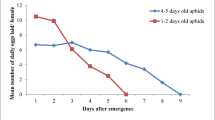
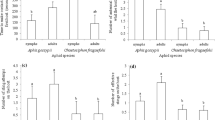
Abstract
Lipaphis erysimi (Kaltenbach) is a specialist crucifer feeding aphid and Myzus persicae (Sulzer) is a generalist feeding aphid. The foraging behavior of Diaeretiella rapae (McIntosh), a parasitoid with the ability to parasitize both of these species, was assessed using a series of attack rate and success bioassays, with turnip, Brassica rapa var rapifera, as the host plant. The attack rate of D. rapae was significantly greater on L. erysimi than on M. persicae when aphids were feeding on turnip leaf discs in Petri dishes, irrespective of the aphid species upon which the parasitoids were originally reared. Attack rate bioassays with leaf discs absent, using both satiated and starved aphids, revealed that background chemistry and internal aphid chemistry may have small effects on attack rate. Excision of D. rapae pupae from mummy cases and subsequent use of the fully developed adults in attack rate bioassays showed that cues received by D. rapae at the time of adult emergence provide cues that prime D. rapae to attack L. erysimi at a greater rate than M. persicae. However, the relative success of D. rapae on these two aphid species, in terms of the percentage of attacks resulting in a successful adult parasitoid, was not significantly different.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bones, A. M. and Rossiter, J. T. 1996. The myrosinase-glucosinolate system, its organisation and biochemistry. Physiol.Plant. 97:194-208.
Bradburne, R. P. and Mithen, R. 2000. Glucosinolate genetics and the attraction of the aphid parasitoid Diaeretiella rapae to Brassica. Proc.R.Soc.Lond.B 267:89-95.
Dawson, G. W., Griffiths, D. C., Pickett, J. A., Wadhams, L. J., and Woodcock, C. M. 1987. Plant-derived synergists of alarm pheromone from turnip aphid, Lipaphis (Hyadaphis) erysimi (Homoptera, Aphididae). J.Chem.Ecol. 13:1663-1671.
Dawson, G. W., Griffiths, D. C., Pickett, J. A., and Woodcock, C. M. 1983. Decreased response to alarm pheromone by insecticide-resistant aphids. Naturwissenschaften 70:254-255.
Jones, A. M. E., Bridges, M., Bones, A. M., Cole, R., and Rossiter, J. T. 2001. Purification and characterisation of a non-plant myrosinase from the cabbage aphid Brevicoryne brassicae (L. ). Insect Biochem.Mol.Biol. 31:1-5.
Larsen, P. O. 1981. Glucosinolates, pp. 501-525, in P. K. Stumpf and E. E. Conn (eds. ). The Biochemistry of Plants. Vol. 7. Academic Press, New York.
Macgibbon, D. B. and Beuzenberg, E. J. 1978. Location of glucosinolase in Brevicoryne brassicae and Lipaphis erysimi (Aphididae). N.Z.J.Sci. 21:389-392.
Pennacchio, F., Digilio, M. C., Tremblay, E., and Tranfaglia, A. 1994. Host recognition and acceptance behaviour in two aphid parasitoid species: Aphidius ervi and Aphidius microlophii (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Bull.Entomol.Res. 84:57-64.
Pike, K. S., Stary, P., Miller, T., Allison, D., Graf, G., Boydston, L., Miller, R., and Gillespie, R. 1999. Host range and habitats of the aphid parasitoid Diaeretiella rapae (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) in Washington State. Environ.Entomol. 28:61-71.
Poulton, J. E. and Moller, B. L. 1993. Glucosinolates, pp. 209-237, in J. P. Lea (ed. ). Methods in Plant Biochemistry. Vol. 9. Academic Press, London.
Storeck, A., Poppy, G. M., Van Emden, H. F., and Powell, W. 2000. The role of plant chemical cues in determining host preferences in the generalist parasitoid Aphidius colemani. Entomol.Exp.Appl. 97:41-46.
Van Emden, H. F., Sponagl, B., Wagner, E., Baker, T., Ganguly, S., and Douloumpaka, S. 1996. Hopkins' "host selection principle," another nail in its coffin. Phys.Ent. 21:325-328.
Vinson, S. B. 1985. The behaviour of parasitoids, pp. 417-469, in G. A. Kerkut and L. I. Gilbert (eds. ). Comprehensive Insect Physiology Biochemistry and Pharmacology. Vol. 9. Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK.
Weber, G., Oswald, S., and Zollner, U. 1986. Suitability of rape cultivars with different glucosino-late content for Brevicoryne brassicae (L. ) and Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J.Plant Dis.Prot. 93:113-124
Wilson, G. B. and Lambdin, P. L. 1987. Suitability of Brevicoryne brassicae and Myzus persicae (Homoptera: Aphididae) as hosts of Diaeretiella rapae (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae). Ent.News. 98:140-146.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blande, J.D., Pickett, J.A. & Poppy, G.M. Attack Rate and Success of the Parasitoid Diaeretiella rapae on Specialist and Generalist Feeding Aphids. J Chem Ecol 30, 1781–1795 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOEC.0000042401.52088.54
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOEC.0000042401.52088.54