Abstract
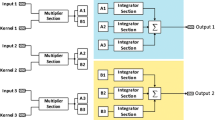
From a system level perspective, this paper presents a 128 × 128 flexible and reconfigurable Focal-Plane Analog Programmable Array Processor, which has been designed as a single chip in a 0.35 μm standard digital 1P-5M CMOS technology. The core processing array has been designed to achieve high-speed of operation and large-enough accuracy (∼7 bits) with low power consumption. The chip includes on-chip program memory to allow for the execution of complex, sequential and/or bifurcation flow image processing algorithms. It also includes the structures and circuits needed to guarantee its embedding into conventional digital hosting systems: external data interchange and control are completely digital. The chip contains close to four million transistors, 90% of them working in analog mode. The chip features up to 330 GOPs (Giga Operations per second), and uses the power supply (180 GOP/Joule) and the silicon area (3.8 GOPS/mm2) efficiently, and is able to maintain VGA processing throughputs of 100 Frames/s with about 10–20 basic image processing tasks on each frame.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saffo, P., “Sensors: The next wave of infotech innovation.” Institute for the Future, 1997 Ten-Year Forecast.
Roska, B. and Werblin, F., “Vertical interactions across ten parallel, stacked representations in the mammalian retina.” Nature (410), pp. 583-587, March 2001.
Koch, C. and Li, H. (eds.), Vision Chips, Implementing Vision Algorithms with Analog VLSI Circuits. IEEE Press, 1995.
Moini, A., Vision Chips. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2000.
Roska, T. and Rodríguez-Vázquez, A. (eds.), Towards the Visual Microprocessor. John Wiley & Sons Ltd., 2000.
Roska, T. and Chua, L. O., “The CNN universal machine: An analogic array computer.” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing 40(3), pp. 163-173, March 1993.
Domínguez-Castro, R., Espejo, S., Rodríguez-Vázquez, A., Carmona, R., Foldesy, P., Zarándy, A., Szolgay, P., Sziranyi, T. and Roska, T., “A 0.8 μm CMOS programmable mixed-signal focal-plane array processor with on-chip binary imaging and instructions storage.” IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits 32(7), pp 1013-1026, July 1997.
Paasio, A., Dawidziuk, A., Halonen, K. and Porra, V., “Minimum size 0.5 μm CMOS programmable 48 × 48 CNN test chip,” in Proc. of the 1997 European Conference on Circuit Theory and Design, Budapest, Hungary, pp. 154-156, September 1997.
Kinget, P. and Steyaert, M., “An analog parallel array processor for real-time sensor signal processing,” in Proc. of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, pp. 92-93, February 1996.
Dudek, P., “A programmable focal-plane analogue processor array.” Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology, May 2000.
Liñán, G., Espejo, S., Domínguez-Castro, R. and Rodríguez-Vázquez, A., “ACE4k: An analog I/O 64 × 64 visual microprocessor chip with 7-bit accuracy.” Int. Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications 30, pp. 89-116, March 2002.
Bernard, T., Zavidovique, B. Y. and Devos, F. J., “A programmable artificial retina.” IEEE J. of Solid State Circuits 28(7), pp. 789-798, July 1993.
Gealow, J. C. and Sodini, C. G., “A pixel-parallel image processor using logic pitch-matched to dynamic memory.” IEEE J. of Solid State Circuits 34(6), pp. 831-839, June 1999.
Ishikawa, M., Ogawa, K., Komuro, T. and Ishii, I., “A CMOS vision chip with SIMD processing element array for 1 ms image processing,” in Proc. of the ISSCC, TP. 12.2, pp. 206-207, 1999.
Yamashita, N. et al., “A 3.84 GIPS integrated memory array processor with 64 processing elements and a 2-Mb RAM.” IEEE J. of Solid State Circuits 29(11), pp. 1336-1343, November 1994.
Etienne-Cummings, R., Kevork Kalayjian, Z. and Cai, D., “A programmable focal plane MIMD image processor chip.” IEEE J. of Solid State Circuits 36(1), pp. 64-73, January 2001.
Texas Instruments on the web: http://www.ti.com.
Jahne, B., Haubecker, H. and Geibler, P. (eds.), Handbook of Computer Vision and Applications. Academic Press, London, ISBN 0-12-37977-1, 1999.
Roska, T., Kék, L., Nemes, L., Zarándy, Á. and Brendel, M., CSL-CNN Software Library-Version 7.2. Analogical and Neural Computing Laboratory, Computer and Automation Institute, Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Budapest, 1998.
Rodríguez-Vázquez, A., Domínguez-Castro, R., Medeiro, F., Huertas, J. L. and Delgado-Restituto, M., “High-resolution CMOS current comparators: Design and applications to current-mode function generation.” Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing 7, pp. 149-165, March 1995.
Espejo, S., Carmona, R., Domínguez-Castro, R. and Rodríguez-Vázquez, A., “A VLSI-oriented continuous-time CNN model.” International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications 24, pp. 341-356, May-June 1996.
Razavi, B., Principles of Data Conversion System Design. IEEE Press, New York, 1995, ISBN: 0-7803-1093-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liñán, G., Espejo, S., Domínguez-Castro, R. et al. Architectural and Basic Circuit Considerations for a Flexible 128 × 128 Mixed-Signal SIMD Vision Chip. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing 33, 179–190 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021272100265
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021272100265