Abstract
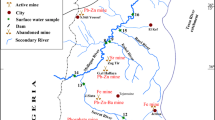
The study of four drinking-water reservoirsdemonstrates how the anthropogenic land use of acatchment may affect binding and mobility ofphosphorus in the sediment. Pdiss concentrationgradients at the sediment–water interface weremeasured to calculate potential diffusive releaserates. P binding forms were determined by sequentialextraction of fresh sediment and settling seston. Mainstudy sites were Saidenbach Reservoir (mesotrophic,densely populated drainage area with 73% agriculturalland use) and Neunzehnhain Reservoir (oligotrophic,unpopulated drainage area forested to 80%) in thesilicate-rich Erzgebirge mountains of eastern Germany.Tot-P concentrations and P binding forms of typicalerosive matter from each catchment were similar to thesediment of both pre-reservoirs and reservoirs' mouth.In Saidenbach Reservoir, diatoms responded to highnutrient loading by incorporating ortho-P. Whilesettling, the org-P was partly transformed toFe(OOH) ≈ P. Apart from hypolimnetic O2depletion, this P binding form dominated in thesurface sediment mainly in front of the dam. Withincreasing sediment depth, org-P and Fe(OOH) ≈ Pnot only redissolved into the pore water, but alsoadsorbed onto Al compounds. In Neunzehnhain Reservoir,acidification of the low buffered catchment favouredloading of humic compounds and Al3+ ions, whichprecipitated and redox-independently adsorbed ortho-Pdue to a pH increase in the lake. Neunzehnhainsediment was able to immobilize Fe(OOH) ≈ P fromSaidenbach sediment in a batch experiment. Comparativesequential P extraction of sediment from SosaReservoir (oligo-mesotrophic, sparsely populateddrainage area forested to 94%) and Kleine KinzigReservoir (nearly unpopulated drainage area forestedto 98%) also demonstrated effective P immobilizationby Al-/humic compounds.
It is concluded that the absence of settlements in thecatchment, together with forestry as dominating landuse, favour not only oligotrophic conditions in thereservoir but also confine internal P loading from thesediment. But attention should be paid toacidification problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnscheidt, J., 1993. Untersuchungen zur Versauerung und zur biologischen Versauerungsindikation in Erzgebirgsbächen unter besonderer Berücksichtigung des Einzugsgebiets der Talsperren Neunzehnhain. Diploma thesis, Technical University of Dresden, 84 pp.
Bak, F., 1988. Sulfatreduzierende Bakterien und ihre Aktivität im Litoralscdiment der unteren Güll (Überlinger Scc). Ph.D. thesis, Konstanzer Dissertationen Bd. 216.
Buffle, J., R. R. De Vitre, D. Perret & G. G. Leppard, 1989. Physico-chemical characteristics of a colloidal iron phosphate species formed at the oxic-anoxic interface of a eutrophic lake. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 53: 399–408.
Danen-Lonwerse, H., L. Lijklema & M. Coenraats, 1993. Iron content of sediment and phosphate adsorption properties. Hydrobiologia 253: 311–317.
De Best, J., H. J. Danen-Louwerse, R. Portielje & L. Lijklema, 1995. Reduction of artificial iron(III) phosphate complexes by hydroxylammonium chloride. Wat. Res. 29: 1885–1894.
Einsele, W., 1936. Über die Beziehung des Eisenkreislaufes zum Phosphatkreislauf im eutrophen See. Arch. Hydrobiol. 29: 664–686.
Einsele, W., 1938. Über chemische und kolloidchemische Vorgänge in Eisen-Phosphat-Systemen unter limnochemischen und limnogeologischen Gesichtspunkten. Arch. Hydrobiol. 33: 361–387.
Faustmann, S., 1993. Mechanismen der Phosphorelimination und ihre Wechselwirkungen am Beispiel der Kläranlage Berlin-Marienfelde. Diploma thesis, Technical University of Dresden, 91 pp.
Golterman, H. L., 1995a. Theoretical aspects of the adsorption of ortho-phosphate onto iron-hydroxide. Hydrobiologia 315: 59–68.
Golterman, H. L., 1995b. The role of the ironhydroxide-phosphate-sulphide system in the phosphate exchange between sediments and overlying water. Hydrobiologia 297: 43–54.
Golterman, H. L., 1996. Fractionation of sediment phosphate with chelating compounds: a simplification, and comparison with other methods. Hydrobiologia 335: 87–95.
He, Q. H., G. G. Leppard, C. R. Paige & W. J. Snodgrass. 1996. Transmission electron microscopy of a phosphate effect on the colloid structure of iron hydroxide. Wat. Res. 30: 1345–1352.
Hieltjes, A. H. M. & L. Lijklema, 1980. Fractionation of inorganic phosphates in calcareous sediments. J. envir. Qual. 9: 405–107.
Hoehn, E., 1994. The effect of a pre-reservoir on the trophic state of an oligo-mesotrophic drinking-water reservoir (Kleine Kinzig) in the northern Black Forest, Germany. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 40: 263–274.
Hoehn, E. & S. Schmidt-Halewicz, 1995. The impact of high flood-nutrient loading and Daphnia grazing on plankton development in the Kleine Kinzig reservoir. J. Water SRT-Aqua 44, Suppl. 1: 102–107.
Hoehn, E., B. Rapp, S. Schmidt-Halewicz & B. Ewig, 1997. Limnologisches Untersuchungsprogramm Trinkwassertalsperre Kleine Kinzig: Hydrochemie, Phytoplankton und Primärproduktion 1989-91.-Zweckverband WKK, Alpirsbach, Germany (in prep.).
Horn, W., H. Horn, L. Paul & D. Geißler, 1988. Eutrophierungsmechanismen in der Talsperre Saidenbach. G4 Abschlußbericht, Technical University of Dresden, Institute of Hydrobiology, 105 pp.
Horn, W. & H. Horn, 1990. A simple and reliable method for the installation of sediment traps in lakes. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 75: 269–270.
Horn, W. & H. Horn, 1995. Limnological features of different acidic drinking water reservoirs in the Erzgebirge (Germany). Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 80: 623–638.
Hupfer, M., 1993, Untersuchungen zur Phosphatmobilität in Gewässersedimenten. Ph.D. thesis, Technical University of Dresden, 144 pp.
Hupfer, M., 1995. Bindungsformen und Mobilität des Phosphors in Gewässersedimenten. In Steinberg, C., H. Bernhardt& H. Klapper (eds), Handbuch Angewandte Limnologie, ecomed, Landsberg/Lech, IV-3.2: 1–22.
Hupfer, M., R. Gächter & R. Giovanoli, 1995a. Transformation of phosphorus species in settling seston and during early sediment diagenesis. Aquat. Sci. 57: 305–324.
Hupfer, M., R. Gächter & H. Rüegger, 1995b. Polyphosphate in lake sediments: 31P NMR spectroscopy as tool for its identification. Limnol. Oceanogr. 40: 610–617.
Jenkins, D., J.F. Ferguson & A. B. Menar, 1971. Chemical processes for phosphate removal. Wat. Res. 5: 369–389.
Jensen, H. S. & B. Thamdrup. 1993. Iron-bound phosphorus in marine sediments as measured by bicarbonate-dithionite extraction. Hydrobiologia 253: 47–59.
Li, Y.-H. & S. Gregory, 1974. Diffusion of ions in sea water and in deep-sea sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 38: 703–714.
Lijklema, L., 1980. Interaction of orthophosphate with iron(III) and aluminium hydroxides. Envir. Sci. Technol. 14: 537–541.
Lijklema, L., 1993. Considerations in modeling the sediment-water exchange of phosphorus. Hydrobiologia 253: 219–231.
Mortlock, R. F., A. T. Bell & C. J. Radke, 1993. 31P and 27A1 NMR investigations of the effects of pH on aqueous solutions containing aluminium and phosphorus. J. Phys. Chem. 97: 775–782.
Nebe, W., 1968. Der Phosphorgehalt sachsischer Grundgesteine und einiger daraus entstandener Waldböden. Fortschr. Wasserchemie 8: 117–130.
Nirel, P. M. V. & F. M. M. Morel, 1990. Pitfalls of sequential extractions. Wat. Res. 24: 1055–1056.
Parfitt, R. L., J. D. Russell & V. C. Farmer, 1976. Confirmation of the surface structures of goethite (α-FeOOH) and phosphated goethite by infrared spectroscopy. J. Chem. Soc. Farad. Trans. 72: 1082–1087.
Pettersson, K., B. Boström & O.-S. Jacobsen, 1988. Phosphorus in sediments-speciation and analysis. Hydrobiologia 170: 91—101.
Pizarro, J., N. Belzile, M. Filella, G. G. Leppard, J.-C. Negre, D. Perret & J. Buffle, 1995. Coagulation/sedimentation of submicron iron particles in a eutrophic lake. Wat. Res. 29: 617–632.
Psenner, R., R. Pucsko & M. Sager, 1984. Die Fraktionierung organischer und anorganischer Phosphor verbindungen von Sedimenten. Versuch einer Definition ökologisch wichtiger Fraktionen. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl, 70: 111–155.
Psenner, R. & R. Pucsko, 1988. Phosphorus fractionation: advantages and limits of the method for the study of sediment P origins and interactions. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 30: 43–59.
Psenner, R., B. Boström, M. Dinka, K. Pettersson, R. Pucsko & M. Sager, 1988. Fractionation of phosphorus in suspended matter and sediment. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 30: 98–110.
Rebohle, P., 1994. Wasserversorgung aus Trinkwassertalsperren in Sachsen. Wasser & Boden 9: 10–14.
Röske, I. & D. Uhlmann, 1992. Eine einfache Methode zur Unterscheidung von Polyphosphat und chemisch gebundenem Phosphat in Belebtschlämmen aus Anlagen mit weitergehender. Abwasserbehandlung, gwf Wasser Abwasser 133: 87–91.
Röske, I. & C. Schönborn, 1994. Interactions between chemical and advanced biological phosphorus elimination. Wat. Res. 28: 1103–1109.
Salomons, W. & U. Förstner, 1980. Trace metal analyses on polluted sediments. II. Evaluation of environmental impact. Envir. Technol. Lett. 1: 506–517.
Schmelter, I., 1996. Kinetik der Phosphorremobilisierung aus dem Sediment eines eutrophen Badesees unter dem Einffuß einer externen Phosphoreliminationsanlage. Diploma thesis, University of Hamburg, 72 pp.
Span, D., J. Dominik, M. A. Lazzaretti & J.-P. Vernet, 1992. The role of sediments in the phosphorus cycle in Lake Lugano. I. Geochemical approach. Aquatic Sciences 54: 277–284.
Tipping, E., C. Woof & D. Cooke, 1981. Iron oxide from a seasonally anoxic lake. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 45: 1411–1419.
Uhlmann, D., I. Röske, M. Hupfer & G. Ohms, 1990. A simple method to distinguish between polyphosphate and other phosphate fractions of activated sludge. Wat. Res. 24: 1355–1360.
Uhlmann, D. amp; H. Horn, 1992. The significance of sedimentation and sediments to phytoplankton growth in drinking-water reservoirs. In Sutcliffe, D. W. & J. G. Jones (eds), Eutrophication. Research and application to water supply. Freshwater Biological Association, Ambleside: 94–106.
Uhlmann, D., M. Hupfer & C. Appelt, 1993. Discrepancies between sediment composition and trophic character of reservoirs. Ver. int. Ver. Limnol. 25: 1181–1182.
Uhlmann, D., M. Hupfer & L. Paul, 1995. Longitudinal gradients in the chemical and microbial composition of the bottom sediment in a channel reservoir (Saidenbach R., Saxony). Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 80: 15–25.
Ulrich, K.-U. & A. Neubert, 1996. Extraktion von Metallen aus Talsperrensediment mit Hilfe der Mikrowellentechnik. In Welz, B. (ed.), CANAS '95 Colloquium Analytische Atomspektroskopie. Bodenseewerk Perkin-Elmer, Überlingen: 361–367.
Wiegleb, K., 1995. Aktuelle Probleme der Aufbereitung von Grundwasser in Sachsen. gwf Wasser Abwasser 136: 145—153.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulrich, KU. Effects of land use in the drainage area on phosphorus binding and mobility in the sediments of four drinking-water reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 345, 21–38 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002919129524
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002919129524