Funding
P. G. acknowledges the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 21975260).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All authors read the manuscript and approved the submission.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Lusheng Liang and Yu Cai are contributed equally to this work
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, L., Cai, Y. & Gao, P. A facile gas-driven ink spray (GDIS) deposition strategy toward hole-conductor-free carbon-based perovskite solar cells. emergent mater. 5, 967–975 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00247-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00247-w