Abstract
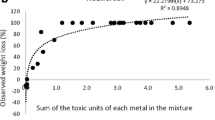
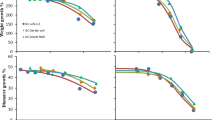
Heavy metal toxicity to an indigenous nematode community was examined following the addition of Cu and Zn, alone or in combination, to agricultural soil. The dissolved Cu or Zn concentrations measured after equilibrating soil samples with a 0.01 M solution of CaCl2 showed that the metal concentrations found in soils with combined metal additions were not significantly different from those with single metal additions. After an exposure period of six months, many nematode community parameters and individual nematode taxa were significantly affected by increasing concentrations of Cu and Zn up to 200 mg kg−1. Some nematode taxa, such as Thonus, Alaimus and Aporcelaimellus were very sensitive and disappeared at Cu and Zn concentrations exceeding 50 mg kg−1. For several nematode community parameters and nematode taxa, EC50 values for single metal exposures were used to calculate TU50 values for the joint toxicity of Cu and Zn. Based on these calculations, it is concluded that the effects of a combined exposure to Cu and Zn were additive or less than additive. Before this conclusion can be generalised, however, more data are needed on other types of soil, other pH values and other combinations of pollutants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asztalos, B., Nemcsok, J., Benedeczky, I., Gabriel, R. and Szabó, A. (1988). Comparison of effects of paraquat and methidation on enzyme activity and tissue necrosis of carp, following exposure to the pesticides singly or in combination. Environ. Pollut. 55, 123-35.
Babich, H., Shopsis, C. and Borenfreund, E. (1986). Cadmium-Nickel toxicity interactions towards a bacterium, filamentous fungi, and a cultured mammalian cell line. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 37, 550-7.
Bongers, T. (1988). De Nematoden van Nederland. KNNV Bibliotheekuitgave nr. 46, Pirola, Schoorl, 408 pp.
Bruce, R.D. and Versteeg, D.J. (1992). A statistical procedure for modelling continuous toxicity data. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 11, 1485-94.
Calamari, D. and Alabaster, J.S. (1980). An approach to theoretical models in evaluating the effects of mixtures of toxicants in the aquatic environment. Chemosphere 9, 533-8.
Christensen, T.H. (1987). Cadmium soil sorption at low concentrations: VI. A model for zinc competition. Water Air Soil Pollut. 34, 305-14.
De Haan, F.A.M., Lexmond, Th.M. and Van Riemsdijk, W.H. (1990). Soil quality indicators. In A.G. Colombo and G. Premazzi (eds) Proceedings Workshop on Indicators and Indices for Environmental Impact Assessment and Risk Analysis, Ispra, EUR 13060EN, pp. 161-74. Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities.
Eifac (1987). Water quality criteria for European freshwater fish. Revised report on combined effects on freshwater fish and aquatic life of mixtures of toxicants in water. Rome.
Hensbergen, P.J. and Van Gestel, C.A.M. (1995). Combinatie-toxiciteit in het terrestrische milieu. TCB R04, Den Haag.
Houba, V.J.G., Novozamsky, I. and Temminghoff, E. (1993). Soil and Plant Analysis: Part 5A. Extraction with 0.01 M CaCl2. Department of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen, the Netherlands.
Ikeda, M. (1994). Complex exposures: potentials for assessing integrated exposures. Clin. Chem. 40, 1444-7.
Könemann, H. (1981). Fish toxicity tests with mixtures of more than two chemicals: a proposal for a quantitative approach and experimental results. Toxicol. 19, 229-38.
Korthals, G.W., Alexiev, A.D., Lexmond, Th.M., Kammenga, J.E. and Bongers, T. (1996a). Long-term effects of copper and pH on the nematode community of an agroecosystem. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15, 979-85.
Korthals, G.W., Van de Ende, A., Van Megen, H., Lexmond, Th.M., Kammenga, J.E. and Bongers, T. (1996b). Shortterm effects of cadmium, copper, nickel and zinc on nematodes from different feeding and life-history strategy groups. App. Soil Ecol. 4, 107-17.
Kraak, M.H.S., Lavy, D., Schoon, H., Toussaint, M., Peeters, W.H.M. and Van Straalen, N.M. (1994). Ecotoxicity of mixtures of metals to the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 13, 109-14.
Kraak, M.H.S., Schoon, H., Peeters, W.H.M. and Van Straalen, N.M. (1993). Chronic ecotoxicity of mixtures of Cu, Zn and Cd to the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 25, 315-27.
Lexmond, Th.M. and Edelman, Th. (1987). Huidige achtergrondwaarden van het gehalte aan een aantal zware metalen en arseen in de grond. Handboek voor milieubeheer, Deel IV Bodembescherming. Samson, Alphen aan de Rijn.
Novozamsky, I., Lexmond, Th.M. and Houba, V.J.G. (1993). A single extraction procedure of soil for evaluation of uptake of some heavy metals by plants. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 51, 47-58.
Oostenbrink, M. (1960). Estimating nematode populations by some selected methods. In J.N. Sasser and W.R. Jenkins (eds) Nematology. pp. 85-102. Chapel Hill: The University of North Carolina Press.
Posthuma, L., Baerselman, R., van Veen, R.P.M. and Dirven-Van Breemen, E.M. (1997). Single and joint toxic effects of copper and zinc on reproduction of Enchytraeus crypticus in relation to sorption of metals in soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 38, 108-21.
Sokal, R.R. and Rohlf, F.J. (1981). Biometry. 300 pp. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman.
Spehar, J.B. and Fiandt, J.T. (1986). Acute and chronic effects of water quality criteria-based metal mixtures on three aquatic species. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 5, 917-31.
Spehar, R.L., Leonard, E.N. and Defoe, D.L. (1978). Chronic effects of cadmium and zinc mixtures on flagfish (Jordanella floridae). Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 107, 354-60.
Sprague, J.B. (1970). Measurement of pollutant toxicity to fish. II. Utilizing and applying bioassay results. Water Res. 4, 3-32.
Sprague, J.B. and Ramsay, B.A. (1965). Lethal levels of mixed copper-zinc solutions for juvenile Salmon. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 22, 425-32.
Van Gestel, C.A.M. and Hensbergen, P.J. (1997). Interaction of Cd and Zn toxicity for Folsomia candida (Collembola: Isotomidae) in relation to bioavailability in soil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 16, 1177-86.
Van Riemsdijk, W.H. and Hiemstra, T. (1993). Adsorption to heterogeneous surfaces. In H.E. Allen, E.M. Perdue and D.S. Brown (eds) Metals in Groundwater. pp. 1-36. Boca Raton, Florida, USA: Lewis Publ.
Van Straalen, N.M. and Denneman, C.A.J. (1989). Ecotoxicological evaluation of soil quality criteria. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 18, 241-51.
Van Straalen, N.M., Leeuwangh, P. and Stortelder, P.B.M. (1994). Progressing limits for soil ecotoxicological risk assessment. In M.K. Donker, H. Eijsackers and F. Heimbach (eds) pp. 397-409. Lewis Publ.
Vegter, J.J. (1995). Soil protection in the Netherlands. In W. Salamons, U. Forstner and P. Mader (eds) Heavy Metals—Problems and Solutions. pp. 79-100. Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
Vranken, G., Tire, C. and Heip, C. (1988). The toxicity of paired metal mixtures to the nematode Monhystera disjuncta Bastian, 1865. Mar. Environ. Res. 26, 161-79.
Yeates, G.W., Bongers, T., De Goede, R.G.M., Freckman, D.W. and Georgieva, S.S. (1993). Feeding habits in soil nematode families and genera—an outline for soil ecologists. J. Nematol. 25, 315-31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korthals, G.W., Bongers, M., Fokkema, A. et al. Joint Toxicity of Copper and Zinc to a Terrestrial Nematode Community in an Acid Sandy Soil. Ecotoxicology 9, 219–228 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008950905983
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008950905983