Abstract
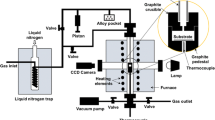
The effect of alloying elements on the wettability of TiC by commercial aluminum alloys (1010, 2024, 6061 and 7075) was investigated at 900°C using a sessile drop technique. Wetting increased in the order 6061 < 7075 < 2024 < 1010 for both, static argon or vacuum atmospheres. Alloys 1010 and 2024 wet TiC under both atmospheres, leading to contact angles in the order of 60° and less, while 7075 only wets under vacuum, with the poorest wettability being exhibited by 6061. Evaporation of Zn and Mg under vacuum conditions contributed to the rupture of the oxide film covering the aluminum drop and thereby improving wetting and spreading. Continuous and isolate Al4C3 was detected in all the cases. CuAl2 precipitation at the interface slightly decreased Al4C3 formation and increased the adhesion of 2024 to TiC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Asthana and S. N. Tewari, Compos.Manuf. 4 (1993) 3.
F. Delannay, L. Froyen and A. Deruyttere, J.Mater.Sci. 22 (1987) 1.
A. Banerji, J. K. Rohatgi and W. Reif, Metall.Tech. 38 (1984) 656.
R. Asthana, J.Mater.Sci. 33 (1998) 1959.
D. Muscat and R. A. L. Drew, J.Mater.Sci.Technol. 8 (1992) 971.
Idem., Metall.Trans. 25A (1994) 2357.
A. Contreras, M. Salazar, E. Bedolla, C. A. Leon and R. A. L. Drew, Mat.Manuf.Process 15 (2000) 163.
A. Albiter, C. A. Leon, R. A. L. Drew and E. Bedolla, Mater.Sci.Eng. 289A (2000) 109.
A. C. Ferro and B. Derby, Acta Metall.Mater. 43 (1995) 3061.
V. Laurent, D. Chatain, C. Chatillon and N. Eustathopoulos, ibid. 36 (1998) 1797.
H. Miyahara, R. Muroaka, N. Mori and K. Ogi, J.Japan Inst.Metals 59 (1995) 660.
S. K. Rhee, J.Amer.Ceram.Soc. 53 (1970) 386.
V. Y. Kononenko, G. P. Shvejkin, A. L. Sukhman, V. I. Lomotsev and B. V. Mitrofanov, Poroshk.Metall. 9 (1976) 48.
N. Froumin, N. Frage, M. Polak and M. P. Dariel, Scripta Metal. 37 (1997) 1263.
N. Eusthatopoulos, J. C. Joud, P. Desre and J. M. Hicter, J.Mater Sci. 9 (1974) 1233.
Z. Lijun, W. Jinbo, Q. Jiting and N. Oiu, in “Interfaces in Metal-Ceramics Composites, ” edited by R. Y. Lin et al. (TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1989) p. 213.
R. N. Lumley, T. B. Sercombe and G. B. Schaffer, Metall.Mater.Trans. 30A (1999) 457.
N. Froumin, N. Frage, M. Polak and M. P. Dariel, Scripta Metal. 48 (2000) 1435.
T. A. Orkasov, High Temperature, 34 (1996) 490.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leon, C.A., Lopez, V.H., Bedolla, E. et al. Wettability of TiC by commercial aluminum alloys. Journal of Materials Science 37, 3509–3514 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016523408906
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016523408906