Abstract
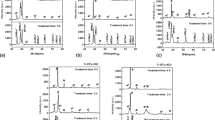
Titanium–zirconium based alloys containing a small amount of niobium were investigated in order to evaluate their possible use as biomedical materials. Zirconium, which belongs to the IVa group, is known to have good corrosion resistance and biocompatibility similar to titanium. As the titanium–zirconium system shows a complete solid solution, a wide variation of alloy design is available and large quantities of solid-solution hardening must be possible. Niobium, having a β-phase stabilizing effect, was chosen as a ternary element in order to control desirably the microstructure. There have been no reports which suggest its harm to a living body. The alloys containing 2% or 3% niobium showed the highest hardness value after aging heat treatment at 773 K. In contrast to this, no alteration of hardness was seen in specimens aged at 1073 K. Through conventional X-ray diffractometry and in situ X-ray analysis using a hot stage, β-phase precipitation in the A matrix was identified. From the above results, it is concluded that alloys containing 2%–3% niobium are hopeful candidates for new kinds of biomedical alloys, when they are heat treated under suitable conditions. © 1998 Kluwer Academic Publishers
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Kobayashi, H. Doi, M. Takahashi, T. Nakano, T. Yoneyama and H. Hamanaka, J. Jpn Dent. Mater. Devices 14 (1995) 406.
ASTM F 1295–92 (American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA, 1992).
A. Yamamoto, R. Honda and M. Sumita, J. Jpn Soc. Biomater 14 (1996) 167.
Y. Okazaki, Y. Ito, A. Ito and T. Tateishi, ibid. 11 (1993) 160.
A. Ogawa, M. Ishikawa, Y. Takasaka and C. Ouchi, Curr. Adv. Mater. Process. Rep. ISIJ Meeting 7 (1994) 654.
J. L. Murray, in “Phase Diagrams of Binary Titanium Alloys” (ASM International, Metals Park, OH, 1987) p. 340.
E. Kobayashi, S. Matsumoto, H. Doi, T. Yoneyama and H. Hamanaka, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 29 (1995) 943.
E. Kobayashi, H. Doi, T. Yoneyama, H. Hamanaka, S. Matsumoto and K. Kudaka, J. Jpn Dent. Mater. Devices 14 (1995) 321.
T. Tsuchiya, A. Nakamura, Y. Ohshima, E. Kobayashi, H. Doi, T. Yoneyama and H. Hamanaka, J. Tiss. Eng. 4 (1998) 197.
E. W. Collings, in “The Physical Metallurgy of Titanium Alloys” (ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1984) p. 69.
E. Kobayashi, H. Doi, T. Yoneyama, H. Hamanaka, S. M. Best, J. C. Shelton and W. Bonfield, in “Fifth World Biomaterials Congress Program and Transactions”, Vol. 2 (1996) p. 481.
Y. Yamamoto, Shimadzu Hyoron 46 (1989) 63.
T. Yoneyama, H. Doi, E. Kobayashi, T. Nakano and H. Hamanaka, J. Jpn Dent. Mater. Devices 13 (1994) 213.
A. G. Ingram, D. N. Williams and H. R. Ogden, J. Less-Common Metals 4 (1962) 217.
O. Okuno, A. Shimizu and I. Miura, J. Jpn Soc. Dent. Mater. Devices 4 (1985) 408.
Y. Etchu, M. Okazaki and H. Noguchi, ibid. 11 Special Issue 20 (1992) 270.
M. Hansen, E. L. Kamen, H. D. Kessler and D. J. Mcpherson, Trans. AIME 191 (1951) 881.
P. S. Rudman, Acta Metall. 12 (1964) 1381.
P. Duwez, J. Inst. Metals 80 (1952) 525.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, E., Doi, H., Yoneyama, T. et al. Influence of aging heat treatment on mechanical properties of biomedical Ti–Zr based ternary alloys containing niobium. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 9, 625–630 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008927407556
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008927407556