Abstract
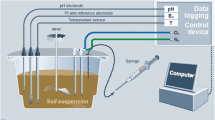
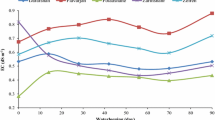
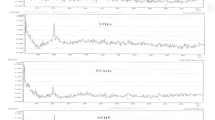
Dissolved trace metals Cd, Pb, Zn, andother solutes were determined after reducingconditions have been imposed to samples of anagricultural polluted soil. The ploughed layer wassampled as undisturbed blocks for floodingexperiments, and sieved samples were incubated inaqueous suspensions at controlled pH (pH 6.2) underdifferent redox conditions. Redox potential and pH,concentrations of major and trace elements, andorganic and inorganic ligands, were measured in thesolutions. Their chemical speciation was calculated byusing the programme Soilchem.These experiments and calculations have shown that pHvariations definitively influence trace metalsolubility, whatever they are induced by reductivedissolution, organic acid formation, or otherprocesses, and that strong acidification can beobtained with well buffered soil when about 1%available carbon is anaerobically transformed intoorganic acids. The organic acids also intervene bycomplexation, particularly for Pb. On another hand,denitrification can limit these effects by consumingprotons and organic substances. Given a steady pH,reducing conditions enhance the mobility of tracemetals, at first by dissolution of manganic and ferricoxides; Pb appeared more sensitive to these processesthan Zn, and finally Cd. As a general rule,hydromorphy in a well-buffered contaminated soil at afirst step should increase the mobility of divalenttrace metals, by decreasing pH and reducing Mn and Feoxides, but prolonged flooding can lead to fix tracemetals again, rather by re-adsorption or precipitationphenomena than by formation of insoluble sulphides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway, B. J.: 1995, Heavy Metals in Soils, 2nd edn, Blackie Academic Professional, London, U.K., pp. 368.
AFES: 1995, Référentiel Pédologique, D. Baize and M. C. Girard (eds.), INRA, Paris.
Ahumada, I. T. and Schalscha, E. B.: 1993, Agrochimica 37, 281.
Bartlett, R. J. and James, B. R.: 1993, Adv. Agron. 50, 151.
Bingham, F. T., Page, A. L., Mahler, R. J. and Ganje, T. J.: 1976, Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. J. 40, 715.
Bjerre, G. K. and Schierup, H. H.: 1985, Plant and Soil 88, 45.
Bohn, H. L.: 1971, Soil Science 112, 39.
Brennan, E. W. and Lindsay, W. L.: 1996, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 60, 3609.
Brown, P. H., Dunemann, L., Schulz, R. and Marschner, H.: 1989, Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenk. 152, 85.
Calmano, W., Hong, J. and Förstner, U.: 1993, Water Sci. Technol. 28, 223.
Cambier, P., Lamy, I., Tercé, M., Bourgeois, S. and Bermond, A.: 1993, Rapport de Contrat SRETIE 90 232, Ministère de l'Environnement-INRA, Paris, France, 33 pp.
Cambier, P. and Charlatchka, R.: 1998, in H. M. Selim and I. K. Iskandar (eds.), Fate and Transport of Heavy Metals in the Vadose Zone, Ann Arbor Press, Chelsea, Michigan, pp. 163–178.
Charlatchka, R.: 1996. Ph.D. Thesis, University Paris 12, France, 200 pp.
Charlatchka, R., Cambier, P. and Bourgeois, S.: 1997, in R. Prost. (ed.), Contaminated Soils: Third Intern. Conf. Biogeochem. Trace Elements, 1995, INRA, Paris, France, pp. 159–174.
Chanmugathas, P. and Bollag, J. M.: 1987, J. Environ. Quality 16, 161.
Chuan, M. C., Shu, G. Y. and Liu, J. C.: 1996, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 90, 543.
Christensen, T. H. and Kjelsen, P.: 1989, in Sanitary Landfilling: Process, Technology and Environmental Impact, pp. 29–49.
Davis, J. A., Fuller, C. C. and Cook, A. D.: 1987, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 51, 1477.
Doner, H. E.: 1978, Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. J. 42, 882.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Rebers, P. A. and Smith, F.: 1956, Anal. Chem. 28, 350.
Dudley, L. M., Mc Neal, B. L. and Baham, J. E.: 1986, J. Environ. Quality 15, 188.
Dutta, D., Mandal, B. and Mandal, L. N.: 1989, Soil Science 147, 187.
Fedorov, V. A., Hohlova, A. I. and Tchernicova, G. E.: 1976, Coordinacionaya himia 2(8), 1027.
Firestone, M. K., Smith, M. S., Firestone, R. B. and Tiedje, J. M.: 1979, Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. J. 43, 1140.
Förstner, U.: 1991, in G. H. Bolt et al. (eds.), Interaction at the Soil Colloid - Soil Solution Interface, NATO ASI series, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 543–582.
Förstner, U.: 1987, in J. W. Patterson and R. Passino (eds.), Metal Speciation, Separation, and Recovery, Lewis Publishers Inc., Michigan, pp. 3–26.
Francis, J. A. and Dodge, C. J.: 1990, Environ. Sci. Technol. 24, 373.
Gambrell, R. P., Khalid, R. A. and Patrick Jr., W. H.: 1980, Am. Chem. Soc. 14(4), 431.
Ghanem, S. A. and Mikkelsen, D. S.: 1987, Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 18, 1217.
Hirsch, D. and Banin, A.: 1990, J. Environ. Quality 19, 366.
Huaiman, C.: 1984, Acta Pedologica Sinica 21(3), 258.
Iu, K. L., Pulford, I. D. and Duncan, H. J.: 1981, Plant and Soil 59, 327.
Iu, K. L., Pulford, I. D. and Duncan, H. J.: 1982, Plant and Soil 66, 423.
Jandik, P. and Bonn, G.: 1993, Capillary Electrophoresis of Small Molecules and Ions, VCH, New York, N.Y., U.S.A., 298 p., p. 260.
Kabata-Pendias A. and Pendias H.: 1992. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, U.S.A., 365 p.
Khalid, R. A., Gambrell, R. P. and Patrick Jr., W. H.: 1981, J. Environ. Quality 10, 523.
Kinniburgh, D. G. and Jackson, M. L.: 1981, in M. A. Anderson and A. J. Rubin (eds.), Adsorption of Inorganic at Solid-Liquid Interfaces, Ann Arbor Sci., Ann Arbor, Michigan, U.S.A., pp. 91–160.
Krumbein, W. E. and Swart, P. K.: 1983, in W. E. Krumbein (ed.), Microbial Geochemistry, Blackwell Scientific, London, U.K., pp. 5–62.
Lamy, I., Cambier P. and Bourgeois, S.: 1994, Environ. Geochem. Health 16, 1.
Lefebvre-Drouet, E. and Bétrémieux, R.: 1984, Science du Sol, 213.
Letey, J., Valoras, N., Hadas A. and Focht, D. D.: 1980, J. Environ. Quality 9, 227.
Lindsay, W. L.: 1979, Chemical Equilibria in Soils, John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, U.S.A., p. 376.
Ministère de l'Environnement: 1994, Recensement des Sites et Sols Pollués, DPPR, Paris, France.
Mench, M. J., Didier, V. L., Löffler, M., Gomez, A. and Masson, P.: 1994, J. Environ. Quality 23(1), 58.
Moalla, S. N. and Pulford, I. D.: 1995, Soil Use and Management 11, 94.
Patrick Jr., W. H., Williams, B. G. and Moraghan, J. T.: 1973, Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc. 37, 331.
Ponnamperuma, F. N.: 1972, Adv. Agron. 24, 29.
Reddy, C. N. and Patrick Jr., W. H.: 1977, J. Environ. Quality 6(3), 259.
Sappin-Didier, V.: 1995, Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Bordeaux, France.
Satawathananont, S., Patrick Jr., W. H. and Moore, P. A.: 1991, Plant and Soil 133, 281.
Schwab, A. P. and Lindsay, W. L.: 1983, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 47, 217.
Silen, L. G. and Martel, A. E.: 1971, Stability Constants of Metal-Ion Complexes, Chemical Society, London, U.K.
Sposito, G.: 1981, The Thermodynamics of Soil Solutions, Clarendon Press, New York, NY, U.S.A.
Sposito, G. and Coves, J.: 1988, Soilchem: A Computer Program for the Calculation of Chemical Speciation in Soils, University of California Riverside and Berkeley, California, U.S.A.
Stumm, W. and Morgan, J.: 1981, Aquatic Chemistry. An Introduction Emphasizing Chemical Equilibria in Natural Waters, 2nd edn, John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, U.S.A.
Tack, F. M., Callewaert, O. W. J. J. and Verloo, M. G.: 1996, Environ. Pollut. 91, 199.
Tamura, K.: 1991, J. Physical Chem. 95, 3425.
Welch, J. E. and Lund, L. J.: 1987, J. Environ. Quality 16, 403.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charlatchka, R., Cambier, P. Influence of Reducing Conditions on Solubility of Trace Metals in Contaminated Soils. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 118, 143–168 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005195920876
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005195920876