Abstract
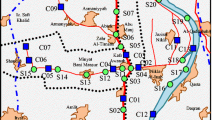
Nine stream sites in the Blackfoot River watershed in southeastern Idaho were sampled in September 2000 for water, surficial sediment, aquatic plants, aquatic invertebrates, and fish. Selenium was measured in these aquatic ecosystem components, and a hazard assessment was performed on the data. Water quality characteristics such as pH, hardness, and specific conductance were relatively uniform among the nine sites examined. Selenium was elevated in water, sediment, aquatic plants, aquatic invertebrates, and fish from several sites suggesting deposition in sediments and food web cycling through plants and invertebrates. Selenium was elevated to concentrations of concern in water at eight sites (>5 μg/L), sediment at three sites (>2 μg/g), aquatic plants at four sites (>4 μg/g), aquatic invertebrates at five sites (>3 μg/g), and fish at seven sites (>4 μg/g in whole body). The hazard assessment of selenium in the aquatic environment suggested low hazard at Sheep Creek, moderate hazard at Trail Creek, upper Slug Creek, lower Slug Creek, and lower Blackfoot River, and high hazard at Angus Creek, upper East Mill Creek, lower East Mill Creek, and Dry Valley Creek. The results of this study are consistent with results of a previous investigation and indicate that selenium concentrations from the phosphate mining area of southeastern Idaho were sufficiently elevated in several ecosystem components to cause adverse effects to aquatic resources in the Blackfoot River watershed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, W.J.: 1976, ‘The Toxicity and Residue Dynamics of Selenium in Fish and Aquatic Invertebrates’, Ph.D. Dissertation, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, USA, 109 pp.
APHA et al. (American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Environment Federation): 1995, ‘Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater’, 19th Edn., American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, USA.
ATI (Analytical Technology Incorporated) Orion: 1994), Model 9346 Nitrite Electrode Instruction Manual, Analytical Technology Incorporated, Boston, MA, USA, 44 pp.
Barnhart, R.A.: 1957, ‘Chemical Factors Affecting the Survival of Game Fish in a Western Colorado Reservoir’, Master's Thesis, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 114 pp.
Barnum, D.A. and Gilmer, D.S.: 1988, ‘Selenium Levels in Biota from Irrigation Drainwater Impoundments in the San Joaquin Valley, California’, Lake Reservoir Manage. 4, 181–186.
Besser, J.M Giesy, J.P., Brown, R.W., Buell, J.M. and Dawson, G.A.: 1996, ‘Selenium Bioaccumulation and Hazards in a Fish Community Affected by Coal Fly Ash Effluent’, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 35, 7–15.
Bryson, W.T., Garrett, W.R., Mallin, M.A., MacPherson, K.A., Partin, W.E. and Woock, S.E.: 1984, Roxboro Steam Electric Plant Environmental Monitoring Studies,Vol. II, Hyco Reservoir Bioassay Studies 1982, Carolina Power and Light, New Hill, NC, USA, 84 pp.
Campbell, K.R.: 1994, ‘Concentrations of Heavy Metals Associated with Urban Runoff in Fish Living in Stormwater Treatment Ponds’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 27, 352–356.
Caribou County Sun: 1999, Toxicologist and Vet Say Dead Sheep Likely Died from Selenium, November 11, Soda Springs, ID, USA.
Conover, W.J.: 1980, Practical Nonparametric Statistics, 2nd Edn., Wiley, New York, NY, USA.
Desborough, G., DeWitt, E., Jones, J., Meier, A. and Meeker, G.: 1999, ‘Preliminary Mineralogical and Chemical Studies Related to the Potential Mobility of Selenium and Associated Elements in Phosphoria Formation Strata, Southeastern Idaho’, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 99–129, 20 pp.
Eisler, R.: 1985, ‘Selenium Hazards to Fish, Wildlife, and Invertebrates: A Synoptic Review’, Contaminant Hazard Reviews Report No. 5, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, 57 pp.
Engberg, R.A., Westcot, D.W., Delamore, M. and Holz, D.D.: 1998, ‘Federal and State Perspectives on Regulation and Remediation of Irrigation-Induced Selenium Problems’, in W.T. Frankenberger, Jr. and R.A. Engberg (eds.), Environmental Chemistry of Selenium, Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, USA, pp. 1–25.
Furr, A.K., Parkinson, T.F., Youngs, W.D., Berg, C.O., Gutenmann, W.H., Pakkala, I.S. and Lisk, D.J.: 1979, ‘Elemental Content of Aquatic Organisms Inhabiting a Pond Contaminated with Coal Fly Ash’, NY Fish Game J. 26, 154–161.
Gillespie, R.B. and Baumann, P.C.: 1986, ‘Effects of High Tissue Concentrations of Selenium on Reproduction by Bluegills’, Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 115, 208–213.
Gutenmann, W.H., Bache, C.A., Youngs, W.D. and Lisk, D.J.: 1976, ‘Selenium in Fly Ash’, Science 191, 966–967.
Hach Company: 1997, Hach Water Analysis Handbook, 3rd Edn., Hach Company, Loveland, CO, USA, 1309 pp.
Hamilton, S.J. and Lemly, A.D.: 1999, ‘Water-Sediment Controversy in Setting Environmental Standards for Selenium’, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 44, 227–235.
Hamilton, S.J.: 2002, ‘Rationale for a Tissue-Based Selenium Criterion for Aquatic Life’, Aquat. Toxicol. 57, 85–100.
Hamilton, S.J.: 2003, ‘Review of Residue-Based Selenium Toxicity Thresholds for Freshwater Fish’, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 56, 201–210.
Hamilton, S.J. and Buhl, K.J.: 2003, ‘Selenium and Other Trace Elements in Water, Sediment, Aquatic Plants, Aquatic Invertebrates, and Fish from Streams in Southeastern Idaho Near Phosphate Mining Operations: September 2000’, Final Report, U.S. Geological Survey, Yankton, SD, USA, 63 pp.
Hamilton, S.J., Buhl, K.J. and Lamothe, P.J.: 2002, ‘Selenium and Other Trace Elements in Water, Sediment, Aquatic Plants, Aquatic Invertebrates, and Fish from Streams in Southeastern Idaho Near Phosphate Mining Operations: June 2000’, Final Report, U.S. Geological Survey, Yankton, SD, USA, 70 pp.
Hamilton, S.J., Holley, K.M., Buhl, K.J., Bullard, F.A., Weston, L.K. and McDonald, S.F.: 2001a, ‘The Evaluation of Contaminant Impacts on Razorback Sucker Held in Flooded Bottomland Sites Near Grand Junction, Colorado—1996’, Final Report, U.S. Geological Survey, Yankton, SD, USA, 302 pp.
Hamilton, S.J., Holley, K.M., Buhl, K.J., Bullard, F.A., Weston, L.K. and McDonald, S.F.: 2001b, ‘The Evaluation of Contaminant Impacts on Razorback Sucker Held in Flooded Bottomland Sites Near Grand Junction, Colorado—1997’, Final Report, U.S. Geological Survey, Yankton, SD, USA, 229 pp.
Hamilton, S.J., Muth, R.T., Waddell, B. and May, T.W.: 2000, ‘Hazard Assessment of Selenium and Other Trace Elements in Wild Larval Razorback Sucker from the Green River, Utah,’ Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 45, 132–147.
Hamilton, S.J., Palmisano, A.N., Wedemeyer, G.A. and Yasutake, W.T.: 1986, ‘Impacts of Selenium on Early Life Stages and Smoltification of Fall Chinook Salmon’, Trans. N. Am. Wildl. Nat. Res. Conf. 51, 343–356.
Hamilton, S.J. and Wiedmeyer, R.H.: 1990, ‘Concentrations of Boron, Molybdenum, and Selenium in Chinook Salmon’, Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 119, 500–510.
Hermanutz, R.O., Allen, K.N., Roush, T.H. and Hedtke, S.F.: 1992, ‘Effects of Elevated Selenium Concentrations on Bluegills (Lepomis macrochirus) in Outdoor Experimental Streams’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 11, 217–224.
Herring, J.R. and Amacher, M.C.: 2001, ‘Chemical Composition of Plants Growing on the Wooley Valley Phosphate Mine Waste Pile and on Similar Rocks in Nearby Dairy Syncline, Caribou County, Southeast Idaho’, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 01–0025, Denver, CO, USA, 47 pp.
Herring, J.R., Castle, C.J., Brown, Z.A. and Briggs, P.H.: 2001, ‘Chemical Composition of Deployed and Indigenous Aquatic Bryophytes in a Seep Flowing from a Phosphate Mine Waste Pile and in the Associated Angus Creek Drainage, Caribou County, Southeast Idaho’, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 01–0026, Denver, CO, USA, 20 pp.
Herring, J.R., Grauch, R.I., Desborough, G.A., Wilson, S.A. and Tysdal, R.G.: 2000b, ‘Chemical Composition of Weathered and Less Weathered Strata of the Meade Peak Phosphatic Shale Member of the Permian Phosphoria Formation. C. Measured Sections E and F, Rasmussen Ridge, Caribou County, Idaho’, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 99–147-C, Denver, CO, USA, 35 pp.
Herring, J.R., Wilson, S.A., Stillings, L.A., Knudsen, A.C., Gunter, M.E., Tysdal, R.G., Grauch, R.I., Desborough, G.A. and Zielinski, R.A.: 2000a, ‘Chemical Composition of Weathered and Less Weathered Strata of the Meade Peak Phosphatic Shale Member of the Permian Phosphoria Formation. B. Measured sections C and D, Dry Valley, Caribou County, Idaho’, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 99–147-B, Denver, CO, USA, 33 pp.
Hilton, J.W., Hodson, P.V. and Slinger, S.J.: 1982, ‘Absorption, Distribution, Half-Life and Possible Routes of Elimination of Dietary Selenium in Juvenile Rainbow Trout (Salmo gairdneri)’, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 71C, 49–55.
Hunn, J.B., Hamilton, S.J. and Buckler, D.R.: 1987, ‘Toxicity of Sodium Selenite to Rainbow Trout Fry’, Water Res. 21, 233–238.
Kleinow, K.M. and Brooks, A.S.: 1986, ‘Selenium Compounds in the Fathead Minnow (Pimephales promelas). I. Uptake, Distribution, and Elimination of Orally Administered Selenate, Selenite and l-Selenomethionine’, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 83C, 61–69.
Lee, D.S., Gilbert, C.R., Hocutt, C.H., Jenkins, R.E., McAllister, D.E. and Stauffer, Jr., J.R.: 1980, Atlas of North American Freshwater Fishes, North Carolina State Museum of Natural History, Raliegh, NC, USA, 854 pp.
Lemly, A.D.: 1982, ‘Response of Juvenile Centrarchids to Sublethal Concentrations of Waterborne Selenium. I. Uptake, Tissue Distribution, and Retention’, Aquat. Toxicol. 2, 235–252.
Lemly, A.D.: 1985, ‘Toxicology of Selenium in a Freshwater Reservoir: Implications for Environmental Hazard Evaluation and Safety’, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 10, 314–338.
Lemly, A.D.: 1993, ‘Guidelines for Evaluating Selenium Data from Aquatic Monitoring and Assessment Studies’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 28, 83–100.
Lemly, A.D.: 1995, ‘A Protocol for Aquatic Hazard Assessment of Selenium’, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 32, 280–288.
Lemly, A.D.: 1996a, ‘Evaluation of the Hazard Quotient Method for Risk Assessment of Selenium’, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 35, 156–162.
Lemly, A.D.: 1996b, ‘Selenium in Aquatic Organisms’, in W.N. Beyer, G.H. Heinz and A.W. Redmon-Norwood (eds.), Environmental Contaminants in Wildlife—Interpreting Tissue Concentrations, CRC Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL, USA, pp. 427–445.
Lemly, A.D.: 1997, ‘Environmental Hazard of Selenium in the Animas La Plata Water Development Project’, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 37, 92–96.
Lemly, A.D.: 1999, ‘Preliminary Assessment of Selenium Hazards on Caribou National Forest, Idaho’, Report, U.S. Forest Service, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 16 pp.
Lemly, A.D. and Smith, G.J.: 1987, ‘Aquatic Cycling of Selenium: Implications for Fish and Wildlife’, Fish and Wildlife Leaflet 12, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Washington, DC, USA, 10 pp.
Maier, K.J. and Knight, A.W.: 1994, ‘Ecotoxicology of Selenium in Freshwater Systems’, Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 134, 31–48.
Maier, K.J., Nelson, C.R., Bailey, F.C., Klaine, S.J. and Knight, A.W.: 1998, ‘Accumulation of Selenium by the Aquatic Biota of a Watershed Treated with Seleniferous Fertilizer’, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 60, 409–416.
Malloy, J.C., Meade, M.L. and Olsen, E.W.: 1999, ‘Small-Scale Spatial Variation of Selenium Concentrations in Chironomid Larvae’, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 62, 122–129.
Moore, S.B., Winckel, J., Detwiler, S.J., Klasing, S.A., Gaul, P.A., Kanim, N.R., Kesser, B.E., De-Bevec, A.B., Beardsley, K. and Puckett, L.K.: 1990, Fish and Wildlife Resources and Agricultural Drainage in the San Joaquin Valley, California, Vol. 2, San Joaquin Valley Drainage Program, Sacramento, CA, USA.
Murphy, B.R., Atchison, G.J., McIntosh, A.W. and Kolar, D.J.: 1978, ‘Cadmium and Zinc Content of Fish from an Industrially Contaminated Lake’, J. Fish Biol. 13, 327–335.
MW (Montgomery Watson): 1999, ‘Final 1998 Regional Investigation Report, Southeast Idaho Phosphate Resource Area Selenium Project’, Report to Idaho Mining Association Selenium Subcom-mittee, Montgomery Watson, Steamboat Springs, CO, USA.
MW (Montgomery Watson): 2000, ‘1999 Interim Investigation Data Report, Southeast Idaho Phosphate Resource Area Selenium Project’, Report to Idaho Mining Association Selenium Subcommittee, Montgomery Watson, Steamboat Springs, CO, USA.
MW (Montgomery Watson): 2001a, ‘Draft 1999–2000 Regional Investigation Data Report for Surface Water, Sediment, and Aquatic Biota Sampling Activities, September 1999. Southeast Idaho Phosphate Resource Area Selenium Project’, Report to Idaho Mining Association Selenium Subcommittee, Montgomery Watson, Steamboat Springs, CO, USA.
MW (Montgomery Watson): 2001b, ‘Draft 1999–2000 Regional Investigation Data Report for Surface Water, Sediment and Aquatic Biota Sampling Activities, May–June 2000, Southeast Idaho Phosphate Resource Area Selenium Project’, Report to Idaho Mining Association Selenium Subcommittee, Montgomery Watson, Steamboat Springs, CO, USA.
MW (Montgomery Watson Harza): 2002, ‘Spring 2001 Area-Wide Inverstigation Data Transmittal’, Final Report to the Idaho Mining Association Selenium Committee, Montgomery Watson Harza, Bellevue, WA, USA.
Nakamoto, R.J. and Hassler, T.J.: 1992, ‘Selenium and Other Trace Elements in Bluegills from Agricultural Return Flows in the San Joaquin Valley, California’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 22, 88–98.
Ney, J.J. and Van Hassel, J.H.: 1983, ‘Sources of Variability in Accumulation of Heavy Metals by Fishes in a Roadside Stream’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 12, 701–706.
NRC (National Research Council): 1980, Recommended Daily Allowances, 9th Edn., National Research Council, Food and Nutrition Board, Committee on Dietary Allowances, National Academy Press, Washington, DC, USA, 187 pp.
Olson, O.E.: 1986, ‘Selenium Toxicity in Animals with Emphasis on Man’, J. Am. College Toxicol. 5, 45–70.
Orion Research: 1990, Model 95–12 Ammonia Electrode Instruction Manual, Orion Research Incorporated, Boston, MA, USA, 36 pp.
Orion Research: 1991, Model 93–07 Nitrate Electrode Instruction Manual, Orion Research Incorporated, Boston, MA, USA, 31 pp.
Peters, G.M., Maher, W.A., Krikowa, F., Roach, A.C., Jeswani, H.K., Barford, J.P., Gomes, V.G. and Reible, D.D.: 1999, ‘Selenium in Sediments, Pore Waters and Benthic Infauna of Lake Macquarie, New South Wales, Australia’, Mar. Environ. Res. 47, 491–508.
Piper, DZ., Skorupa, J.P., Presser, T.S., Hardy, M.A., Hamilton, S.J., Huebner, M. and Gulbrandsen, R.A.: 2000, ‘The Phosphoria Formation at the Hot Springs Mine in Southeast Idaho: A Source of Selenium and Other Trace Elements to Surface Water, Ground Water, Vegetation, and Biota’, U.S. Geological Survey Open File Report 00–050, Menlo Park, CA, USA, 73 pp.
Platts, W.S. and Martin, S.B.: 1978, ‘Hydrochemical Influences on the Fishery Within the Phosphate Mining Area of Eastern Idaho’, U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service Research Note INT-246, Intermountain Forest and Range Experiment Station, Odgen, UT, USA, 15 pp.
Presser, T.S., Sylvester, M.A. and Low, W.H.: 1994, ‘Bioaccumulation of Selenium from Natural Geologic Sources in Western States and its Potential Consequences’, Environ. Manage. 18, 423–436.
Rand, G.M. and Petrocelli, S.R. (eds.): 1985, Fundamentals of Aquatic Toxicology: Methods and Applications, Hemisphere Publishing, Washington, DC, USA, 666 pp.
Rich and Associates: 1999, ‘FMC Phosphate Mine Expansion’, Fishery Resources Technical Report, A.A. Rich and Associates, San Anselmo, CA, USA.
Saiki, M.K.: 1986, ‘Concentrations of Selenium in Aquatic Food-Chain Organisms and Fish Exposed to Agricultural Tile Drainage Water’, in A.Q. Howard (ed.), Selenium and Agricultural Drainage: Implications for San Francisco Bay and the California Environment, The Bay Institute of San Francisco, Tiburon, CA, USA, pp. 25–33.
Saiki, M.K., Jennings, M.R. and Brumbaugh, W.G.: 1993, ‘Boron, Molybdenum, and Selenium in Aquatic Food Chains from the Lower San Joaquin River and Its Tributaries, California’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 24, 307–319.
Saiki, M.K. and Lowe, T.P.: 1987, ‘Selenium in Aquatic Organisms from Subsurface Agricultural Drainage Water, San Joaquin Valley, California’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 16, 657–670.
SAS (Statistical Analysis System, Inc.): 2002, Software: Windows Version 8, SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA.
Schuler, C.A., Anthony, R.G. and Ohlendorf, H.M.: 1990, ‘Selenium in Wetlands and Waterfowl Foods at Kesterson Reservoir, California, 1984’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 19, 845–853.
Skorupa, J.P.: 1998, ‘Selenium Poisoning of Fish and Wildlife in Nature: Lessons from Twelve Real-World Examples’, in W.T. Frankenberger Jr. and R.A. Engberg (eds.), Environmental Chemistry of Selenium, Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, USA, pp. 315–354.
Sorensen, E.M.B.: 1988, ‘Selenium Accumulation, Reproductive Status, and Histopathological Changes in Environmentally Exposed Redear Sunfish’, Arch. Toxicol. 61, 324–329.
Steele, M.: 2003, ‘Vegetation High in Selenium Kills 327 Sheep at Study Site’, Caribou County Sun, June 19, Soda Springs, ID, USA.
Stephan, C.E., Mount, D.I., Hansen, D.J., Gentile, J.H., Chapman, G.A. and Brungs, W.A.: 1985, ‘Guidelines for Deriving Numerical National Water Quality Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Organisms and Their Uses’, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Report PB85–227049, Washington, DC, USA, 98 pp.
Stephens, D., Waddell, B., DuBois, K. and Peterson, E.: 1997, ‘Field Screening of Water Quality, Bottom Sediment, and Biota Associated with the Emery and Scofield Project Areas, Central Utah, 1994’, Water-Resources Investigations Report 96–4298, U.S. Geological Survey, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 39 pp.
TRC Environmental: 1999, ‘Maybe Canyon Site Investigation, Caribou National Forest, Caribou County, Idaho,’ Report to U.S. Forest Service, Soda Springs, ID, TRC Environmental Corporation, Englewood, CO and Laramie, WY, USA.
USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency): 1983, ‘Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes’, EPA 600/4–79–020, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, OH, USA.
USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency): 1987, ‘Ambient Water Quality Criteria for Selenium—1987’, EPA 440/5–87–006, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, USA.
USGS (U.S. Geological Survey): 1998, ‘Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations, Book 9, Chapters A1–A6’, National Field Manual for the Collection of Water-Quality Data, U.S. Geological Survey, Reston, VA, USA.
Wiener, J.G. and Giesy Jr., J.P.: 1979, ‘Concentrations of Cd, Cu, Mn, Pb, and Zn in Fishes in a Highly Organic Softwater Pond’, J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 36, 270–279.
Woock, S.E.: 1984, ‘Accumulation of Selenium by Golden Shiners Notemigonus crysoleucas: Hyco Reservoir N.C. Cage Study 1981–1982’, Carolina Power and Light Company, New Hill, NC, USA, 19 pp.
Zhang, Y. and Moore, J.N.: 1996, ‘Selenium Fractionation and Speciation in a Wetland System,’ Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 2613–2619.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamilton, S.J., Buhl, K.J. Selenium in Water, Sediment, Plants, Invertebrates, and Fish in the Blackfoot River Drainage. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 159, 3–34 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000049143.55199.76
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000049143.55199.76