Abstract
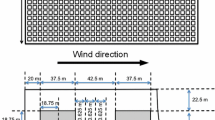
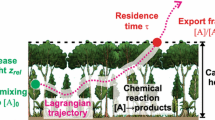
The air flow and vertical distribution of sources/sinks inside aforest canopy have been taken into accountin the analysis of the contribution of sources/sinks to measured fluxes and concentrations above a forest. Thestochastic estimators for concentrations and fluxes are described and their evaluation is performed by simulationof an ensemble of fluid parcel trajectories. The influence of the forest canopy on the footprint is important forobservation levels up to a few times the forest height. The influence of along-wind turbulent diffusion, whichanalytical atmospheric surface layer (ASL) footprint models do not account for, is significant even at higherlevels. The footprint analysis has been performed to deduce the Douglas fir canopy carbon dioxide uptake from eddycovariance flux measurements above a mixed Douglas fir–beech forest during the pre-leaf periods of the beech.The scatter in the results indicates that such an analysis is limited, presumably due to horizontal inhomogenetiesin flow statistics, which were not included in trajectory simulation. The analysis, however, is useful for theestimation of the qualitative effect of the forest canopy on the footprint function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubinet, M., Grelle, A., Ibrom, A., Rannik, Ñ., Moncrieff, J., Foken, T., Kowalski, A. S., Martin, P. H., Berbigier, P., Bernhofer, Ch., Clement, R., Elbers, J., Granier, A., Grünwald, T., Morgenstern, K., Pilegaard, K., Rebmann, C., Snijders, W., Valentini, R., and Vesala, T.: 2000, ‘Estimates of the Annual Net Carbon and Water Exchange of Forests: The EUROFLUX Methodology’, Adv. Ecol. Res. 30, 113–175.
Baldocchi, D.: 1997, ‘Flux Footprints within and over Forest Canopies’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 85, 273–292.
Bartelink, H. H.: 1998, Simulation of Growth and Competition in Mixed Stands of Douglas-Fir and Beech, Ph.D. Dissertation, Landbouwuniversiteit Wageningen, 222 pp.
Cellier, P. and Brunet, Y.: 1992, ‘Flux-Gradient Relationships above Tall Plant Canopies’, Agric. For. Meteorol. 58, 93–117.
De Bruin, H. A. R., Kohsiek, W., and Van Den Hurk, B. J. J. M.: 1993, ‘A Verification of Some Methods to Determine the Fluxes of Momentum, Sensible Heat, and Water Vapour Using Standard Deviation and Structure Parameter of Scalar Meteorological Quantities’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 63, 231–257.
Finn, D., Lamb, B., Leclerc, M. Y., and Horst, T. W.: 1996, ‘Experimental Evaluation of Analytical and Lagrangian Surface-Layer Footprint Models’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 80, 283–308.
Flesch, T. K.: 1996, ‘The Footprint for Flux Measurements, from Backward Lagrangian Stochastic Models’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 78, 399–404.
Flesch, T. K. and Wilson, J. D.: 1992, ‘A Two-Dimensional Trajectory-Simulation Model for Non-Gaussian, Inhomogeneous Turbulence within Plant Canopies’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 61, 349–374.
Groß, G.: 1993, Numerical Simulation of Canopy Flows, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 167 pp.
Högström, U.: 1988, ‘Non-Dimensional Wind and Temperature Profiles in the Atmospheric Surface Layer: A Reevaluation’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 42, 55–78.
Horst, T. W. and Weil, J. C.: 1992, ‘Footprint Estimation for Scalar Flux Measurements in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 59, 279–296.
Horst, T. W. and Weil, J. C.: 1994, ‘How Far Is Far Enough?: The Fetch Requirements for Micrometeorological Measurement of Surface Fluxes’, J. Atmos. Oceanic Tech. 11, 1018–1025.
Kader, B. A. and Yaglom, A. M.: 1990, ‘Mean Fields and FluctuationMoments in Unstably Stratified Turbulent Boundary Layers’, J. Fluid. Mech. 212, 637–662.
Kaimal, J. C. and Finnigan, J. J.: 1994, Atmospheric Boundary Layer Flows. Their Structure and Measurement, Oxford University Press, New York, 289 pp.
Kurbanmuradov, O. and Sabelfeld, K. K.: 2000, ‘Stochastic Lagrangian Models for Turbulent Dispersion in Atmospheric Boundary Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol., in press.
Kurbanmuradov, O., Rannik, Ñ, Sabelfeld, K. K., and Vesala, T.: 1999, ‘Direct and Adjoint Monte Carlo for the Footprint Problem’, Monte Carlo Meth. Appl. 5, N2, 85–111.
Leclerc, M. Y. and Thurtell, G. W.: 1990, ‘Footprint Prediction of Scalar Fluxes Using a Markovian Analysis’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 52, 247–258.
Monin, A. S. and Yaglom, A. M.: 1975, Statistical FluidMechanics. Vol. 2,M.I.T. Press, Cambridge, MA, 874 pp.
Paulson, C. A.: 1970, ‘The Mathematical Representation ofWind Speed and Temperature Profiles in the Unstable Atmospheric Surface Layer’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 9, 857–860.
Rannik, Ñ. and Vesala, T.: 1999, ‘Autoregressive Filtering versus Linear Detrending in Estimation of Fluxes by the Eddy Covariance Method’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 91, 259–280.
Raupach, M. R.: 1988, ‘Canopy Transport Processes’, in W. L. Steffen and O. T. Denmead (eds.), Flow and Transport in Natural Environment: Advances and Applications, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 95–127.
Reynolds, A. M.: 1998, ‘On the Formulation of Lagrangian Stochastic Models of Scalar Dispersion within Plant Canopies’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 88, 77–86.
Sawford, B. L. and Guest, F. M.:1988, ‘Uniqueness and Universality of Lagrangian Stochastic Models of Turbulent Dispersion’, in Proceedings of the 8th Symposium on Turbulence and Diffusion, AMS, San Diego, pp. 96–99.
Schmid, H. P.: 1994, ‘Source Areas for Scalar and Scalar Fluxes’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 67, 293–318.
Schmid, H. P. and Oke, T. R.: 1990, ‘A Model to Estimate the Source Area Contributing to Turbulent Exchange in the Surface Layer over Patchy Terrain’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 116, 965–988.
Schuepp, H. P., Leclerc, M. Y., MacPherson, J. I., and Desjardins, R. L.: 1990, ‘Footprint Prediction of Scalar Fluxes from Analytical Solutions of the Diffusion Equation’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 50, 355–373.
Su, H.-B., Shaw, R. H., Paw U, K. T., Moeng, C.-H., and Sullivan, P. P.: 1998, ‘Turbulent Statistics of Neutrally Stratified Flow within and above a Sparse Forest from Large-Eddy Simulation and Field Observations’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 88, 363–397.
Thomson, D. J.: 1987, ‘Criteria for the Selection of Stochastic Models of Particle Trajectories in Turbulent Flows’, J. Fluid. Mech. 180, 529–556.
Wilson, J. D. and Sawford, B. L.: 1996, ‘Review of Lagrangian Stochastic Models for Trajectories in the Turbulent Atmosphere’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 78, 191–210.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rannik, Ü., Aubinet, M., Kurbanmuradov, O. et al. Footprint Analysis For Measurements Over A Heterogeneous Forest. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 97, 137–166 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002702810929
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002702810929