Abstract
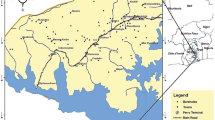
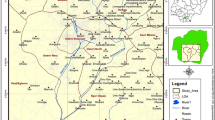
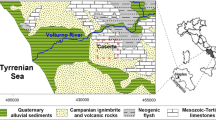
Pollution vulnerability of theOwerri regional water supply aquifer wasevaluated as a basis for developing appropriateprotection strategy for the groundwaterresource. The assessment was accomplished usingLegrand, GOD, Siga and DRASTIC models.Techniques of the models generally involvedparameters rating and point count systems, whichare based on the evaluation of various parameterin relation to their capacity for enhancing orattenuating contaminants in the groundwatersystem. Field and laboratory evaluations of theparameters indicate that the Owerri areagenerally occupies a nearly, flat topographywith a relatively high groundwater recharge. Thearea is underlain by predominantly sandyfacies in the Northern area which grades intogravelly sequences towards the southwest. TheSoutheastern area is distinguished by thickclayey facies that thin westwards towards theOwerri metropolis. Effective hydraulicconductivity (Kz) in the downward directionranges from 1.44 × 10-3 to 5.6 × 10-9 m s-1; with the upper limits reflecting coarsesands and gravelly units. The amount of clay andclay-size particles in the sandy and gravellyunits is negligible, suggesting that thesorptive capacity of the units is low. Depth towater table decreases southwards while hydraulichead gradients vary between 0.09 and 0.22.Groundwater occurs in unconfined conditions inmost places except in the southeastern zonewhere it is semi-confined due to the presence ofa clayey unit. The groundwater vulnerabilitymap developed on the basis of the models andseveral other thematic maps shows that theOwerri metropolis and the southwest area ofOwerri have high vulnerability, indicatinggroundwater pollution. The existing wastedisposal sites in these sub-areas should beabandoned and rehabilitated to forstall furtherpollution of the groundwater system. Areas tothe North and Southeast of Owerri have moderateand low vulnerabilities, respectively,indicating the relatively lower sensitivity ofthe groundwater system in the sub-areas tocontamination. The lower sensitivity couldfurther be matched with properly engineeredsanitary landfills in the event of choice ofsites, as an additional protective strategy forthe groundwater system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albinet, M. and Margat, J.: 1970, ‘Mapping of groundwater vulnerability to contamination’, 2nd serie, Orleans, France, Bull. BRAM. 3(4),13–22.
Aller, L., Bennet, T., Hehr, J. H., Petty, R. J. and Hackett, G.: 1987,DRASTIC: A Standardized System for Evaluation Groundwater Pollution Potential using Hydrogeologic Settings,U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Ada. Ok, EPA/600/2-87-036, 455 p.
Ananaba, S. E., Onu, N. N. and Iwuagwu, C. J.: 1993, ‘Geophysical Study of the Gravel Deposit in Ihiagwa, Owerri, Nigeria’,Jour. Min. and Geol. 29(2),95–100.
Anyaogu, C. N.: 1992,Hydrologic and Water Quality Improvement Characteristics of a Small Riverine Wetland at Ulakwo near Owerri, Imo State,M.Sc. Thesis, Department of Geoscience, Federal University of Technology, Owerri.
Avbovbo, A. A.: 1970, ‘Tertiary Lithostratigraphy of the Niger Delta’,Bull. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. 62,295–306.
Bordoni, G.: 1984,Atlas of Imo State, Planital Srl for G and G.
Civita, M.: 1993,Groundwater Vulnerability Maps: A Review,Poc. Ix Symp. On Pesticide chemistry. Degradation and Mobility of Xenobiotics, Piacenze, Italy, October 11–13,Edizioni Biagini, Lucca, Italy, 587–631.
Dike, C. E.: 1992,Groundwater Seepage Force and Gully Propagation at Amucha Gullies of Imo State, B.Sc. Thesis Department of Geosciences, Federal University of Technology, Owerri.
Egboka, B. C. E., Nwankwor, G. I. and Orajiaka I. P.: 1989, ‘Principles and problems of environmental pollution of groundwater resources with case examples from developing countries’, Environmental Health Perspectives 83,36–68.
Enuvie, G. A., Ophori, D. U., Enebeli, V. O. and Nwadibia, E. O.: 1991, ‘Anomalous delay in the response of groundwater level to seasonal rainfall variations in parts of Imo State. A preliminary study’,Nig. Jour. Min. and Geol. 27(1),55–60.
Ezigbo, H. I.: 1989, ‘Groundwater quality problems in parts of Imo State Nigeria’,Jour. Min. and Geol. 25(1–2),1–9.
Freeze, R. A. and Cherry, J. A.:1976,Groundwater,Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey.
Howard, K. W. F. and Livingstone, S.:1994,Impact of Urban development on surface water as a result of shallow groundwater flow-a case study from the Great Lakes Basin of North America, in congress of the International Association of Hydrogeologists, 25th Adelaide, 1994, Proceedings: International Association of Hydrogeologists,1, pp. 133–139.
Ibe, K. M., Sowa, A. H. O. and Osondu, O. C.: 1992, ‘Environmental contamination and other anthropogenic impacts on Otamiri and Nworie rivers, Owerri’,Nigerian Jour. Min. and Geol. 28(1),87–91.
LeGrand, H.-E.: 1964,A Standard System for Evaluating Waste Disposal Sites,National Water Well Assoc. Dublin, OH, 49 p.
Marcolongo, B. and Pretto, L.: 1987,Aquifer vulnerability of the plain northwards of Vicenza, Publ. G.N.D. C.I.C.N.R. n. 28, 13 p., Map 1:25000.
Monanu, S. and Inyang, F.: 1975, ‘Climatic Regimes’, in G. E. K. Ofomata (ed.), Nigeria in Maps,Ethiope Publ. House, Benin, pp. 27–29.
Novakovic, B. and Jagger, D.: 1992, ‘Application of hydraulic confinement concept on landfill design and operation’, in Ms. A. Dupont (ed.), Modern Trends in Hydrogeology, Conference of the Canadian National Chapter, IAH.
Nwankwor, G. I., Egboka, B. C. and Orajiaka, I. P.: 1988, ‘Groundwater occurrence and flow pattern in the Enugu Coal Mine area’, Anambra State, Nigeria, Hydrological Science Journal 33,465–482.
Nwankwor, G. I. and Etche, B. C.: 1990, ‘Hydrogeological Evaluation of the Greater Onitsha Water Scheme’, Anambra State Nigeria, Jour. Min. and Geol.26(2),261–267.
Nwankwor, G. I.: 1995, ‘A grain-size technique for estimating elastic storage for sand aquifers’. Water Resources 6(1–2),46–51.
Ofoegbu, C. O.: 1988,Groundwater and Mineral Resources of Nigeria,Earth Evolution Sciences, Vieweg, Germany, pp.45–47.
Okogbue, C. O. and Agbo. J. U.: 1989, ‘Evidence of Downward Displacement Theory in Natural Groundwater Recharge’, in G. E. Oteze (ed.), Water Resources, Jour. Nig. Assoc. Hydrogeology, 1(2), pp.143–146.
Olmer, M. Q. and Rezec, B.: 1974, Methodical Principles of Maps for Protection of Groundwater in Bohemia and Moravia, scale 1:200 000. Intl. Assoc. Hydrogeologists, Memoris, Tomex, Congress de Montpellier, 1. Communications, pp. 105–107.
Onyeagocha, A. C.: 1980, ‘Petrography and depositional environment of the Benin Formation’,Nig. Journ. Min. Geol. 17, 147–151.
Reyment, R. A.: 1965,Aspects of the Geology of Nigeria, Ibadan University Press.
Rowe, R. K.: 1992, ‘Integration of Hydrogeology and Engineering in the Design of Waste Management Sites’, in Ms. A. Dupont (ed.), Modern Trends in Hydrogeology, Conference of the Canadian Nat. Chapt. IAH.
Rowe, R. K.: 1992b, Leachate Detection or Hydraulic Control: Two Design Options,Proceedings 3rd Intl. Symposium on Sanitary Landfills, Sardina, pp. 977–987.
Short, K. C. and Stauble, A. J.: 1967, ‘Outline of the Geology of Niger Delta’, Am. Ass. Petro. Geol. Bull. 51,661–779.
Uma, K. O.: 1984,Water Resources Potential of Owerri Area and the Evironments, M.Sc. Thesis, University of Nigeria, Nsukka (unpublished).
Uma, K. O. and Egboka, B. C. E.: 1986, ‘Water Resources of Owerri and its Environments’, Imo State, Nigeria, Journ. Min. Geol. 22(1–2),57–64.
Villumsen, A. and Sonderskov, C.: 1982, ‘Vulnerability maps: A promising tool in groundwater protection’, Aqua 5,406–468.
Vrba, J. and Zaporozec, A.: 1994, ‘Guidebook on mapping groundwater and vulnerability’,Journ. IAH. 16,39–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibe, K.M., Nwankwor, G.I. & Onyekuru, S.O. Assessment of Ground Water Vulnerability and its Application to the Development of Protection Strategy for the Water Supply Aquifer in Owerri, Southeastern Nigeria. Environ Monit Assess 67, 323–360 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006358030562
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006358030562