Abstract
Transmission and reflectance are the two main modes of pulse oximetry. In obstetrics, due to the absence of a transilluminable fetal part for transmission oximetry, the only feasible option is the reflectance mode, in which sensor and detector are located on the same surface of the body part. However, none of the reflectance pulse oximeters developed for intrapartum use are fully satisfactory, as indicated by the fact that none have entered routine use. We have designed, developed, constructed and tested a reflectance pulse oximeter with the possibility to adjust the electronic circuits and signal processing in order to determine the effects of various parameters on signal amplitude and wave-form and to optimize the sensitivity and spatial arrangement of the optical elements.
Following an explanation of the principles of reflectance pulse oximetry, we report our experience with the design, development, construction and field-testing of an in-house reflectance pulse oximetry system for obstetric application.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Severinghaus JW, Astrup PB. History of blood gas analysis, VI. Oximetry. J Clin Monit 1986; 2: 270-288
Huch R, Ullrich GJ, König V, Huch A. Reflectance pulse oximetry-potentials and problems. In: Ehrly et al. (eds). Clinical oxygen pressure measurements III. Berlin: Blackwell Ueberreuter Wissenschaft 1992: 14-31
Mendelson Y, Kent JC, Yocum BL, Birle MJ. Design and evaluation of a new reflectance pulse oximeter sensor. Med Instr 1988; 22: 167-173
Johnson N, Johnson VA, Fisher J, Jobbings B, Bannister J, Lilford RJ. Fetal monitoring with pulse oximetry. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1991; 98: 36-41
Knitza R, Buschmann J, Rall G. Ein neues Verfahren zur kontinuierlichen Messung der fetalem Sauerstoffsättigung sub partu. Geburts Frauenheilk 1992; 52: 319-321
Dildy GA, Clark SL, Loucks CA. Preliminary experience with intrapartum fetal pulse oximetry in humans. Obstet Gynecol 1993; 81: 630-635
Hypoxische Gefährdung des Fetus sub partu. In: Knitza R (ed). Darmstadt: Steinkopf 1994
Wukitsch MW, Petterson MT, Tobler DR, Pologe JA. Pulse oximetry: Analysis of theory, technology and practice. J Clin Monit 1988; 4: 290-301
Graaff R. Tissue optics applied to reflectance pulse oximetry. Thesis Rijksuniversiteit Groningen The Netherlands 1993
Steinke JM, Shepherd AP. Role of light scattering in whole blood oximetry. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 1986; BME-33: 294-301
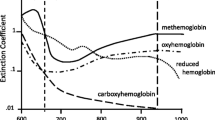
Zijlstra WG, Buursma A, Meuwsen-van der Roest WP. Absorption spectra of human fetal and adult oxyhemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin and methemoglobin. Clin Chem 1991; 37: 1663-1638
Yount JE. Practical aspects of calibrating fetal pulse oximetry. In: Knitza R (ed). Hypoxische Gefährdung des Fetus sub partu. Darmstadt: Steinkopff 1994: 45-82
König V, Huch R, Huch A.Wie kann ein Pulsoximeter kalibriert werden? In: Knitza R, ed. Hypoxische Gefährdung des Fetus sub partu. Darmstadt: Steinkopff 1994: 111-116
Faisst K, König V, Fanconi D, Schmid ER, Huch A, Huch R. Kalibration eines Reflexions-Pulsoximeters. Biomed Tech 1996; 41 (Ergänzungsband): 508-509
Dassel AC, Graaff R, Aarnoudse JG, Elstrodt JM, Heida P, Koelink MH, de Mul FF, Greve J. Reflectance pulse oximetry in fetal lambs. Pediatr Res 1992; 31: 266-269
Carter AM, Stiller R, König V, Jörgensen JS, Svendsen P, Huch R, Huch A. Calibration of a reflectance pulse oximeter for arterial oxygen saturations below 70% (to be published)
König V, Ullrich GJ, Faisst K, Joergensen JS, Huch R, Huch A. Reflexions-Pulsoximetrie-Untersuchungen mit eigenem Mess-System. Biomed Tech 1992; 37: 39-40
Faisst K, Hannon W, Jörgensen JS, König V, Bucher HU, Huch A, Huch R. Reflectance pulse oximetry in neonates. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1995; 61: 117-122
Faisst K, König V, Huch A, Huch R. Reflexions-Pulsoximetrie mit Vakuum-Ein Beitrag zur Fixierung. In: Marius (ed). Fetale Pulsoximetrie sub partu, Bücherei des Frauenarztes. Stuttgart: Enke 1996; 50: 28-32
Faisst K, Kirkinen P, König V, Huch A, Huch R. Intrapartum reflectance pulse oximetry: Effects of sensor location and fixation duration on oxygen saturation readings. J ClinMonit 1997; 13: 299-302
König V, Ullrich GJ, Huch A, Huch R. Reflection pulse oximetry-experience in Zürich. In: Lafeber HN (ed). Fetal and neonatal physiological measurements. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1991; 111-117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
König, V., Huch, R. & Huch, A. Reflectance Pulse Oximetry – Principles and Obstetric Application in the Zurich System. J Clin Monit Comput 14, 403–412 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009983010772
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009983010772