Abstract
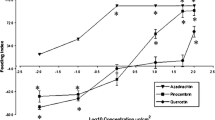
Four recently identified isoflavonoids, isolated from wild relatives of chickpea, Cicer arietinum, were shown to deter larval feeding by Heliocoverpa armigera at 100 ppm, judaicin and maackiain retained their antifeedant activity at 50 ppm and 10 ppm, respectively. The isoflavonoids were tested in combinations and with chlorogenic acid; the combinations containing judaicin and maackiain were most active, and chlorogenic acid enhanced the antifeedant activity of all four isoflavonoids. H. armigera was the only one of four noctuids to be deterred by all four isoflavonoids. Spodoptera littoralis was deterred by judaicin alone and S. frugiperda by maackiain alone. Heliothis virescens and S. exigua were not deterred from feeding by any of the isoflavonoids. When incorporated into a diet, isoflavonoids decreased the weight gain of early stadia larvae of H. armigera more than they did later stadia, and maackiain and judaicin were most potent. We conclude that the isoflavonoids, especially maackiain and judaicin, could play a role in decreasing the susceptibility of Cicer to attack by H. armigera.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
BERNAYS, E. A., and CHAPMAN, R. F. 1994. Host-Plant Selection by Phytophagous Insects. Chapman and Hall, New York.
BLANEY, W. M., SIMMONDS, M. S. J., LEY, S. V., ANDERSON, J. C., and TOOGOOD, P. L. 1990. Antifeedant effects of azadirachtin and structurally related compounds on lepidopterous larvae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 55:149-160.
COWGILL, S. E., and LATEEF, S. S. 1996. Identification of antibiotic and antixenotic resistance to Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in chickpea. J. Econ. Entomol. 89:224-229.
DANIEL, S., and BARZ, W. 1990. Elicitor induced metabolic changes in cell cultures of chickpea cultivars resistant and susceptible to Aschochyta rabiei. Planta 182:279-286.
FELTON, G. W., and GATEHOUSE, J. A. 1996. Antinutritive plant defence mechanisms, pp. 373-416, in M. J. Lehane and P. F. Billingsley (eds.). Biology of the Insect Midgut. Chapman and Hall, London.
FREEDMAN, B., NOWAK, L. J., KWOLEK, W. F., BERRY, D. C., and GUTHRIE, W. D. 1979. A bioassay for plant-derived pest control agents using the Eurpean corn borer. J. Econ. Entomol. 72:541-545.
GLENDINNING, J. L., and SLANSKY, D. 1995. Consumption of a toxic food by caterpillars increases with dietary exposure: Support for a role of induced detoxification enzymes. J. Comp. Physiol. A 176:337-345.
GORDON, M. A., LAPA, E. W., FITTER, M. S., and LINDSAY, M. 1980. Susceptibility of zoopathogenic fungi to phytoalexins. Antimicob. Agents Chemother. 17:120-123.
HOOVER, K., STOUT, M. J., ALANIZ, S. A., HAMMACK, B. D., AND DUFFEy, S. S. 1998. Influence of induced plant defences in cotton and tomato on the efficacy of baculoviruses on noctuid larvae. J. Chem. Ecol. 24:253-271.
ISMAN, M. B., and DUFFEY, S. S. 1982. Toxicity of the tomato phenolic compounds to the fruitworm Heliothis zea. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 31:370-376.
KIMMINS, F. M., PADGHAM, D. E., and STEVENSON, P.C. 1995. Growth inhibition of the cotton bollworm larvae by caffeoyl quinic acids from the wild groundnut Arachis paraguariensis. Insect Sci. Appl. 16:363-368.
LAZZARO, M. D., and THOMSON, W. W. 1995. Seasonal variation in hydrochloric acid, malic acid, and calcium ions secretered by the trichomes of chickpea (Cicer arietinum). Physiol. Plant. 94:291-297.
NOLDUS, L. P. J. J. 1991. The observer: a software system for collection and analysis of observational data. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 23:415-429.
PATANKAR, A. G., HARSULKAR, A. M., GIRI, A. P., GUPTA, V. S., SAINANI, M. N., RANJEKER, P. K., and DESHPANDE, V. V. 1999. Diversity in inhibitors of trypsin and Helicoverpa armigera gut proteinases in chickpea (Cicer arietinum) and its wild relatives. Theor. Appl. Genet. 99: 3-4.
SCHOONHOVEN, L. M., JERMY, T., and VAN LOON, J. J. A. 1998. Insect-Plant Biology from Physiology to Evolution. Chapman & Hall, London.
SIMMONDS, M. S. J., and BLANEY, W. M. 1990. Gustatory codes in lepidopterous larvae. Symp. Biol. Hung. 39:17-27.
SIMMONDS, M. S. J., BLANEY, W. M., and FELLOWS, L. E. 1990. Behavioural and electrophysiological study of antifeedant mechanisms associated with polyhydroxyalkaloids. J. Chem. Ecol. 16:3167-3196.
SIMMONDS, M. S. J., BLANEY, W. M., and SCHOONHOVEN, L. M. 1992. Effects of larval diet and larval age on the responsiveness of taste neurones of Spodoptera littoralis to sucrose. J. Insect Physiol. 38:249-257.
STEVENSON, P. C., and HAWARE, M. P. 1999. Maackiain in Cicer bijugum associated with resistance to Botrytis Grey Mould. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 27:761-767.
STEVENSON, P. C., and VEITCH, N. C. 1996. Isoflavenes from the roots of Cicer judaicum. Phytochemistry 43:695-700.
STEVENSON, P. C., and VEITCH, N. C. 1998a. A 2-arylbenzofuran from roots of Cicer bijugum associated with fusarium wilt resistance. Phytochemistry 48:947-951.
STEVENSON, P. C., and VEITCH. N. C. 1998b. The distribution of isoflavonoids in Cicer. Phytochemistry 48:995-1001.
STEVENSON, P. C., TURNER, H. C., and HAWARE M. P. 1997. Phytoalexin accumulation in the roots of chickpea seedlings associated with resistance to fusarium wilt. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 50:167-178.
VEITCH, N. C., and STEVENSON, P. C. 1997. 2-Methoxyjudaicin, an isoflavene from the roots of Cicer bijugum. Phytochemistry 44:1587-1589.
YOSHIDA, M., COWGILL, S. E., and WIGHTMAN, J. A. 1995. Mechanism of resistance to Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae) in chickpea-role of oxalic-acid in leaf exudates as an antibiotic factor. J. Econ. Entomol. 88:1783-1786.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simmonds, M.S.J., Stevenson, P.C. Effects of Isoflavonoids from Cicer on Larvae of Heliocoverpa armigera. J Chem Ecol 27, 965–977 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010339104206
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010339104206