Abstract
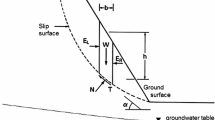
In order to investigate the effect of the pore air flow in the soil slope stability analysis, a water-air two-phase flow model, based on the multi-phase flow theory, is proposed and with the model, the water-phase and air-phase seepages of the soil slope in the stable seepage and rainfall situations are simulated. The soil slope safety coefficients are obtained according to the simulated pore air pressure and pore water pressure. The calculation results show that in the stable seepage situation, the influence of the pore air pressure on the soil slope stability can be neglected, while in the rainfall situation, the pore air pressure generated in the unsaturated zone will reduce the safety coefficient, and the larger the distance between the slip surface and the underground water level is, the greater the influence of the pore air pressure on the soil slope stability will be.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SUN Dong-mei, ZHU Yue-ming and ZHANG Ming-jin. Study on numerical for water-air two-phase flow in unsaturated soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2007, 29(4): 560–565(in Chinese).
FU Jun-feng, JIN Sheng. The seepage computation based on saturation description[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2008, 23(6): 668–674(in Chinese).
XU Jiong, WANG Tong and YANG Bo et al. The measurement and analysis of motion behavior of bubbles in calm water[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2008, 23(6): 709–714(in Chinese).
GAGANIS P., KARAPANAGIOTI H. K. and BURGANOS V. N. Modeling multicomponent NAPL transport in the unsaturated zone with the constituent averaging technique[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2002, 25(7): 723–732.
KEES C. E., MILLER C. T. Higher order time integration methods for two-phase flow[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2002, 25(2): 159–177.
OOSTROM M., LENHARD R. J. Comparison of relative permeability-saturation-pressure parametric models for infiltration and redistribution of a light nonaqueous-phase liquid in sandy porous media[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 1998, 21(2): 145–157.
LAROCHE C., VIZIKA O. Two-phase flow properties prediction from small-scale date using pore-network modeling[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2005, 61(1): 77–91.
HU Li-ming, XING Wei-wei and ZHOU Xiao-wen. Laboratory testing and numerical simulation of multiphase flow in unsaturated soils[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2008, 25(11): 162–166(in Chinese).
SCHROTH M. H., ISTOK J. and SELKER J. S. et al. Multifluid flow in bedded porous media: Laboratory experiments and numerical simulation[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 1998, 22(2): 169–183.
CLASS H., HELMIG R. and BASTIAN P. Numerical simulation of non-isothermal multiphase multi-component processes in porous media[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2002, 25(5): 533–550.
MA Cui-lin, ZHU Ming and WANG Jian-hua. Application of finite difference method FLAC in analyzing slope stability[J]. Chinese Mine Engineering, 2008, 37(5): 19–22(in Chinese).
BETTINA A. A multiscaling problem for a model of partially saturated soils[C]. Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Long Term Effects and Seepage Behavior of Dams. Nanjing: Hohai University Press, 2008, 203–213.
LU Dong-qiang. Unsteady waves due to an impulsive oseenlet beneath the capillary surface of a viscous fluid[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2008, 20(1): 23–29.
KOLDITZ O., DE JONGE J. Non-isothermal two-phase flow in low-permeable porous media[J]. Computational Mechanics, 2004, 33(5): 345–364.
ZHU Yue-ming, CHEN Jian-yu and GONG Dao-yong et al. Refined solution to seepage in arch dam foundation with FEM[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2003, 25(3): 326–330(in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the China-Austria scientific and technological cooperative project of National Science and Technology Ministry (Grant No. CN 01/2007), the Ministry of Water Resources’ 948 plan, namely technical innovation and transformation projects (Grant No. CT200515).
Biography: ZHANG Xiao-yue (1984-), Female, Ph. D. Candidate
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Xy., Zhu, Ym. & Fang, Ch. The Role Fore Air Flow in Soil Slope Stability Analysis. J Hydrodyn 21, 640–646 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(08)60195-X
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(08)60195-X