Abstract
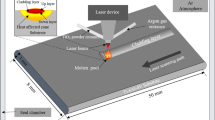
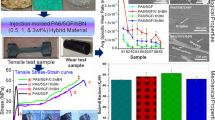
Biomimetic surface is an effective ways to promote the performance grade and applied range of materials without altering their substrate. Many improved properties such as resisting fatigue, enduring wear, etc, have been achieved by applying biomimetic morphology or structure to some engineering material surfaces. In this paper, aiming to reveal the relationship between thermal cracking behavior and mechanical properties of engineering materials with biomimetic surface, biomimetic specimens were fabricated using laser technique by imitating the heterogeneous structure on the surface of plant leaves. The effect of thermal fatigue cycling on the tensile properties of H13 die steel specimens with different surfaces (several types of biomimetic surfaces and a smooth surface) was compared and investigated. As a result, due to the coupling effects of the morphological features on the surface and the microstructure characteristics within unit zone, these specimens with biomimetic surface exhibit remarkably enhanced Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) and 0.2% Yield Strength (YS) compared with reference specimens while corresponding ductility remains largely unaffected even heightened, whether the thermal fatigue loads or not. The relative mechanisms leading to these improvements have been discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Revel P, Kircher D, Bogard V. Experimental and numerical simulation of a stainless steel coating subjected to thermal fatigue. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 290, 25–32.
Anders P, Sture H, Jens B. Thermal fatigue cracking of surface engineered hot work tool steels. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2005, 191, 216–227.
Pellizzari M, Molinari A, Straffelini G. Thermal fatigue resistance of gas and plasma nitrided 41CrAlMo7 steel. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 352, 186–194.
Starling C M D, Branco J R T. Thermal fatigue of hot work tool steel with hard coatings. Thin Solid Films, 1997, 308-309, 436–442.
Ren L Q. Progress in the bionic study on anti-adhesion and resistance reduction of terrain machines. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 2009, 52, 273–284.
Ren L Q, Han Z W, Li J Q, Tong J. Effects of non-smooth characteristics on bionic bulldozer blades in resistance reduction against soil. Journal of Terramechanics, 2003, 39, 221–230.
Zhang Z H, Ren L Q, Zhou H, Tong X. Biomimetic coupling effect of non-smooth mechanical property and microstructural features on thermal fatigue behavior of medium carbon steel. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54, 584–591.
Barthoott W, Neinhuis C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surface. Planta, 1997, 202, 1–8.
Wang C A, Huang Y, Zan Q F, Guo H, Cai S Y. Biomimetic structure design: A possible approach to change the brittleness of ceramics in nature. Material Science and Engineering C, 2000, 11, 9–12.
Ren L Q, Liang Y H. Biological couplings: Classification and characteristic rules. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 2009, 52, 2791–2800.
Zhou H, Zhang Z H, Ren L Q, Song Q F, Chen L. Thermal fatigue behavior of medium carbon steel with striated non-smooth surface. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2006, 200, 6758–6764.
Zhang Z H, Zhou H, Ren L Q, Tong X, Shan H Y, Liu L. Effect of units in different sizes on thermal fatigue behavior of 3Cr2W8V die steel with biomimetic non-smooth surface. International Journal of Fatigue, 2009, 31, 468–475.
Zhou H, Shan H Y, Tong X, Zhang Z H, Ren L Q. The adhesion of bionic non-smooth characteristics on sample surfaces against parts. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 417, 190–196.
Zhou H, Chen L, Wang W, Ren L Q, Shan H Y, Zhang Z H. Abrasive particle wear behavior of 3Cr2W8V steel processed to bionic non-smooth surface by laser. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 412, 323–327.
Ren L Q, Deng S Q, Wang J C, Han Z W. Design principles of the non-smooth surface of bionic plow moldboard. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2004, 1, 9–19.
Lawrence J, Li L. A laser-based technique for the coating of mild steel with a vitreous enamel. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2001, 140, 238–243.
Leszek Z, Takeshi S, Naoto K. Ambient gas effects on iron oxide particle aggregated films prepared by laser ablation. Scripta Materialia, 2001, 44, 1869–1872.
Song Q M, Shen L. Microstructural feature of laser surface melting 1Cr17Ni2 stainless steel. Scripta Materialia, 1997, 36, 531–534.
Kobryn P A, Moore E H, Semiatin S L. The effect of laser power and traverse speed on microstructure, porosity, and build height in laser-deposited Ti-6Al-4V. Scripta Materialia, 2000, 43, 299–305.
Schino A D, Kenny J M. Grain size dependence of the fatigue behaviour of a ultrafine-grained AISI 304 stainless steel. Materials Letters, 2003, 57, 3182–3185.
Ma X Y, Humphreys A O, Nemes J, Hone M, Nickoletopoulos N, Jonas J J. Effect of microstructure on the cold headability of a medium carbon steel. ISIJ International, 2004, 44, 905–913.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Ren, L., Zhou, H. et al. Effect of thermal fatigue loading on tensile behavior of H13 die steel with biomimetic surface. J Bionic Eng 7, 390–396 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6529(10)60271-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6529(10)60271-5