Abstract
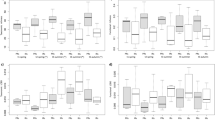
Spatial distribution and temporal variations of fish communities in a channelized portion of the Vltava River (Central Europe) were investigated from May to October 1992. Fish abundance and species number were collected monthly during diel samples in the main channel and a large oxbow. To determine differences in fish communities we chose the low-flow period when maximal differences in physical environment between habitats are expected. Fish community patterns from the main channel and oxbow differed only in abundance of ecological groups; the main channel had higher abundance of rheophilic species, whereas eurytopic species were more abundant in the oxbow. However, our analysis revealed significant differences in temporal variations between habitats. Fish abundance usually varied unpredictably over day-night periods in the main channel, whereas in the oxbow we observed a pronounced peak in fish abundance from morning to mid-afternoon. Diel changes in fish abundance in the oxbow corresponded to occurrence of low dissolved oxygen during afternoon and night-time periods. The effect of oxygen depletion induced by strong organic pollution limited the oxbow suitability for fishes. Similar habitats are usually occupied by limnophilic and phytophilic species that were absent in our samples. Our results suggested that man-induced high variability of physical environment decreased variability in fish community.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balon, E.K. 1961. Zist'ovanie dennej aktivity rýb pomocou lovu čereňom (A survey of the diel activity in fishes by means of a liftnet). Biológia (Bratislava) 16: 523–537.
Balon, E.K. 1975. Reproductive guilds of fishes: a proposal and definition. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 32: 821–864.
Balon, E.K. 1990. Epigenesis of an epigeneticist: the development of some alternative concepts on the early ontogeny and evolution of fishes. Guelph Ichthyol. Rev. 1: 1–42.
Balon, E.K., S.S. Crawford & A. Lelek. 1986. Fish communities of the upper Danube (Germany, Austria) prior to the new Rhein-Main-Donau connection. Env. Biol. Fish. 15: 243–271.
Bart, L.H., Jr. 1989. Fish habitat association in an Ozark stream. Env. Biol. Fish. 24: 173–186.
Bodensteiner, L.R. & W.M. Lewis. 1992. Role of temperature, dissolved oxygen, and backwaters in the winter survival of fresh drum, Aplodinotus grunniens, in the Mississippi River. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 49: 173–184.
Cody, R.P. & J.K. Smith. 1997. Applied statistics and the SAS programming language. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River. 437 pp.
Gelwick, F.P. 1990. Longitudinal and temporal comparisons of riffle and pool fish communities in a northeastern Oklahoma Ozark stream. Copeia 1990: 1072–1082.
Gido, B.K., D.L. Propst & M.C. Molles. 1997. Spatial and temporal variation of fish communities in secondary channels of the San Juan River, New Mexico and Utah. Env. Biol. Fish. 49: 417–434.
Greenberg, L.A., P. Svendsen & A. Harby. 1996. Availability of microhabitats and their use by brown trout, Salmo trutta, and grayling, Thymallus thymallus, in the River Vojman, Sweden. Reg. Rivers 12: 287–303.
Grossman, G.D., P.B. Moyle & J.O. Whitaker, Jr. 1982. Stochasticity in structural and functional characteristics of an Indiana stream fish community: a test of community theory. Amer. Nat. 120: 423–454.
Grossman, G.D., A. de Sostoa, M.C. Freeman & J. Lobon-Cervia. 1987. Microhabitat use in a Mediterranean riverine fish community-fishes of the upper Matarrana. Oecologia (Berlin) 73: 501–512.
Grossman, G.D., J.F. Dowd & M. Crawford. 1990. Community stability in stream fishes: a Review. Env. Manag. 5: 661–671.
Harvey, B.C. 1987. Susceptibility of young-of-the-year fishes to downstream displacement by flooding. Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 116: 851–855.
Hayes, B.D., C.P. Ferreri & W.W. Taylor. 1996. Active fish capture methods. pp. 193–218. In: R.B. Murphy & D.W. Willis (ed.) Fisheries Techniques, Amer. Fish. Soc., Bethesda.
Hubert, A.W. 1996. Passive capture techniques. pp. 157–182. In: R.B. Murphy & D.W. Willis (ed.) Fisheries Techniques, Amer. Fish. Soc., Bethesda.
Jurajda, P. 1995. Effect of channelization and regulation on fish recruitment in a floodplain river. Regul. Riv. 10: 207–215.
Kubečka, J. & A. Duncan. 1998. Diurnal changes of fish behavior in a lowland river monitored by dual-beam echosounder. Fish. Res. 35: 55–63.
Kubečka, J. & J. Vostradovský 1995. Effect of dams, regulation and pollution on fish stock in the Vltava River in Prague. Regul. Riv. 10: 93–98.
Kwak, T.J., M.J. Wiley, L.L. Osborne & R.W. Larimore. 1992. Application of diel feeding chronology to habitat suitability analysis of warmwater stream fishes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 49: 1417–1430.
Lelek, A. 1989. The Rhine River and some of its tributaries under human impact in the last two centuries. pp. 469–487. In: D.P. Dodge (ed.) Proceedings of the International Large River Symposium, Can. Spec. Publ. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 106.
Mathews, W.J., R.C. Cashner & F.P. Gelwick. 1988. Stability and persistence of fish faunas and communities in three midwestern streams. Copeia 1988: 947–957.
Mathews, W.J., C.B. Harvey & M.E. Power. 1994. Spatial and temporal patterns in the fish communities of individual pools in a midwestern stream (U.S.A). Env. Biol. Fish. 39: 381–397.
Mathews, K.R. & N.H. Berg. 1997. Rainbow trout response to water temperature and dissolved oxygen stress in two southern California streams pools. J. Fish Biol. 50: 50–67.
McCarthy, D.T. 1985. The adverse effect of channelization and their amelioration. pp. 83–97. In: J.S. Alabaster (ed.) Habitat Modification and Freshwater Fisheries, Butterwords, London.
Moyle, P.B. & B. Vondracek. 1985. Persistence and structure of the fish communities in a small California stream. Ecology 66: 1–13.
Peňáz, M., V. Baruš & M. Prokeš. 1999. Changes in structure of fish communities in a river used for energy production. Regul. Riv. 15: 169–180.
Penczak, T. & I. Koszalinska. 1993. Populations of dominant fish species in the Narew River under human impacts. Pol. Arch. Hydrobiol. 4: 59–75.
Petts, G.E. 1985. Impoundment rivers. pp. 296. In: Perspectives for Ecological Management, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Portt, C.B., E.K. Balon & D.L. Noakes. 1986. Biomass and production of fishes in natural and channelized streams. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 43: 1926–1934.
Saint-Paul, U. & G.M. Soares. 1987. Diurnal distribution and behavioral responses of fishes to extreme hypoxia in an Amazon floodplain lake. Env. Biol. Fish. 20: 91–104.
Schiemer, F. & H. Waidbacher. 1992. Strategies for conservation of Danubian fish fauna. pp. 363–382. In: P.J Boon, P. Calow & G.E. Petts (ed.) River Conservation and Management, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester.
Schlosser, J.I. 1982. Fish community structure and function along two habitat gradients in a headwater stream. Ecological Monographs 4: 395–414.
Slavík, O. 1996. Changes in abundance and diversity of fish communities in the Podbaba navigation channel on the Vltava River. Acta Universitatis Carolinae, Biologica 40: 193–202.
Slavík, O. & L. Bartoš. 1997. Effect of water temperature and pollution on young-of-the-year fishes in the regulated stretch of the River Vltava, Czech Republic. Folia Zoologica 4: 367–374.
Suthers, T.M. & J.H. Gee. 1986. Role of hypoxia in limiting diel spring and winter distribution of juvenile yellow perch in a prairie marsh. Can J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 43: 1562–1570.
Townsend, C.R. 1989. The patch dynamics concept of stream community ecology. J. N. Amer. Benthol. Soc. 8: 36–50.
Vostradovský, J. 1994. Impact of urbanization on the fish community of the River Vltava upstream and downstream of Prague, Czechoslovakia. pp. 458–466. In: I.G. Cowx (ed.) Rehabilitation of Freshwater Fisheries, Fishing News Books, Blackwell.
Watkins, M.S., S. Doherty & G.H. Copp. 1997. Microhabitat use by 0+ and older fishes in a small English chalk stream. J. Fish Biol. 50: 1010–1024.
Yount, J.D. & G.J. Niemi. 1990. Recovery of lotic communities and ecosystems from disturbance - a narrative review of case studies. Env. Manag. 14: 547–570.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slavík, O., Bartoš, L. Spatial Distribution and Temporal Variance of Fish Communities in the Channelized and Regulated Vltava River (Central Europe). Environmental Biology of Fishes 61, 47–55 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011089026140
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011089026140