Abstract
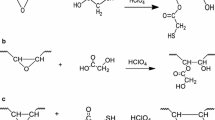
Biobased polyurethanes from soybean oil–derived polyols and polymeric diphenylmethane diisocyanate (pMDI) are prepared and their thermomechanical properties are studied and evaluated. The cross-linked biobased polyurethanes being prepared from soy phosphate ester polyols with hydroxyl contents ranging from 122 to 145 mg KOH/g and pMDI within 5 min of reaction time at 150°C in absence of any catalyst show cross-linking densities ranging from 1.8 × 103 to 3.0 × 103 M/m3, whereas glass transition temperatures vary from approximately 69 to 82°C. The loss factor (tan δ) curves show single peaks for all these biobased polyurethanes, thus indicating a single-phase system. The storage moduli (G′) at 30°C range from 4 × 108 to 1.3 × 109 Pa. Upon postcure at 150°C, the thermomechanical properties can be optimized. Cross-link densities are improved significantly for hydroxyl content of 139 and 145 mg KOH/g at curing time of 24 h. Similarly, glass transition temperature (Tg) and storage moduli around and after Tg are increased. Meanwhile, tan δ intensities decrease as result of restricted chain mobility. Longer exposure time (∼24 h) induces thermal degradation, as evidenced by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The dynamic mechanical (DMA) analysis shows that postcure at 100°C for times exceeding 24 h also leads to improved properties. However, cross-linking densities are lower compared to postcure carried out at 150°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
D. L. Kaplan (1998) Biopolymers from Renewable Resources, Springer, New York.
G. S. Kumar (1987) Biodegradable Polymers: Prospects and Progress, Marcel Dekker, New York.
S. N. Khot, J. J. Lascala, E. Can, S. S. Morye, G. I. Williams, G. R. Palmese, S. H. Kusefoglu, and R. P. Wool (2001) J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 82, 703–723.
M. W. Formo (1982) in D. Swern Ed., Bailey's Industrial Oil and Fat Products, Vol. 2, 4th ed., Wiley, New York.
J. H. Saunders and K. C. Frisch (1962) Polyurethanes: Chemistry and Technology, Interscience New York, parts I and II.
M. Szycher (1999) Szycher's Handbook of Polyurethanes, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
S. A. Baser and D. V. Khakhar (1993) Cell. Polym. 12, 390–401.
E. N. Frankel and F. L. Thomas (1972) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 49, 10–14.
E. N. Frankel, U. S. Patent 3,787,459.
C. K. Lyon, V. H. Garrett, and E. N. Frankel (1974) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 51, 331–334.
Z. S. Petrovic, A. Guo, and R. Fuller, U.S. Patent 6,107,433.
A. Guo, I. Javni, and Z. Petrovic (2000) J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 77, 467–473.
A. Guo, Y.J. Cho, and Z. S. Petrovic (2000) J. Polym Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 38, 4062–4069.
K. S. Chian and L. H. Gan (1998) J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 68, 509–515.
Y. H. Hu, Y. Gao, D. N. Wang, C. P. Hu, S. Zu, L. Vanoverloop, and D. Randall (2002) J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 84, 591–597.
V. M. Mannari, Y. Guo, and J. L. Massingill ACS Polymer Preprint (2002) Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 86, 383–384.
L. E. Nielsen and R. F. Landel (1994) Mechanical Properties of Polymers and Composites, 2nd ed., Chap. 4, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Z. Petrovic, M. Ilavsky, K. Dusek, M. Vidakovic, I. Javni, and B. Banjanin (1991) J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 42, 391–398.
W. Chang, T. Baranowski, and T. Karalis (1994) J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 51, 1077–1085.
Z. Petrovic, I. Javni, and V. Divjakovic (1998) J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. 36, 221–235.
E. Kontou, G. Spathis, M. Niaounakis, and V. Kefalas (1990) Colloid Polym. Sci. 268, 636–644.
F. Li and R. C. Larock (2000) J. Appl. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 38, 2721–2738.
D. W. Schiering, J. E. Katon, L. T. Drazal, and V. B. Gupta (1987) J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 34, 2367–2375.
B. G. Min, Z. H. Stachurski, and J. H. Hodgkin (1993) Polymer 34, 4908–4912.
K. Ueberreiter and G. Kanig (1950) J. Chem. Phys. 18, 399–406.
O. Persenaire, M. Alexandre, P. Degée, P. Dubois (2001) Biomacromolecules 2, 288–294.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dwan'Isa, JP.L., Mohanty, A.K., Misra, M. et al. Novel Biobased Polyurethanes Synthesized from Soybean Phosphate Ester Polyols: Thermomechanical Properties Evaluations. Journal of Polymers and the Environment 11, 161–168 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026004431534
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026004431534