Abstract
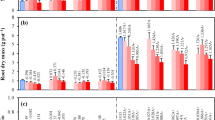
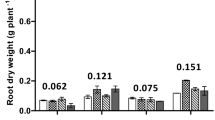
Root exudates were collected from radish and rape plants grown in P sufficient and P deficient nutrient solution. In radish, tartaric, malic and succinic acids were the dominant organic acids which increased between 15 times (succinic acid) and 60 times (malic acid) under P deficient conditions. In another experiment in quartz sand culture supplied with either Ca3(PO4)2 or AlPO4, radish utilized P from AlPO4 much better than from Ca3(PO4)2 whereas the opposite was true for rape. The results demonstrated the role of a particular organic acid in mobilizing sparingly soluble P and were in accordance with the preferential growth of two plants on acid (radish) and calcareous (rape) soils in China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ae N Arihara, J Okada K, Yoshihara T and Johansen C 1990 Phosphorus uptake by pigeonpea and its role in cropping systems of Indian Subcontinent. Science 248, 477-480.
Dai X, Yi C Z, Yan Y, L and Han Y S 1989 Gas chromatographic determination of organic acid in fruits and vegetables. Acta Agriculture Universitatis Pekinensis 15(1), 51-55.
Dinkelaker B, Römheld V and Marschner H 1989 Citric acid excretion and precipitation of calcium citrate in the rhizosphere of white lupine (Lupinus albusL.). Plant Cell Environ. 12, 285-292.
Gardner W K, Parbery D G and Barber D A 1982a The acquisition of phosphorus by Lupinus albusL., I. Some characteristics of soil/root interface. Plant and Soil 68, 19-32.
Gardner W K, Parbery D G and Barber D A 1982b The acquisition of phosphorus by Lupinus albusL., II. The effect of varying phosphorus supply and soil type on some characteristics of the soil/root interface. Plant and Soil 68, 33-41.
Gardner W K, Barber D A and Parbery D G 1983 The acquisition of phosphorus by Lupinus albusL. III. The probable mechanism by which phosphorus movement in the soil/root interface is enhanced. Plant and Soil 70, 107-124.
Graham J H, Leonard R T and Menge J A 1981 Membrane mediated decrease in root exudation responsible for phosphorus inhibition of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza formation. Plant Physiol. 68, 548-552.
Grierson P F 1992 Organic acids in the rhizosphere of Banksia integrifoliaL. F. Plant and Soil 44, 259-265.
Hoffland E 1992 Quantitative evaluation of the role of organic acid exudation in the mobilization of rock phosphate by rape. Plant and Soil 140, 279-289.
Hoffland E, Boogaard R V D, Nelemans J A and Findenegg G R 1992 Biosynthesis and root exudation of citric and malic acids in phosphate-starved rape plants. New Phytol. 122, 675-680.
Hoffland E, Findenegg G R and Nelemans J A 1989 Solubilization of rock phosphate by rape. II. Local root exudation of organic acids as a response to P-starvation. Plant and Soil 113, 161-165.
Hoffland E, Nelemans J A and Findenegg G R 1990 Origin of organic acids exuded by roots of phosphorus-stressed rape (Brassica napus) Plants. InPlant Nutrition Physiology and Applications. Ed. M C Van Beusichem. pp 179-183. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Ohwaki Y and Hirata H 1992 Differences in carboxylic acid exudation among P-starved leguminous crops in relation to carboxylic acid contents in plant tissues and phospholipid level in roots. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 38(2), 235-243.
Ström L, Olsson T and G Tyler 1994 Differences between calcifuge and acidifuge plants in root exudation of low-molecular organic acids. Plant and Soil 167, 239-245.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Ma, J. & Cao, Y.P. Phosphorus deficiency enhances root exudation of low-molecular weight organic acids and utilization of sparingly soluble inorganic phosphates by radish (Raghanus satiuvs L.) and rape (Brassica napus L.) plants. Plant and Soil 196, 261–264 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004214410785
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004214410785