Abstract
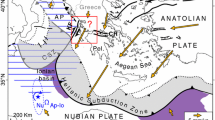
The Wadi Araba Valley is a morphotectonic depression along part of theDead Sea Transform (DST) plate boundary that separates the Arabian plateon the east from the Sinai subplate on the west. The Wadi Araba fault(WAF) is the main strike-slip faults one of between the Gulf of Aqaba and the E-Wtrending Khunayzira (Amatzayahu) fault that bounds the southern end ofthe Dead Sea. Just south of the Dead Sea, the WAF cuts across severalgenerations of alluvial fans that formed on tributaries to the Wadi Dahalafter the regression of Late Pleistocene Lake Lisan ca. 15 ka. Geomorphicand stratigraphic evidence of active faulting, including left-laterally offsetstream channels and alluvial-fan surfaces, yielded fault slip-rate data for thenorthern segment of WAF. Typical cumulative displacements of 54 m,39 m, and 22.5 m of stream channels and alluvial-fan surfaces acrossthe fault were measured from detailed geologic and topographic mapping.The 54 m offset of the oldest alluvial-fan surface (Q f1 ) occurredafter the final lowering of Lake Lisan (16–15 ka) and before 11 ka yieldinga slip-rate range of 3.4 mm/yr to 4.9 mm/yr. Based on radiocarbonages of charcoal and landsnail shell samples from the buried Q f2 alluvial-fan deposits exposed in trenches excavated across the fault, the39 m and 22.5 m offsets occurred after 9 ka and 5.8 ka, respectively. These data yield a slip-rate range between 3.9 mm/yr and 6.0 mm/yr.The small variability in these slip-rate estimates for different time periodssuggests that the northern Wadi Araba fault has maintained a relativelyconstant slip rate in the past 15 ka. We calculate an average slip rate of 4.7± 1.3 mm/yr since 15 ka based on the three separate displacementsand age estimates. Five separate offsets of 3 m were measured from gullybends and the offset of small fault-scarp alluvial fans. These displacementdata suggest a coseismic slip of 3 m in the last earthquake, or acumulative slip of 3 m in the past few earthquakes. A maximum slip of3 m correspond to a Mw 7 earthquake that ruptures about 49 km offault length. Using an average slip rate of 4.7 ± 1.3 mm/yr togetherwith a 3-m slip-per-event suggests a maximum earthquake recurrence intervalof this fault segment of 500 to 885 years.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, C.R., 1986, Seismological and paleoseismological techniques of research in active tectonics, In: Wallace, R.E. (ed.), Active Tectonics: Studies in Geophysics, Washington, D.C., Natl. Acad. Press, pp. 148–154.
Ambraseys, N., Melville, C. and Adams, R., 1994, The Seismicity of Egypt, Arabia, and the Red Sea, Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 181 pp.
Ambraseys, N. and Jackson, J.A., 1998, Faulting associated with historical and recent earthquakes in the Eastern Mediterranean region, Geophys. J. Int. 133, 390–406.
Amiran, D.H.K., Arieh, E. and Turcotte, T., 1994, Earthquakes in Israel and adjacent areas – macroseismic observations since 100 B.C.E., Israel Expl. J. 44(3-4), 260–305.
Amit, R., Harrison, J.B.J. and Enzel, Y., 1995, Use of soils and colluvial deposits in analyzing tectonic events – The southern Arava rift, Israel, Geomorph. 12, 91–107.
Amit, R., Harrison, J.B.J., Enzel, Y. and Porat, N., 1996, Soils as a tool for estimating ages of Quaternary fault scarps in a hyperarid environment – the southern Arava Valley, the Dead Sea rift, Israel, Catena 28, 21–45.
Amit, R., Zilberman, E., Porat, N. and Enzel, Y., 1999, Relief inversion in the Avrona playa as evidence of large-magnitude historical earthquakes, southern Arava Valley, Dead Sea rift, Quat. Res. 52, 76–91.
Bartov, Y., 1999, The Geology of the Lisan Formation in Massada Plain and the Lisan Peninsula, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Master thesis (in Hebrew with English abstract), 63 pp.
Begin, Z.B., Ehrlich, A. and Nathan, Y., 1974, Lake Lisan. The Pleistocene precursor of the Dead Sea, Geol. Surv. Isr. Bull. 63, 30 pp.
Begin, Z.B., Broecker, W., Buchbinder, B., Druckman, Y., Kaufman, A., Magaritz, M. and Neev, D., 1985, Dead Sea and Lake Lisan levels in the last 30,000 years, A preliminary report, Geol. Surv. Isr. Rep. GSI/29/85, 18 pp.
Bender, F., 1974, Geological map of Jordan, 1:100,000: Geological Survey of the Federal Republic of Germany, Hannover.
Ben-Menahem, A., 1979, Earthquake catalog for the Middle East (92 B. C. – 1980 A.D.), Bull. Geof. Teor. Appl. 84, 245–310.
Ben-Menahem, A. and Aboodi, E., 1981, Micro and macroseismicity of the Dead Sea rift and offcoast eastern Mediterranean, Tectonophysics 80, 199–233.
Ben-Menahem, A., 1991, Four thousand years of seismicity along the Dead Sea Rift, J. Geophy. Res. 96(B12), 20,195–20,216.
Blake, G.S., 1939, Geological Map of Palestine: Jerusalem, Survey of Palestine, scale 1:250,000.
Bowman, D., 1988, The declining but non-rejuvenating base level – the Lisan Lake, the Dead Sea area, Israel, Earth Surf. Proc. and Landforms 13, 239–249.
Bowman, D. and Gross, T., 1992, The highest stand of Lake Lisan: –150 meter below MSL, Isr. J. Earth Sci. 41, 233–237.
Bowman, D., 1995, Active surface ruptures on the northern Araba fault, the Dead Sea rift, Isr. J. Earth Sci. 44, 51–59.
Bowman, D., 1997, Geomorphology of the Dead Sea western margin, In: Niemi, T.M., Ben-Avraham, Z. and Gat, J.R. (eds), The Dead Sea – The lake and its setting, Oxford Monographs on Geology and Geophysics 36, pp. 217–225.
Clark, G.A., 1988, Some thoughts on the southern extent of the Lisan Lake as seen from the Jordan side, Bull. Am. School of Oriental Res. 272, 42–43.
Courtillot, V., Armijo, R. and Tapponnier, P., 1987, Kinematics of the Sinai triple junction and a two phase model of Arabia-Africa rifting, Geol. Soc. Spec. Pub. 28, 559–573.
Druckman, Y., Magaritz, M. and Sneh, A., 1987, The shrinking of Lake Lisan, as reflected by the diagenesis of its marginal oolitic deposits, Isr. J. Earth Sci. 36, 101–106.
El-Isa, Z.H. and Mustafa, H., 1986, Earthquake deformations in the Lisan deposits and seismotectonic implications, Geophys. J. Royal Astron. Soc. 86, 413–424.
Enzel, Y., Amit, R., Zilberman, E., Harrison, J.B.J. and Porat, N., 1996, Estimating the ages of fault scarps in the Arava, Israel, Tectonophysics 253, 305–317.
Freund, R., 1965, A model of the structural development of Israel and adjacent areas since Upper Cretaceous times, Geol. Mag. 102, 189–205.
Freund, R., Zak, I. and Garfunkel, Z., 1968, Age and rate of the sinistral movement along the Dead Sea rift, Nature 220, 253–255.
Freund, R., Garfunkel, Z., Zak, I., Goldberg, M., Derin, B. and Weissbrod, T., 1970, The shear along the Dead Sea rift, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. A. 267, 107–130.
Frumkin, A., 1997, The Holocene history of Dead Sea levels, In: Niemi, T.M., Ben-Avraham, Z. and Gat, J.R. (eds), The Dead Sea – The Lake and its Setting, Oxford Monographs on Geology and Geophysics No. 36, pp. 237–248.
Gardosh, M., Reches, Z. and Garfunkel, Z., 1990, Holocene tectonic deformation along the western margins of the Dead Sea, Tectonophysics 180, 123–137.
Garfunkel, Z. and Ben-Avraham, Z., 1996, The structure of the Dead Sea basin, Tectonophysics 266, 155–176.
Garfunkel, Z., Zak, I. and Freund, R., 1981, Active faulting in the Dead Sea rift, Tectonophysics 80, 1–26.
Garfunkel, Z., 1970, The Tectonics of the Western Margins of the Southern Arava, Ph.D. Thesis, Hebrew University, Jerusalem, 204 pp. (In Hebrew, English abstract)
Gerson, R., Grossman, S., Amit, R. and Greenbaum N., 1993, Indicators of faulting events and period of quiescence in desert alluvial fans, Earth Surf. Proc. and Landforms 18, 181–202.
Ginat, H., Enzel, Y. and Avni, Y., 1998, Translocated Plio-Pleistocene drainage systems along the Arava fault of the Dead Sea transform, Tectonophysics 284, 151–160.
Guidoboni, E. (ed.), 1994, Catalogue of Ancient Earthquake in the Mediterranean Area up to the 10 th Century, Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica, Rome, Italy.
Horowitz, A., 1992, Palynology of Arid Lands, Amsterdam, Elsevier, 546 pp.
Ibrahim, K., 1991, The Geology of the Wadi Rahma, Bulletin 15, Geological Mapping Division, Geology Directorate, Natural Resources Authority, Jordan, 122 pp.
Ibrahim, K., 1993, The Geology of the Wadi Gharandal Area, Bulletin 24, Geological Mapping Division, Geology Directorate, Natural Resources Authority, Jordan, 77 pp.
Joffe, S. and Garfunkel, Z., 1987, Plate kinematics of the circum Red Sea – a re-evaluation, Tectonophysics 141, 5–22.
Kaufman, A., 1971, U-series dating of Dead Sea basin carbonates, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 35, 1269–1281.
Kaufman, A., Yechieli, Y. and Gardosh, M., 1992, Reevaluation of the lake-sediment chronology in the Dead Sea basin, Israel, based on new 230Th/U dates, Quat. Res. 38, 292–304.
Klinger Y., 1999, Seismotectonics of the Levantine fault zone, Universite Louis Pasteur – Strasbourg I., Ph.D. dissertation (in French and English), 238 pp.
Klinger Y., Avouac, J.P., Abou Karaki, N., Dorbath, L., Bourles, D. and Reyss, J.L., 2000a, Slip rate on the Dead Sea transform in northern Araba Valley (Jordan), Geophys. J. Int. 142(3), 755–768.
Klinger Y., Avouac, J.P., Dorbath, L. and Abou Karaki, N., 2000b, Seismic behaviour of the Dead Sea fault along Araba Valley Jordan, Geophys. J. Int. 142(3), 769–782.
Leonard, G., Steinberg, D.M. and Rabinowitz, N., 1998, An indication of time-dependent seismic behavior – An assessment of paleoseismic evidence from the Arava fault, Israel, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 88(3), 767–776.
Leroi-Gourhan, A. and Darmon, F., 1987, Analyses palynologiques de sites archeologiques de Pleistocene final dans la Vallee du Jourdain, Isr. J. of Earth Sci. 36, 65–72.
Mansoor, N. and Niemi, T.M., 1999, Active oblique-slip faults across the Wadi Yutim fan complex at the head of the Gulf of Aqaba, Dead Sea Transform, Jordan, Geol. Soc. Am. Absts. with Prog. 31(7), A-377.
Marco, S., Agnon, A., Ellenblum, R., Eidelman, A., Basson, U. and Boas, A., 1997, 817-year-old walls offset sinistrally 2.1 m by the Dead Sea Transform, Israel, J. Geodyn. 24(1-4), 11–20.
Marco, S. and Agnon, A., 1995, Prehistoric earthquake deformations near Masada, Dead Sea graben, Geology 23(8), 695–698.
McCalpin, J.P., 1996, Paleoseismology, Academic Press, San Diego, 588 pp.
Neev, D. and Emery, K.O., 1967, The Dead Sea, depositional processes and environments of evaporites, Geol. Surv. Isr. Bull. 41, 147 pp.
Neev, D. and Hall, J.K., 1977, Climatic fluctuations during the Holocene as reflected by the Dead Sea levels, In: Greer, D.C. (ed.), Terminal Lakes, Int. Conf. on Desertic Terminal Lakes, Ogden Utah, 1977, Proc., pp. 53–60.
Niemi, T.M., 2000, Wadi Araba earthquake project, In: Egan, V., Bikai, P.M. and Zamora, K. (eds), ‘Archaeology in Jordan’, Am. J. Archaeology 104(3), pp. 567–568.
Niemi, T.M. and Atallah, M., 2000, Offset of the Early Islamic ruins of Qasr Tilah along the Wadi Araba fault, Dead Sea transform, Jordan (abst), Geol. Soc. Am. Absts. with Prog. 32(7), 443.
Niemi, T.M. and Smith, A.M., II, 1999, Initial results of the southeastern Wadi Araba, Jordan geoarchaeological study: Implications for shifts in late Quaternary aridity, Geoarchaeology 14(8), 791–820.
Niemi, T.M., 1997, Fluctuations of Late Pleistocene Lake Lisan in the Dead Sea Rift, In: Niemi, T.M., Ben-Avraham, Z. and Gat, J.R. (eds), The Dead Sea – The Lake and its Setting, Oxford Monographs on Geology and Geophysics No. 36, N.Y., Oxford University Press, pp. 226–236.
Poirier, J.P. and Taher, M., 1980, Historical seismicity in the Near and Middle East, north Africa and Spain from Arabic documents (VIIth – XVIII century), Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 70, 2185–2201.
Porat, N., Wintle, A.G., Amit, R. and Enzel, Y., 1996, Late Quaternary earthquake chronology from luminescence dating of colluvial and alluvial deposits of the Arava Valley, Israel, Quat. Res. 46, 107–117.
Quennell, A.M., 1956, The Geological Map of the Kingdom of Trans-Jordan, scale 1: 250,000.
Quennell, A.M., 1959, Tectonics of the Dead Sea rift, Int. Geol. Congr., 20 th , Mexico. Assoc. Serv. Geol. Afr., pp. 385–403.
Rashdan, M., 1988, The Regional Geology of the Aqaba-Wadi Araba Area, Bulletin 7, Geological Mapping Division, Geology Directorate, Natural Resources Authority, Jordan, 87 pp.
Russel, K., 1985, The earthquake chronology of Palestine and northwest Arabia from the 2nd through the mid-8th century A.D., Bull. Am. School Oriental Res. 260, 37–59.
Schramn, A., Stein, M. and Goldstein, S.L., 2000, Calibration of the 14C time scale to >40 ka by 234U – 230Th dating of Lake Lisan sediments (last glacial Dead Sea), Earth and Planet. Sci. Lett. 175, 27–40.
Schwartz, D.P. and Coppersmith, K.J., 1984, Fault behavior and characteristic earthquakes – Examples from theWasatch and San Andreas faults, J. Geophys. Res. 89, 5681–5698.
Shapira, A., 1981, Assessment of the potential earthquake risk in Israel and adjacent areas, Isr. J. Earth Sci. 30, 135–141.
Shaw, S.H., 1947, Geological Map of Southern Palestine with Explanatory Notes, Govt. Printer, Jerusalem, 42 pp., scale 1:250,000.
Shtivelman, V., Frieslander, U., Zilberman, E. and Amit, R., 1998, Mapping shallow faults at the Evrona playa site using high-resolution reflection methods, Geophysics 63, 1257–1264.
Steinitz, G., Bartov, Y. and Hunziker, J.C., 1978, K-Ar age determination of some Miocene-Pliocene basalts in Israel – their significance to the tectonics of the rift valley, Geol. Mag. 115(5), 329–340.
Stuiver, M., Reimer, P.J., Bard, E., Beck, J.W., Burr, G.S., Hughen, K.A., Kromer, B., McCormac, G.V.D., Plicht, J. and Spurk, M., 1998, INTCAL 98 radiocarbon age calibration, 24,000 – 0 cal BP, Radiocarbon 40, 1040–1083.
Tarawneh, B., 1992, The Geology of the Fifa Area, Bulletin 20, Geological Mapping Division, Geology Directorate, Natural Resources Authority, Jordan, 44 pp.
Wallace, R.E., 1970, Earthquake recurrence intervals on the San Andreas fault, California, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 81, 2875–2890.
Wells, D.L. and Coppersmith, K.J., 1994, Empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture area, and surface displacement, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 84, 974–1002.
Wetzel, R. and Morton, D.M., 1959, Contribution a la geologie de la Transjordan, Noteset Mem. Moyen Orient. 7, 95–191.
Yeats, R.S., Sieh, K. and Allen C.R., 1997, The Geology of Earthquakes, Oxford University Press, New York, 568 pp.
Yechieli, Y., Magaritz, M., Levy, Y., Weber, U., Kafri, U., Woelfli, W. and Bonani, G., 1993, Late Quaternary geological history of the Dead Sea area, Israel, Quat. Res. 39, 59–67.
Zak, I. and Freund, R., 1966, Recent strike-slip movements along the Dead Sea rift, Isr. J. Earth Sci. 15, 33–37.
Zhang, H., 1998, Late Pleistocene and Holocene Slip Rate of the Northern Wadi Araba Fault, Dead Sea Transform, Jordan, University of Missouri – Kansas City, Master's thesis, 128 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niemi, T.M., Zhang, H., Atallah, M. et al. Late Pleistocene and Holocene slip rate of the Northern Wadi Araba fault, Dead Sea Transform, Jordan. Journal of Seismology 5, 449–474 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011487912054
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011487912054