Abstract
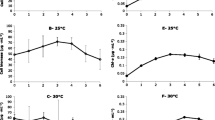
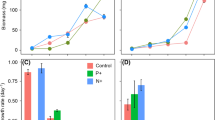
The objective of this work was to determine the influence of total dissolved solids/salinity (TDS mgL-1) on growth and biomass specific rates of nodularin (hepatotoxin) production by Nodularia spumigena 001E isolated from Lake Alexandrina, South Australia. Maximum biomass yield (dry matter, chlorophyll a and particulate organic carbon/POC) at 80 μmol photon m-2 s-1 was recorded at 3300 mg TDS L-1 and decreased at salinities above or below this value (p < 0.05). The maximum biomass yield (dry matter and chlorophyll a) at 30 μmol m-2 s-1 occurred at a higher salinity of 9900 mg TDS L-1. Cultures grown at 80 μmol m-2 s-1, at a TDS> 6600 mg L-1, had significantly (p < 0.05) lower nodularin content (ml-1 medium) than cultures grown at the same salinities at 30 μmolm-2 s-1. The maximum total toxin concentration (mL-1 medium) occurred at 9900 and 3300 mg TDS L-1 at 30 μmol m-2 s-1and 80 μmol m-2 s-1 respectively. Toxin per unit biomass, expressed as dry matter, chlorophyll a and POC was similar for cultures grown at 30 μmol m-2 s-1 or 80 μmol m-2s-1 at salinities < 6600 mg TDS L-1. At salinities > 9900 mg TDS L-1 the toxin content per unit biomass decreased at both irradiances, however, cultures grown at 30 μmol m-2s-1 had a higher toxin content than those grown at 80 μmol m-2 s-1. The results indicate that not only do changes in irradiance and salinity directly influence growth and toxin production but that changes in irradiance affected the influence of salinity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blackburn SI, McCausland MS, Bolch CJS, Newman SJ, Jones GJ (1996) Effect of salinity on growth and toxin production in cultures of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena from Australian waters. Phycologia 35: 511–522.
Carmichael WW (1992) Cyanobacteria secondary metabolites – the cyanotoxins. J. appl. Bact. 72: 445–459
Carmichael WW (1994) The toxins of cyanobacteria. Scientific American, January 1994, 64–72.
Codd GA, Steffensen DA, Burch MD, Baker PD (1994) Toxic blooms of cyanobacteria in Lake Alexandrina, South Australia – Learning from History. Aust. J.mar. Freshwat. Res. 45: 731–736.
Dubinsky Z, Falkowski PG, Post AF, Van Hes UM (1987) A system for measuring phytoplankton photosynthesis in a defined light field with oxygen electrode. J. Plankton Res. 9: 607–612.
Francis G (1878) Poisonous Australian lake. Nature 18: 11–12.
Gorham PR, McLachlan S, Hammer UT, Kim WK (1964) Isolation and culture of toxic strains of Anabaena flos-aquae (Lyngb.) de Bréb. Mitt. int. Ver. Limnol. 15: 796.
Greenberg AE, Clesceri LS, Eaton AD (1985) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewaters. American Public Health Association Washington DC, U.S.A.
Heresztyn T, Nicholson BC (1996) Nodularin concentrations in lakes Alexandrina and Albert, South Australia, during a bloom of the cyanobacterium (blue-green algae) Nodularia spumigena and degradation of toxin. Envir. Toxicol. Water. Qual. 12: 273–282.
Jones GJ, Blackburn SI, Parker NS (1994) A toxic bloom of Nodularia spumigena Mertens in Orielton Lagoon, Tasmania. Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 45: 787–800.
Kirk JTO (1994) Light and Photosynthesis in Aquatic Ecosystems. Cambridge University Press, Great Britain.
Lehtimaki J, Sivonen K, Luukkainen R, Niemela SI (1994) The effects of incubation time, temperature, light, salinity and phosphorus on growth and hepatotoxin production by Nodularia strains. Arch. Hydrobiol. 130: 269–282.
Lehtimaki J, Moisander P, Sivonen K and Kononen K (1997) Growth, nitrogen fixation, and nodularin production by two Baltic Sea cyanobacteria. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 63: 1647–1656.
Ohta T, Sueoka E, Iida N, Komori A, Suganuma M, Nishiwaki R, Tatematsu M, Kim S, Carmichael WW, Fujiki H (1994) Nodularin, a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A, is a new environmental carcinogen in male F344 rat liver. Cancer Res. 54: 6402–6406.
Ressom R, Soong FS, Fitzgerald J, Turczynowicz L, Saadi OE, Roder D, Maynard T, Falconer I (1993) Health effects of toxic cyanobacteria (blue green algae). Report to the Environmental Standing Committee of the National Health and Medical Research Council by the University of Adelaide and the South Australian Health Commission. Lutheran Publishing House, Australia.
Sivonen K, Carmichael WW, Namikoshi M, Rinehart KL, Dahlem AM, Niemela SI (1990) Effects of light, temperature, nitrate, orthophosphate and bacteria on growth of and hepatotoxin production by Oscillatoria agardhii strains. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 56: 2658–2666.
Utkilen H, Gjolme N (1992) Toxin production by Microcystis aeruginosa as a function of light in continuous cultures and its ecological significance. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 58: 1321–1325.
Van der Westhuizen AJ, Eloff JN (1985) Effect of temperature and light on the toxicity and growth of the blue green alga Microcystis aeruginosa (UV-006). Planta 163: 55–59.
Watanabe MF, Oishi S (1985) Effects of environmental factors on toxicity of a cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa) under culture conditions. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 49: 1342–1344.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hobson, P., Burch, M. & Fallowfield, H. Effect of total dissolved solids and irradiance on growth and toxin production by Nodularia spumigena . Journal of Applied Phycology 11, 551–558 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008193918189
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008193918189