Abstract
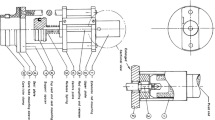
A freeze corer was developed specifically for the sampling of unconsolidated surface sediments by in-situ freezing. The new device which is presented here is designed to be used to a water depth of up to 1000 meters and was successfully tested at a depth of 200 m. The corer consists of a high pressure resistant housing with a vacuum insulated jacket for the ethanol which can be chilled by separate cooling agents, adjustable stabilizing legs, an electrical pump and a freezing wedge of 100 cm length. The freeze coring can be performed from a platform or a boat by using only a single cable to pull it up or to lower it. All other equipment is inside of the resistant housing. The core sample can easily be cut into two distinct slabs by use of the freeze-protectors on the small sides of the freeze wedge.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huttunen P. and Meriläinen J. 1978. New freezing device providing large unmixed sediment samples from lakes. Ann. Bot. Fenn. 15: 128-130.
Klee R. and Schmidt R. 1987. Eutrophication of Mondsee (Upper Austria) as indicated by the diatom stratigraphy of a sediment core. Diatom Res. 2: 55-76.
Lotter A.F., Renberg I., Hanson H., Stockli R. and Sturm M. 1997. A remote controlled freeze corer for sampling unconsolidated surface sediments. Aquat. Sci. 59: 295-303.
Merkt J. 1971. ZuverlässigeAuszählungen von Jahresschichten in Seesedimenten mit Hilfe von Groβ-Dünnschliffen. Arch. Hydrobiol. 69: 145-154.
Miskimmin B.M., Curtis P.J., Schindler D.W. and Lafaut N. 1996. A new hammer-driven freeze corer. J. Paleolim. 15: 265-269.
Pachur H.-J., Denner H.-D. and Walter H. 1984. A freezing device for sampling the sediment-water interface of lakes. Catena 11: 65-70.
Renberg I. 1982. Improved methods for sampling, photographing and varve-counting of varved lake sediments. Boreas 10: 255-258.
Renberg I. and Hanson H. 1993. A pump freeze corer for recent sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 38: 1317-1321.
Shapiro J. 1958. The core-freezer-a new sampler for lake sediments. Ecology 39: 758.
Verschuren D. 2000. Freeze coring soft sediments in tropical lakes. J. Paleolim. 24: 361-365.
Wright H.E. 1980. Coring of soft lake sediments. Boreas 9: 107-114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulbe, T., Niederreiter, R. Freeze coring of soft surface sediments at a water depth of several hundred meters. Journal of Paleolimnology 29, 257–263 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023209632092
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023209632092