Abstract
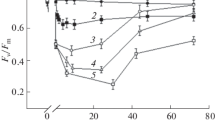
Activities of oxygen evolution, fluorescence Fv (a variable part of chlorophyll fluorescence) values, and amounts of the 33 kDa protein remaining bound to the thylakoids in intact spinach chloroplasts were measured during and after high-temperature treatment. The following results were obtained. (1) Both the Fv value and the flash-induced oxygen evolution measured by an oxygen electrode were decreased at high temperatures, but they showed partial recovery when the samples were cooled down and incubated at 25°C for 5 min after high-temperature treatment. (2) Oxygen evolution was more sensitive to high temperatures than the Fv value, and the decrease in the Fv/Fm ratio at high temperatures rather corresponded to that in the oxygen evolution measured at 25°C after high-temperature treatment. (3) Photoinactivation of PS II was very rapid at high temperatures, and this seems to be a cause of the difference between the Fv values and the oxygen-evolving activities at high temperatures. (4) At around 40°C, the manganese-stabilizing 33 kDa protein of PS II was supposed to be released from the PS II core complexes during heat treatment and to rebind to the complexes when the samples were cooled down to 25°C. (5) At higher temperatures, the charge separation reaction of PS II was inactivated, and the PS II complexes became less fluorescent, which was recovered partially at 25°C. (6) Increases in the Fv value due to a large decrease in the electron flow from QA to QB became prominent after high-temperature treatment at around 50°C. This was the main cause of the discrepancy between the Fv values and the oxygen-evolving activities measured at 25°C. Relationship between the process of heat inactivation of PS II reaction center complexes and the fluorescence levels is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khatib K and Paulsen GM (1989) Enhancement of thermal injury to photosynthesis in wheat plants and thylakoids by high light intensity. Plant Physiol 90: 1041–1048
Butler WL (1978) Energy distribution in the photochemical apparatus of photosynthesis. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 29: 345–378
Butler WL and Kitajima M (1975) Fluorescence quenching in Photosystem II of chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta 376: 116–125
Cao J and Govindjee (1990) Chlorophyll a fluorescence transient as an indicator of active and inactive Photosystem II in thylakoid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1015: 180–188
Cheniae GM and Martin IF (1970) Sites of function of manganese within Photosystem II. Roles in O2 evolution and system II. Biochim Biophys Acta 197: 219–239
Debus RJ (1992) Themanganese and calcium ions of photosynthetic oxygen evolution. Biochim Biophys Acta 1102: 269–352
Eisenberg-Domovich Y, Oelmüller R, Herrmann RG and Ohad I (1995) Role of the RC II-D1 protein in the reversible association of the oxygen-evolving complex proteins with the lumenal side of Photosystem II. J Biol Chem 270: 30181–30186
Enami I, Kitamura M, Tomo T, Isokawa Y, Ohta H and Katoh S (1994) Is the primary cause of thermal inactivation of oxygen evolution in spinach PS II membranes release of the extrinsic 33 kDa protein or of Mn? Biochim Biophys Acta 1186: 52–58
Fork DC, Sen A and Williams WP (1987) The relationship between heat-stress and photobleaching in green and blue-green algae. Photosynth Res 11: 71–87
Genty B, Briantais JM and Baker NR (1989) The relationship between the quantum yield of photosynthetic electron transport and quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence. Biochim Biophys Acta 990: 87–92
Ikeuchi M and Inoue Y (1988) A new 4.8-kDa polypeptide intinsic to the PS II reaction center, as revealed by modified SDS-PAGE with improved resolution of low-molecular-weight proteins. Plant Cell Physiol 29: 1233–1239
Katoh S and San Pietro A (1967) Ascorbate-supported NADP photoreduction by heated Euglena chloroplasts. Arch Biochim Biophys 122: 144–152
Kimimura M and Katoh S (1972) On the functional site of manganese in photosynthetic electron transport system. Plant Cell Physiol 13: 287–296
Lichtenthaler HK (1988) Applications of Chlorophyll Fluorescence in Photosynthesis Research, Stress Physiology, Hydrobiology and Remote Sensing. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands
Lilley RM, Fitzgerald MP, Rienits KG and Walker DA (1975) Criteria of intactness and the photosynthetic activity of spinach chloroplast preparations. New Physiol 75: 1–10
Ludlow MM (1987) Light stress at high temperature. In: Kyle DJ, Osmond CB and Arntzen CJ (eds) Photoinhibition, pp 89–109. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Malkin S and Kok B (1966) Fluorescence induction studies in isolated chloroplasts I. Number of components involved in the reaction and quantum yields. Biochim Biophys Acta 126: 413–432
Miyao M, Murata N, Lavorel J, Maison-Peteri B, Boussac A and Etienne AL (1987) Effect of the 33-kDa protein on the S-state transitions in photosynthetic oxygen evolution. Biochim Biophys Acta 890: 151–159
Mohanty P, Mar T and Govindjee (1971) Action of hydroxylamine in the red alga porphyridium cruentum. Biochim Biophys Acta 253: 213–221
Nash D, Miyao M and Murata N (1985) Heat inactivation of oxygen evolution in Photosystem II particles and its acceleration by chloride depletion and exogenous manganese. Biochim Biophys Acta 807: 127–133
Neubauer C and Schreiber U (1987) The polyphasic rise of chloropyll fluorescence upon onset of strong continuous illumination: I. Saturation characteristics and partial control by the Photosystem II acceptor side. Z Naturforsch 42c: 1246–1254
Santarius KA (1975) Sites of heat sensitivity in chloroplasts and differential inactivation of cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation by heating. J Thermal Biol 1: 101–107
Schreiber U (1986) Detection of rapid induction kinetics with a new type of high-frequency modulated chlorophyll fluorometer. Photosynth Res 9: 261–272
Schreiber U and Armond PA (1978) Heat-induced changes of chlorophyll fluorescence in isolated chloroplasts and related heat-damage at the pigment level. Biochim Biophys Acta 502: 138–151
Schreiber U and Neubauer C (1987) The polyphasic rise of chloropyll fluorescence upon onset of strong continuous illumination: II. Partial control by the Photosystem II donor side and possible ways of interpretation. Z Naturforsch 42c: 1255–1264
Siegenthaler PA and Dumont N (1990) Characteristics of spinach chloroplast envelope, thylakoid and stroma polypeptide as revealed by Triton X-114 phase partition. Plant Cell Physiol 31: 1101–1108
Yamane Y, Kashino Y, Koike H and Satoh K (1997) Increases in the fluorescence F0 level and reversible inhibition of Photosystem II reaction center by high-temperature treatment in higher plants. Photosynth Res 52: 57–64
Yamashita T and Butler WL (1968) Inhibition of chloroplasts by UV-irradiation and heat-treatment. Plant Physiol 43: 2037–2040
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamane, Y., Kashino, Y., Koike, H. et al. Effects of high temperatures on the photosynthetic systems in spinach: Oxygen-evolving activities, fluorescence characteristics and the denaturation process. Photosynthesis Research 57, 51–59 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006019102619
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006019102619