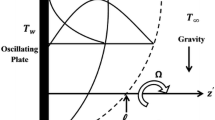
Abstract
This paper is concerned with the mutual effects of viscous dissipation and slip effects on a rotating vertical cone in a viscous fluid. Similarity solutions for rotating cone with wall temperature boundary conditions provides a system of nonlinear ordinary differential equations which have been treated by optimal homotopy analysis method (OHAM). The obtained analytical results in comparison with the numerical ones show a noteworthy accuracy for a special case. Effects for the velocities and temperature are revealed graphically and the tabulated values of the surface shear stresses and the heat transfer rate are entered in tables. From the study it is seen that the slip parameter γ enhances the primary velocity while the secondary velocity reduces. Further it is observed that the heat transfer rate NuRe x −½ increases with Eckert number Ec and Prandtl number Pr.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HERING R. G., GROSH R. J. Laminar free convection from a non-isothermal cone[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1962, 5(11): 1059–68.
HIMASEKHAR K., SARMA P. K. and JANARDHAN K. Laminar mixed convection from a vertical rotating cone[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 1989, 16(1): 99–106.
ANILKUMAR D., ROY S. Unsteady mixed convection flow on a rotating cone in a rotating fluid[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2004, 155(2): 545–561.
CHAMKHA A. J., AL-MUDHAF A. Unsteady heat and mass transfer from a rotating vertical cone with a magnetic field and heat generation or absorption effects[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2005, 44(3): 267–276.
RAVINDRAN R., ROY S. and MOMONIAT E. Effects of injection (suction) on a steady mixed convection boundary layer flow over a vertical cone[J]. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat and Fluid Flow, 2009, 19(19): 432–444.
NADEEM S., SALEEM S. Analytical study of rotating non-Newtonian nanofluid on a rotating cone[J]. Journal of Thermophysics Heat Transfer, 2014, 28(2): 295–302.
HAYAT T., ELLAHI R. and ASGHAR S. Hall effects on unsteady flow due to noncoaxially rotating disk and a fluid at infinity[J]. Chemical Engineering Communications, 2008, 195(8): 958–976.
MAKINDE O. D., OSALSUI E. MHD steady flow in a channel with slip at the permeable boundaries[J]. Romanian Journal of Physics, 2006, 51: 319–328.
ELLAHI R., HAYAT T. and MAHOMED F. M. Generalized Couette flow of a third grade fluid with slip: The exact solutions[J]. Zeitschrift Für Naturforschung A, 2010, 65: 1071–1076.
ELLAHI R., HAYAT T. and MAHOMED F. M. et al. Effects of slip on the non-linear flows of a third grade fluid[J]. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 2010, 11(1): 139–146.
MAKINDE O. D. Computational modeling of MHD unsteady flow and heat transfer towards flat plate with Navier slip and Newtonian heating[J]. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2012, 29(1): 159–166.
HAJMOHAMMADI M. R., NOURAZAR S. S. On the insertion of a thin gas layer in micro cylindrical Couette flows involving power-law liquids[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2014, 75: 97–108.
HAJMOHAMMADI M. R., NOURAZAR S. S. and CAMPO A. Analytical solution for two-phase flow between two rotating cylinders filled with power law liquid and a micro layer of gas[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2014, 28(5): 1849–1854.
KHAN W. A., KHAN Z. H. and RAHI M. Fluid flow and heat transfer of carbon nanotubes along a flat plate with Navier slip boundary[J]. Applied Nanoscience, 2014, 4(5): 633–641.
QASIM M., KHAN Z. H. and KHAN W. A. et al. MHD boundary layer slip flow and heat transfer of ferrofluid along a stretching cylinder with prescribed heat flux[J]. PLoS ONE, 2014, 9(1): e83930.
HAYAT T., ELLAHI R. and ASGHAR S. The influence of variable viscosity and viscous dissipation on the non-Newtonian flow: An analytical solution[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2007, 12(3): 300–313.
KHAN Z. H., RAHIM G. and KHAN W. A. Effect of variable thermal conductivity on heat transfer from a hollow sphere with heat generation using homotopy perturbation method[C]. ASME 2008, Heat Transfer Summer Conference. Jacksonville, Florida, USA, 2008, 301–309.
RAHIM G., KHAN Z. H. and KHAN W. A. Heat transfer from solids with variable thermal conductivity and uniform internal heat generation using homotopy perturbation method[C]. ASME 2008 Heat Transfer Summer Conference collocated with the Fluids Engineering, Energy Sustainability, and 3rd Energy Nanotechnology Conferences. Jacksonville, Florida, USA, 2008, 1: 311–319.
LIAO S. An optimal homotopy-analysis approach for strongly nonlinear differential equations[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulations, 2010, 15(8): 2003–2016.
NADEEM S., MEHMOOD R. and AKBAR N. S. Optimized analytical solution for oblique flow of a Casson-nano fluid with convective boundary conditions[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2014, 78(1): 90–100.
ABBASBANDY S. Homotopy analysis method for generalized Benjamin-Bona-Mahony equation[J]. Zeitschrift Für Angewandte Mathematik Und Physik Zamp, 2008, 58: 51–62.
ELLAHI R. The effects of MHD and temperature dependent viscosity on the flow of non-Newtonian nanofluid in a pipe: Analytical solutions[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2013, 37(3): 1451–1467.
NADEEM S., HUSSAIN S. T. Heat transfer analysis of Williamson fluid over exponentially stretching surface[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2014, 35(4): 489–502.
QASIM M., NOREEN S. Falkner-Skan flow of a maxwell fluid with heat transfer and magnetic field[J]. International Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 2013, Article ID 692827.
NADEEM S., SALEEM S. Unsteady mixed convection flow of nanofluid on a rotating cone with magnetic field[J]. Applied Nanoscience, 2013, 4(4): 405–414.
ELLAHI R., RAZA M. and VAFAI K. Series solutions of non-Newtonian nanofluids with Reynolds’ model and Vogel’s model by means of the homotopy analysis method[J]. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 2012, 55(7): 1876–1889.
HAJMOHAMMADI M. R., NOURAZAR S. S. and MANESH A. H. Semi-analytical treatments of conjugate heat transfer[ J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2012, 227: 492–503.
HAJMOHAMMADI M. R., NOURAZAR S. S. On the solution of characteristic value problems arising in linear stability analysis. Semi analytical approach[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2014, 239(2): 126–132.
NADEEM S., SALEEM S. Mixed convection flow of eyring-powell fluid along a rotating cone[J]. Results in Physics, 2014, 4: 54–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Biography: SALEEM S. (1986-), Male, Ph. D., Assistant Professor
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saleem, S., Nadeem, S. Theoretical analysis of slip flow on a rotating cone with viscous dissipation effects. J Hydrodyn 27, 616–623 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(15)60523-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(15)60523-6