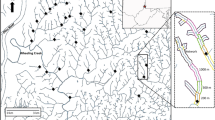
Abstract
We examined biotic and physiochemical responses in urbanized Anchorage, Alaska, to the percent of impervious area within stream basins, as determined by high-resolution IKONOS satellite imagery and aerial photography. Eighteen of the 86 variables examined, including riparian and instream habitat, macroinvertebrate communities, and water/sediment chemistry, were significantly correlated with percent impervious area. Variables related to channel condition, instream substrate, water chemistry, and residential and transportation right-of-way land uses were identified by principal components analysis as significant factors separating site groups. Detrended canonical correspondence analysis indicated that the macroinvertebrate communities responded to an urbanization gradient closely paralleling the percent of impervious area within the subbasin. A sliding regression analysis of variables significantly correlated with percent impervious area revealed 8 variables exhibiting threshold responses that correspond to a mean of 4.4 – 5.8% impervious area, much lower than mean values reported in other, similar investigations. As contributing factors to a subbasin's impervious area, storm drains and roads appeared to be important elements influencing the degradation of water quality with respect to the biota.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, C. L., P. J. Boison & P. C. Patton, 1982. Sawmill Brook: an example of rapid geomorphic change related to urbanization. J. Geol. 90: 155- 166.
Arnold, C. L. & C. J. Gibbons, 1996. Impervious surface coverage - The emergence of a key environmental indicator. J. am. Plan. Assoc. 62: 243- 258.
Baines, S. B., N. S. Fisher & R. Stewart, 2002. Assimilation and retention of selenium and other trace elements from crustacean food by juvenile striped bass (Morone saxatilis). Limnol. Oceanogr. 47: 646- 655.
Barbour, M. T., G. L. Nelson, B. D. Snyder & J. B. Stribling, 1999. Rapid bioassessment protocols for use in streams and wadeable rivers - Periphyton, benthic macroinvertebrates, and fish (2nd edn). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency EPA 841-B-99–002.
Besser, J. M., W. G. Brumbaugh, T. W. May, S. E. Church & B. A. Kimball, 2001. Bioavailability of metals in stream food webs and hazards to brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) in theUpper Animas River Watershed, Colorado. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 40: 48- 59.
Booth, D. B., 1991. Urbanization and the natural drainage system— Impacts, solutions, and prognoses. Northwest Environ. J. 7: 93- 118.
Booth, D. B. & C. R. Jackson, 1997. Urbanization of aquatic systems: Degradation thresholds, stormwater detection, and the limits of mitigation. J. am. Wat. Resour. Assoc. 33: 1077- 1090.
Brabets, T. P., G. L. Nelson, J. M. Dorava & A. M. Milner, 1999. Water-quality assessment of the Cook Inlet Basin, Alaska - Environmental Setting. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 99- 4025: 65 pp.
Canadian Council of Ministers for the Environment, 1999. Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life - Summary tables, in Canadian environmental quality guidelines, 1999: Winnipeg, Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment.
Crowther, R. A. & H. B. N. Hynes, 1977. The effect of road deicing salt on the drift of stream benthos. Environ. Poll. 14: 113- 126.
Cuffney, T. F., M. E. Gurtz & M. R. Meador, 1993. Methods for collecting benthic invertebrate samples as part of the National Water-Quality Assessment Program. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 93- 406: 66 pp.
Deering, D.W., J.W. Rouse, R. H. Haas & J. A Schell, 1975. Measuring forage production of grazing units from Landsat MSS data. Proceedings, 10th International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment 2: 1169- 1178.
Dinicola, R. S., 1989. Characterization and simulation of rainfallrunoff relations for headwater basins in western King and Snohomish Counties, Washington State. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 89- 4052: 52 pp.
Fitzpatrick, F. A., I. R. Waite, P. J. D Arconte, M. R. Meador, M. A. Maupin & M. E. Gurtz, 1998. Revised methods for characterizing stream habitat in the NationalWater-Quality Assessment Program. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 98- 4052: 67 pp.
Frenzel, S. A., 2000. Selected organic compounds and trace elements in streambed sediments and fish tissues, Cook Inlet Basin, 130 Alaska. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 00-4004: 39 pp.
Furniss, M. J., T. D. Roelofs & C. S. Lee, 1991. Road construction and maintenance. In Meehan, W. R. (ed.), Influences of Forest and Rangeland Management on Salmonid Fishes and their Habitats. American Fisheries Society Special Publication 19, Bethesda (MD): 297- 323.
Garie, H. L. & A. McIntosh, 1986. Distribution of benthic macroinvertebrates in a stream exposed to urban runoff. Wat. Res. Bull. 22: 447- 451.
Gauch, H. G., Jr., 1982. Multivariate Analysis in Community Ecology. Cambridge University Press, New York: 298 pp.
Gilliom, R. J., D. K. Mueller & L. H. Nowell, 1998. Methods for comparing water-quality conditions among National Water-Quality Assessment study units, 1992- 95. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 97- 589: 54 p.
Glass, R. L., 1999. Water-quality assessment of the Cook Inlet basin, Alaska - Summary of data through 1997. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 99- 4116: 110 p.
Hilsenhoff, W. L. 1988. Rapid field assessment of organic pollution with a family-level biotic index. J. n. am. Benthol. Soc. 7: 65- 68.
Jones, R. C. & C. C. Clark, 1987. Impact of watershed urbanization on stream insect communities. Wat. Res. Bull.23: 1047- 1055.
Kearns, B. L. & J. R. Karr, 1994. A benthic index of biotic integrity (B-IBI) for rivers of the Tennessee Valley. Ecol. Appl. 4: 768- 785.
Klein, R. D., 1979. Urbanization and stream quality impairment. Wat. Res. Bull. 15: 948- 963.
Koryak, M., L. J. Stafford, R. J. Reilly & P. M. Magnuson, 2001. Highway deicing salt runoff events and major ion concentrations along a small urban stream. J. Freshwat. Ecol. 16: 125- 134.
Lemly, A. D., 1995. A protocol for aquatic hazard assessment of selenium. J. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 32: 280- 288.
May, C. W., R. R. Horner, J. R. Karr, B. W. Mar & E. B. Welch, 1997. Effects of urbanization on small streams in the Puget Sound Lowland Ecoregion. Watershed Protection Techniques 2: 483- 494.
McMahon, G. & T. F. Cuffney, 2000. Quantifying urban intensity in drainage basins for assessing stream ecological conditions. J. am. Wat. Resour. Ass. 36: 1247- 1261.
Milner, A. M. & M. W. Oswood, 2000. Urbanization gradients in streams of Anchorage, Alaska: a comparison of multivariate and multimetric approaches to classification. Hydrobiologia 422/423: 209- 223.
Moulton, S. R., II, J. L. Carter, S. A. Grotheer, T. F. Cuffney & T. M. Short, 2000. Methods of analysis by the U.S. Geological Survey National Water Quality Laboratory - processing, taxonomy, and quality control of benthic macroinvertebrate samples. U.S. Geological Survey, Open-File Report 00- 212: 49 pp.
MVSP, 1999. Multivariate Statistical Package, Version 3.1. Kovach Computing Services, Pentraeth, Wales, U.K.
Ourso, R. T., 2001. Effects of urbanization on benthic macroinvertebrate communities in streams, Anchorage, Alaska. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 01-4278: 38 p.
Paul, M. J. & J. L. Meyer, 2001. Streams in the urban landscape. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. (Palo Alto) 32: 333- 365.
Pizzuto, J. E., W. C. Hession & M. McBride, 2000. Comparing gravel-bed rivers in paired urban and rural catchments of southeastern Pennsylvania. Geology 28: 79- 82.
Porcella, D. B. & D. L. Sorensen, 1980. Characteristics of non-point source urban runoff and its effects on stream ecosystems. EPA-600/3-80-032, Corvallis, Oregon: 99 pp.
Roth, N. E., J. D. Allan & D. L. Erickson, 1996. Landscape in-fluences on stream biotic integrity assessed at multiple spatial scales. Landscape Ecol. 11: 141- 156.
Schueler, T., 1994. The importance of imperviousness. Watershed Protection Techniques 1: 100- 111.
Schueler, T., 1995. The architecture of urban stream buffers. Watershed Protection Techniques 1: 159- 163.
Shaw, D. C. & K. Bible, 1996. An overview of forest canopy ecosystem functions with reference to urban and riparian systems. Northwest Sci. 70: 1- 6.
Shelton, L. R., 1994. Field guide for collecting and processing stream-water samples for the National Water-Quality Assessment Program. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 94- 455: 42 pp.
Shelton, L. R. & P. D. Capel, 1994. Guidelines for collecting and processing samples of stream bed sediment for analysis of trace elements and organic contaminants for the National Water-Quality Assessment Program. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 94- 458: 20 pp.
Shutes, R. B. E., 1984. Influence of surface runoff on the macroinvertebrate fauna of an urban stream. Sci. Tot. Environ. 33: 271- 282.
Sloane-Richey, J., M. A. Perkins & K. W. Malueg, 1981. The effects of urbanization and stormwater runoff on the food quality of two salmonid streams. Verh. int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. 21: 812- 818.
StatSoft, Inc., 2001. STATISTICA, data analysis software system, version 6. http://www.statsoft.com.
Sutherland, R. A., 2000. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ. Geol. 39: 611- 627.
Sutherland, R. A. & C. A. Tolosa, 2001. Variation in total and extractable elements with distance from roads in an urban watershed, Honolulu, Hawaii. Wat. Air Soil Poll. 127: 315- 338.
Turer, D., J. B. Maynard & J. J. Sansalone, 2001. Heavy metal contamination in soils of urban highways: comparison between runoff and soil concentrations at Cincinnati, Ohio. Wat. Air Soil Poll. 132: 293- 314.
Vannote, R. L., G.W. Minshall, K.W. Cummins, J. R. Sedel & C. E. Cushing, 1980. The river continuum concept. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 37: 130- 137.
Wang, L., J. Lyons, P. Kanehl, R. Bannerman & E. Emmons, 2000. Watershed urbanization and changes in fish communities in southeastern Wisconsin streams. J. am. Wat. Resour. Assoc. 36: 1173- 1189.
Waters, T. F., 1995. Sediment in streams: sources, biological effects and control. American Fisheries Society Monographs 7:251 pp.
Wear, D. N., M. G. Turner & R. J. Naiman, 1998. Land cover along an urban-rural gradient: implications for water quality. Ecol. Appl. 8: 619- 630.
Whiting, E. R. & H. F. Clifford, 1983. Invertebrates and urban runoff in a small northern stream, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. Hydrobiologia 102: 73- 80.
Winter, J. G. & H. C. Duthie, 1998. Effects of urbanization on water quality, periphyton and invertebrate communities in a southern Ontario stream. Can. Wat. Res. J. 23: 245- 257.
Zar, J. H., 1996. Biostatistical Analysis. Prentice Hall, New Jersey: 662 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ourso, R.T., Frenzel, S.A. Identification of linear and threshold responses in streams along a gradient of urbanization in Anchorage, Alaska* . Hydrobiologia 501, 117–131 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026211808745
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026211808745