Abstract
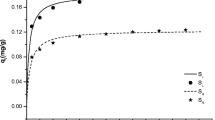
The adsorption characteristics of cadmium on bed sediments ofriver Hindon in western Uttar Pradesh (India) have been studied.The effect of various operating variables, viz., initial concentration, solution pH, sediment dose, contact time, particlesize and temperature has been studied. The optimum equilibrationtime was found to be 60 min, which was independent of initialconcentration of cadmium ions. The adsorption curves were smoothand continuous leading to saturation, suggesting the possible monolayer coverage of cadmium ions on the surface of the adsorbent. The adsorption of cadmium increased with an increasein pH. Furthermore the adsorption of cadmium increased with increasing adsorbent concentration and decreased with adsorbentparticle size. The important geochemical phases, iron and manganese oxide, support the adsorption of cadmium ions. The adsorption data were analysed using the Langmuir and Freundlichadsorption models to determine the mechanistic parameters relatedto the adsorption process. Thermodynamic parameters, viz., freeenergy change, enthalpy change and entropy change, were alsodetermined. The negative values of free energy change (ΔG°) indicated the spontaneous nature ofthe adsorption and positive values of enthalpy change (ΔG°) suggested the endothermic nature ofthe adsorption process. The intraparticle diffusion of cadmium through pores in the adsorbent was found be the main rate-limiting step.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson, A. W.: 1967, Physical Chemistry of Surfaces, 2nd Edition, Interscience Publishers, Inc., New York.
Ajmal, M., Khan, A. H., Ahmad, S. and Ahmad, A.: 1998, ‘Role of sawdust in the removal of copper (II) from industrial wastes’, Water Res. 32(10), 3085–2091.
Bajracharya, K., Barry, D. A., Vigneswaran, S. and Gupta, A. D.: 1996, ‘Heavy metal adsorption in soil: Comparision of bisolute adsorption models and laboratory experiments’, in V. P. Singh and B. Kumar (eds), Water Quality Hydrology, Kluwer Academic Publishers, the Netherlands, Vol. 3, pp. 19–26.
Banerjee, K., Cheremisinoff, P. N. and Chang, S. L.: 1997, ‘Adsorption kinetics of o-xylene by flyash’, Water Res. 31(2), 249–267.
Catena, G. C. and Bright, F. V.: 1989, ‘Thermodynamic study on the effects of β-cyclodixtrin inclusion with anilino-naphthalene sulfonates’, Analyt. Chem. 61, 905–909.
Christensen, T. H.: 1984, ‘Cadmium soil sorption at low concentrations: I. Effect of time, cadmium load, pH, and calcium’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 21, 105–114.
Delgado, M., Bigeriego, M. and Guardiola, E.: 1993, ‘Uptake of Zn, Cr, and Cd by water hyacinth’, Water Res. 27(20), 269–272.
Encyclopedia of Environmental Sciences: 1980, 2nd edn., McGraw-Hill, Newyork, 354 pp.
Fraiji, L. K., Hayer, D. M. and Werner, T. C.: 1992, ‘Static and dynamic fluorescence quenching experiments for the physical chemistry laboratory’, J. Chem. Edu. 69, 205–215.
Fu, G. and Allen, H. E.: 1992, ‘Cadmium adsorption by oxic sediments’, Water Res. 26, 225–233.
Gagnon, C., Arnac, M. and Brindle, J. R.: 1992, ‘Sorption interactions between trace metals (Cd and Ni) and phenolic substances on suspended clay minerals’, Water Res. 26, 1067–1072.
Gardiner, J.: 1974, ‘The chemistry of cadmium in natural water - II. Adsorption of cadmium on river muds and naturally occurring solids’, Water Res. 8, 157–164.
International Agency for Research on Cancer: 1976, ‘Mongraphs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risk of chemicals to man’, in Cadmium and cadmium compounds 11, 3974.
Jain, C. K. and Ali, I.: 2000, ‘Adsorption of cadmium on riverine sediments: Quantitative treatment of the large particles’, Hydrol. Process. 14, 261–270.
Jain, C. K. and Ram, D.: 1997a, ‘Adsorption of lead and zinc on bed sediments of the river Kali’, Water Res. 31(1), 154–162.
Jain, C. K. and Ram, D.: 1997b, ‘Adsorption of metal ions on bed sediments’, Hydrol. Sci. J. 42(5), 713–723.
Jain, C. K. and Sharma, M. K.: 1998, Hydro-chemical Studies on River Hindon, Technical Report, CS(AR)19, National Institute of Hydrology, Roorkee, India.
Juang, R. S., Wu, F. C. and Tseng, R. L.: 1997, ‘The ability of activated clay for the adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions’, Environ. Technol. 18, 525–531.
Koelmans, A. A. and Lijklema, L.: 1992, ‘Sorption of Tetrachlorobenzene and cadmium to sediments and suspended solids in lake Volkerak/Zoom’, Water Res. 26(3), 327–337.
Low, K. S. and Lee, C. K.: 1991, ‘Cadmium uptake by the moss calympers delesertii, besch.’, Bioresour. Technol. 38, 1–6.
Low, K. S., Lee, C. K. and Tan, S. G.: 1997, ‘Sorption of trivalent chromium from tannery waste by moss’, Environ. Technol. 18, 449–454.
Munaf, E. and Zein, R.: 1997, ‘The use of rice husk for removal of toxic metals from waste water’, Environ. Technol. 18, 359–362.
Namasivayam, C. and Ranganathan, K.: 1995, ‘Removal of Cd(II) from waste water by adsorption on waste Fe(III)/Cr(III) hydroxide’, Water Res. 29, 1737–1744.
Palheiros, B., Duarte, A. C., Oliveira, J. P. and Hall, A.: 1989, ‘The influence of pH, ionic strength and chloride concentration of the adsorption of cadmium by a sediment’, Water Sci. Technol. 21, 1873–1876.
Raji, C. and Anirudhan, T. S.: 1998, ‘Batch Cr(VI) removal by polyacrylamide grafted sawdust: Kinetics and thermodynamics’, Water Res. 32(12), 3772–3780.
Sakai, H., Kojima, Y. and Saito, K.: 1986, ‘Distribution of metals in water and sieved sediments in the Toyohira river’, Water Res. 20, 559–567.
Singh, A. K., Singh, D. P., Pandey, K. K. and Singh, V. N.: 1988, ‘Wollastonote as adsorbent for removal of Fe(II) from water’, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 42, 39–49.
Singh, D. B., Prasad, G., Rupainwar, D. C. and Singh, V. N.: 1989, ‘As(III) removal from aqueous solution by adsorption’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 42, 373–386.
Srivastava, S. K., Tyagi, R. and Pant, N.: 1989, ‘Adsorption of heavy metal ions on carbonaceous material developed from the waste slurry generated in local fertilizer plants’, Water Res. 23(9), 1161–1165.
Srivastava, S. K., Gupta, V. K. and Mohan, Dinesh: 1997, ‘Removal of lead and chromium by activated slag - A blast-furnace waste’, J. Environ. Engg., ASCE 123(5), 461–468.
Subramanian, V., Griken, R. V. and Vant D. L.: 1987, ‘Heavy metal distribution in the sediments of Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers’, Environ. Geol. Wat. Sci. 9(2), 93–103.
Vishwakarma, P. P., Yadava, K. P. and Singh, V. N.: 1989, ‘Nickel(II) removal from aqueous solutions byadsorptionon fly ash’, Pertanika 12, 357–366.
Weber, W. J. Jr. and Moris, J. C.: 1962, Advances in Water Pollution Research, Proc. 1st International Conference on Water Pollution Research, Vol. 2, p. 231, Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Weber, W. J. Jr.: 1972, Physico-Chemical Processes for Water Quality Control, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, N.Y., pp. 208–210.
Weber, W. J. Jr. and Moris, J. C.: 1963, J. Sanit. Eng. Div., ASCE, SA2, 31, cited in Faust S. D. and Aly O. M., 1987. Adsorption Processes for Water Treatment, 65-122, Butterworth, London.
Wiley, J. O. and Nelson, P. O.: 1984, ‘Cadmium adsorption by aerobic lake sediments’, J. Environ. Engg., ASCE 110(1), 226–243.
Zhang, L., Zhao, L., Yu, Y. and Chen, C.: 1998, ‘Removal of lead from aqueous solution by non-living rhizopus nigricans’, Water Res. 32(5), 1437–1444.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, C.K., Sharma, M.K. Adsorption of Cadmium on Bed Sediments of River Hindon: Adsorption Models and Kinetics. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 137, 1–19 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015530702297
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015530702297