Abstract
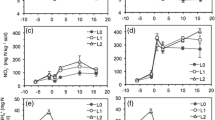
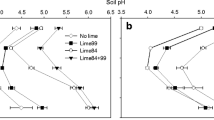
The effect of liming (3.45 and 8.75 t ha-1 dolomite; 16 yr after application) on the biodegradation of three low molecular weight organic acids (citrate, oxalate and propionate) in forest soils was investigated. The concentration of organic acids in the soil solution followed the series propionate > citrate > oxalate with liming having no significant impact on soil solution concentrations (mean organic acid concentration = 8.7 ± 2.3 μM). Organic acid mineralization by the soil microbial community was rapid in surface organic horizons (mean half-life for citrate = 2–6 h), with biodegradation rate gradually declining with soil depth. Concentration-dependent biodegradation studies (0 to 350 μM) showed that the mineralization kinetics generally conformed well to a single Michaelis–Menten equation with Vmax values following the series oxalate > citrate > propionate (mean = 9.8 ± 1.0 nmol g-1 h-1) and KM values following the series oxalate = citrate > propionate (mean 168 ± 25 μM). The Vmax values declined with soil depth, which was consistent with a general reduction in microbial activity down the soil profile. Liming induced a significant increase in Vmax for citrate with no change for propionate and reduction in Vmax for oxalate. The latter was probably due to adsorption and precipitation of Ca-oxalate making it unavailable for microbial uptake. The higher adsorption/precipitation capacity for oxalate in the limed soils was confirmed by adsorption isotherms. Generally, liming increased soil microbial activity by approximately 10 to 35% with calculations based on soil solution concentrations indicating that organic acid mineralization constituted approximately 3 to 15% of the total soil respiration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, T.-H.: 1998,'The influence of acid irrigation and liming on the soil microbial biomass in a Norway spruce (Picea abies [L.] K.) stand',Plant Soil 199, 117–122.
Aritovskaya, T. V. and Zykina, L. V.: 1977,' Biological factors of aluminium migration and accumulation in soils and weathering crusts', in Problems of Soil Science, Publishing Office NAUKA, Moscow, pp. 175–182.
Badalucco, L., Grego, S., Dell'Orco, S. and Nannipieri, P.: 1992,' Effect of liming on some chemical, biochemical, and microbiological properties of acid soils under spruce (Picea abies L.)', Biol.Fertil.Soils 14, 76–83.
Bååth, E.and Arnebrandt, K.: 1994,' Growth-rate and response of bacterial communities to pH in limed and ash treated forest soils', Soil Biol. Biochem. 26, 995–1001.
Boudot, J.-P.: 1992,' Relative effiency of complexed aluminium, noncrystalline Al hydroxide, allophane and imogolite in retarding the biodegradation of citric acid', Geoderma 52, 29–39.
Boudot, J.-P., Bel Hadj Brahim, A., Steiman, R. and Seigle-Murandi, F.: 1989,' Biodegradation of synthetic organo-metallic complexes of iron and aluminium with selected metal to carbon ratios', Soil Biol. Biochem. 21, 961–966.
Brynhildsen, L.and Allard, B.: 1994,' Influence of metal complexation on the metabolism of citrate by Klebsiella-oxytoca', Biometals 7, 163–169.
Coody, P.,N., Sommers, L. E. and Nelson, D. W.: 1986,' Kinetics of glucose uptake by soil microorganisms 'Soil Biol. Biochem. 18, 283–289.
Geary, R. J. and Driscoll, C. T.: 1996,' Forest soil solution: Acid/base chemistry and response to calcite treatment', Biogeochem. 32, 195–220.
Geibe, C.E., Holmström, S. J. M., van Hees, P. A. W. and Lundström, U. S.: 2003,' Impact of lime and ash applications on soil solution chemistry of an acidified podzolic soil', Water, Air, Soil Pollut. Focus 3, 77–96.
Giesler, R. and Lundström U. S.: 1993,' Soil solution chemistry – The effects of bulking soil samples and spatial variation', Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 57, 1283–1288.
van Hees, P. A. W. and Lundström, U. S.: 2000, Equilibrium models of aluminium and iron complexation with different organic acids in soil solution', Geoderma 94, 201–221.
van Hees, P. A.W., Lundström, U. S. and Giesler, R.: 2000,' Low molecular weight acids and their Al complexes in soil solution – Composition, distribution and seasonal variation in three podzolized soils', Geoderma 94, 173–200.
van Hees, P. A.W., Jones, D. L. and Godbold, D. L.: 2002,' Biodegradation of low molecular weight organic acids in forest soils', Soil Biol. Biochem. 34, 1261–1272.
Holmström, S.J.M., Riise, G., Tau Strand, L.,Geibe, C., van Hees, P. A.W., Wu, Q. and Lundström, U. S.: 2003,' Effects of lime and ash treatments on DOC fractions and low molecular weight organic acids in soil solutions of acidified podzolic soils', Water, Air, Soil Pollut. Focus 3, 97–120.
Huettl, R. F.and Zoettl, H. W.: 1993,' Liming as a mitigation tool in Germany's declining forests – reviewing results from former and recent trials', For.Ecol. Manag. 61, 325–338.
Jones, D.L.: 1998,' Organic acids in the rhizosphere – a critical review', Plant Soil 205, 25–44.
Jones, D. L. and Darrah, P. R.: 1994,' Role of root derived organic acids in the mobilization of nutrients from the rhizosphere', Plant Soil 166, 247–257.
Jones, D. L. and Edwards, A. C.: 1998, 'Influence of sorption on the biological utilization of two simple carbon substrates', Soil Biol. Biochem. 30, 1895–1902.
Jones, D. L. and Brassington, D. S.: 1998, 'Sorption of organic acids in acid soils and its implications in the rhizosphere', Eur. J. Soil Sci. 49, 447–455.
Jones, D. L., Prabowo, A. M. and Kochian, L. V.: 1996, 'Kinetics of malate transport and decomposition in acid soils and isolated bacterial populations: The effect of microorganisms on root exudation of malate under Al stress', Plant Soil 182, 239–247.
Kreutzer, K.: 1995, 'Effects of forest liming on soil processes', Plant Soil 168–169, 447–470.
Kwon, Y. M., Salinas, J. R., Durant, J. A., Nisbet, D. J. and Ricke, S. C.: 1997, 'Volatile fatty acid sensitivity of Veillonella CF3 from a continuous-flow probiotic culture', J. Food Sci. 17, pp59–67.
Lehle, E.: 1994, 'The effects of fertilization and liming on the soil ciliates (protozoa, ciliophora) of a spruce stand in the Black Forest (Southern Germany)', Arch. Protistendkd 144, 113–125.
Lohm, U., Larsson, K. and Nômmik, H.: 1984, 'Acidification and liming of coniferous forest soil: Long term effects on turnover rates of carbon and nitrogen during an incubation experiment',Soil Biol. Biochem. 16, 343–347.
Lundström, U. and Öhman, L. O.: 1990, 'Dissolution of feldspars in the presence of natural organic solutes', J. Soil Sci. 41, 359–369.
Lundström, U. S., van Breemen, N., Bain, D. C., van Hees, P. A. W., Giesler, R., Gustafsson, J.P., Ivesniemi, H., Karltun, E., Melkerud, P.-A., Olsson, M., Riise, G., Wahlberg, O, Bergelin, A., Bishop, K., Finlay, R., Jongmans, A. G., Magnusson, T., Mannerkoski, H., Nordgren, A., Nyberg, L., Starr, M. and Tau Strand, L.: 2000, 'Advances in understanding the podzolization process resulting from a multidisciplinary study of three coniferous forest soils in the Nordic Countries', Geoderma 94, 335–353.
Meiwes, K. J.: 1995, 'Application of lime and wood ash to decrease acidification of forest soils', Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 85, 143–152.
Nilsson, S. I., Andersson, S., Valeur, I., Persson, T., Bergholm, J. and Wirén, A.: 2001, 'Influence of dolomite lime on leaching and storage of C, N and S in a Spodosol under Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.)', Forest Ecol. Manag. 146, 55–73.
Nodar, R., Acea, M. J. and Carballas, T.: 1992, 'Microbiological response to Ca(OH)2 attreatments in a forest soil', FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 86, 213–219.
Prohaszka, L.: 1986, 'Antibacterial mechanism of volatile fatty-acids in the intestinal-tract of pigs against Escherichia coli', J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 33, 166–173.
Qualls, R. G. and Haines, B. L.: 1992, 'Biodegradability of dissolved organic matter in forest throughfall, soil solution and stream water', Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J 56, 578–586.
Seyferth, U.: 1998, 'Effects of soil temperature and moisture on carbon and nitrogen mineralisation in coniferous forests', Licentiate thesis No. 1, ISSN 1403–770X, Department of Ecology and Environmental Research, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Uppsala.
Smolander, A. and Mälkönen, E.: 1994, 'Microbial biomass C and N in limed soil of Norway spruce stands', Soil Biol. Biochem. 26, 503–509.
Soil Survey Staff: 1999, Soil Taxonomy, A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys, second ed., United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, Agricultural Handbook Number 436.
Vinolas, L. C., Healey, J. R. and Jones, D. L.: 2001, 'Kinetics of soil microbial uptake of amino acids', Biol. Fert. Soils 33, 67–74.
Westergaard, B., Hansen, H. C. B. and Borggaard, O. K.: 1998,'Determination of anions in soil solutions by capillary zone electrophoresis', Analyst 123, 721–724.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Hees, P.A.W., Jones, D.L. & Godbold, D.L. Biodegradation of Low Molecular Weight Organic Acids in a Limed Forest Soil. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution: Focus 3, 121–144 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024127514103
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024127514103