Abstract
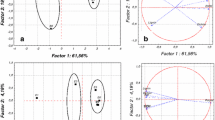
Eucalyptus grandis wood was biodegraded by eight basidiomycetes and two ascomycetes. Four groups of decayed wood samples were recognized based on the principal component analysis (PCA) of weight and component loss data. Among the 10 fungal species studied, no selective lignin biodegradation was achieved. PCA was very efficient in recognizing wood decay patterns and seems to be a useful tool to analyse large group of weight- and component-loss data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akthar, M., Kirk, T.K. & Blanchette, R.A. 1996 An overview of consortia research. In Biotechnology in the Pulp and Paper Industry. Recent Advances in Applied and Fundamental Research, eds Srebotnik, E. & Messner, K. pp. 187–192. Vienna: Facultas-Universitätsverlag.
Akhtar, M., Artridge, M.C., Myers, G.C. & Blanchette, R.A. 1993 Biomechanical pulping of loblolly pine chips with selected white-rot fungi. Holzforschung 47, 36–40.
Beebe, K.R. & Kowalski, K. 1987 An introduction to multivariate calibration and analysis. Analytical Chemistry 59, 1007A–1017A.
Bettucci, L., Speranza, M. & Piaggio, M. 1992 Selection of whiterot fungi for biopulping. Proceedings of 2nd Brazilian Symposium on the Chemistry of Lignin and Other Wood Components 3, 394–401.
Blanchette, R.A., Burnes, T.A., Gary, F.L. & Effland, M.J. 1998 Selection of white-rot fungi for biopulping. Biomass 15, 93–101.
Daniel, G., Binarova, P. & Kubatova, E. 1996 Cytochemical and immunocytochemical studies on sites of H2O2 production and catalase activity in hyphae of Phanerochaete chrysosporium growth in liquid culture and on wood. In Biotechnology in the Pulp and Paper Industry. Recent Advances in Applied and Fundamental Research, eds Srebotnik, E. & Messner, K. pp. 583–590, Vienna: Facultas-Universitätsverlag.
Daniel, G. 1994 Use of electron microscopy for aiding our understanding of wood biodegradation. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 13, 199–205.
El-Gammal, A.A., Nagleb, Z.H. & Helmy, S.M. 1995 Ultrastructural aspects of lignocellulose degradation by some microorganisms. Polymer Degradation and Stability 50, 199–202.
Enoki, A., Tanaka, H. & Fuse, G. 1988 Degradation of lignin related compounds, pure cellulose and wood components by white-rot and brown-rot fungi. Holzforschung 42, 85–93.
Esposito, E., Canhos, V.P. & Duraá, N. 1991 Screening of lignin-degrading fungi for removal of colour from kraft mill wastewater with no additional extra carbon-source. Biotechnology Letters 13, 571–576.
Ferraz, A., Baeza, J. & Duraá, N. 1991 Softwood biodegradation by an ascomycete Chrysonilia sitophila (TFB 27441). Letters in Applied Microbiology 13, 82–86.
Ferraz, A., Mendoncç, R., Cotrim, A.R. & da Silva, F.T. 1996 The use of white-rot decay as a pretreatment for organosolv delignification of Eucalyptus grandis wood. In Biotechnology in the Pulp and Paper Industry. Recent Advances in Applied and Fundamental Research, eds Srebotnik, E. & Messner, K. pp. 221–224, Vienna: Facultas-Universitätsverlag.
Fischer, K., Akhtar, M., Messner, K., Blanchette, R.A. & Kirk, T.K. 1996 Pitch reduction with the white-rot fungus Cerisporiopsis subvermispora. In Biotechnology in the Pulp and Paper Industry. Recent Advances in Applied and Fundamental Research, eds Srebotnik, E. & Messner, K. pp. 193–197, Vienna: Facultas-Universitätsverlag.
Nicole, M., Xixuan, X. & Ouellette, G.B. 1995 Wood degradation by Phellinus noxius: ultrastructure and cytochemistry. Canadian Journal of Microbiology 41, 253–257.
Scarminio, I.S. & Bruns, R.E. 1989 An adaptation of ARTHUR for microcomputers. Trends in Analytical Chemistry 8, 326–328.
Setliff, E.C., Marton, R., Granzow, S.G. & Eriksson, K.L. 1990 Biomechanical pulping with white-rot fungi. TAPPI Journal 73(8), 141–147.
Speranza, M., Bettucci, L. & Duraá, N. 1995a Delignification of E. grandis and E. globulus in vitro by Panus tigrinus. Proceedings of 4th Brazillian Symposium on the Chemistry of Lignins and Other Wood Components 5, 149–152.
Speranza, M., Ferraz, A., Duraá, N., & Bettucci, L. 1995b Eucalyptus grandis wood decayed by white-rot fungi. Proceedings of 4th Brazillian Symposium on the Chemistry of Lignins and Other Wood Components 5, 153–156.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferraz, A., Esposito, E., Bruns, R. et al. The use of principal component analysis (PCA) for pattern recognition in Eucalyptus grandis wood biodegradation experiments. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 14, 487–490 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008875730177
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008875730177