Abstract
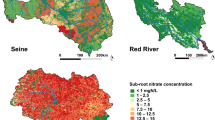
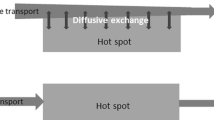
A new version of the `Riverstrahler' model has been developed for modelling riverine transfers of nitrogen from diffuse sources within the watershed, using land use data as a forcing function, together with an adjustable riparian transfer coefficient. Application of the model to the Seine river system (divided into four main sub-basins and one main branch) allows to establish a comprehensive budget of nitrogen transfers through the whole drainage network and to quantify the overall retention by riparian wetlands. According to the sub-basins, the figures indicate that 25 – 55% of the nitrogen coming from below the root-zone of agricultural land or from the aquifers is retained or eliminated before reaching surface water. The lower retention is found in areas where dense agricultural draining has been installed, thus by-passing riparian wetlands. At the scale of the Seine catchment, riparian retention represents 70 – 110 103 tonN y-1, while in-stream retention accounts for only 24–32 103 tonN y-1. The data suggest that landscape management, like restoration of efficient riparian systems in areas where they have been suppressed or by-passed, might be an efficient alternative or complimentary strategy for reducing nitrate contamination of surface water, with respect to tertiary treatment of point wastewater discharges.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AESN, 1987. Etat des eaux en 1981 Bilans et perspectives. Oise-Aisne, Le bassin de la Marne, Seine-Aval. Agence de l'Eau Seine-Normandie. Nanterre (France).
Ballif, J. L. et al., 1996. Les lysimètres en sols de craie de Chalonssur-Marne. In “Trente ans de lysimétrie en France 1960-1990”. J. C. Muller, coordinateur. INRA editions, Paris.
Benoît, M., D. Saintot & F. Gaury 1995. Mesures en parcelles d'agriculteurs des pertes en nitrates. Variabilité sous divers systèmes de culture et modélisation de la qualité de l'eau d'un bassin d'alimentation. C.R. Acad. Agric. Fr. 81: 175-188.
Behrendt, H., 1996. Inventories of point and diffuse sources and estimated nutrient loads. A comparison for different river basins in Central Europe. Wat. Sci. Techn. 33: 99-107.
Behrendt, H. & D. Opitz, 1999. Retention of nutrients in river systems: dependence on specific runoff and hydraulic load. Hydrobiologia 410: 111-122.
Belamie, R., 1980. Influence of cropping practices and hydrological factors on the variation of nitrates in the discharges from a representative basin in the Paris region. Proceedings of the Helsinki symposium IAMS IAM publ: 130.
Benneton, J. P., 1986. Eutrophisation des plans d'eau. Inventaire des principales sources de substances nutritives azotées et phosphorées. Etude bibliographique. Partie III. Trib. Cebedeau. 39: 16-34.
Billen G., C. Lancelot & M. Meybeck, 1991. N, P and Si retention along the aquatic continuum from land to ocean. In R. F. C. Mantoura, J. M. Martin & R. Wollast, (eds), Ocean margin processes in global change. Dahlem Workshop Reports, Wiley: 19-44.
Billen G., J. Garnier & P. Hanset, 1994. Modelling phytoplankton development in whole drainage networks: The 'Riverstrahler' model applied to the Seine river system. Hydrobiologia 289: 119-137.
Billen, G. & J. Garnier, 1996. Transfert et métabolisme de l'azote et du phosphore dans l'hydrosystème Seine. In C. Le Coz, B. Tassin & D. Thévenot (eds), Transfert des polluants dans les hydrosystèmes. Presses de l'Ecole Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées: 121-140.
Billen, G. & J. Garnier, 1997. The Phison River Plume: coastal eutrophication in response to changes in land use and water management in the watershed. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 13: 3-17.
Boniface, R. et al., 1996. Lysimètres en sols de Versailles. Bilan 1974-1990. In 'Trente ans de lysimétrie en France 1960-1990'. J. C. Muller, coordinateur. INRA editions, Paris.
Brion, N., 1998. Etude du processus de nitrification à l'échelle de grands réseaux hydrographiques anthropisés. Thesis. Université Libre de Bruxelles.
Chesterikoff, A., B. Garban, G. Billen & M. Poulin, 1992. Inorganic nitrogen dynamics in the River Seine downstream from Paris (France). Biogeochemistry 17: 147-164.
Fritz, M., 1994. Etude statistique sur la contamination en nitrates des cours d'eau et des nappes principales du bassin de l'Yonne et de la Seine en amont de Montereau. Mémoire de DEA, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris.
Garnier, J., G. Billen & M. Coste, 1995. Seasonal succession of diatoms and chlorophyecae in the drainage network of the River Seine: Observations and modelling. Limnol. Oceanogr. 40: 750-765.
Garnier, J., G. Billen & L. Palfner, 1999. Understanding the oxygen budget and related ecological processes in the river Mosel: the RIVERSTRAHLER approach. Hydrobiologia 410: 151-166.
Garnier, J., Leporcq, B., Sanchez, N. & Philippon, X., 1999. Biogeochemical budgets in three large reservoirs of the Seine basin (Marne, Seine & Aube reservoirs). Biogeochemistry 47: 119-146.
Haycock, N. E., G. Pinay & C. Walker, 1993. Nitrogen retention in river corridors: European perspective. Ambio 22: 340-346.
Howarth R. W., G. Billen, D. Swaney, A. Townsend, N. Jaworski, K. Lajtha, J. A. Downing, R. Elmgren, N. Caraco, T. Jordan, F. Berendse, J. Freney, V. Kudeyarov, P. Murdoch & Z. Zhao-liang, 1996. Regional nitrogen budgets and riverine N & P fluxes for the drainages to the North Atlantic ocean: natural and human influences. Biogeochemistry 35: 75-139.
IFEN, 1997. Corine Land Cover. Base de données géographiques de l'occupation du sol. Institut Français de l'Environnement. Orléans.
Jordan, T. E., D. L. Correll & D. E. Weller, 1993. Nutrient interception by a riparian forest receiving inputs from adjacent cropland. J. Envir. Qual. 22: 467-473.
Krug, A., 1993. Drainage history and land use pattern of a swedish river system. Their importance for understanding nitrogen and phosphorus load. Hydrobiologia 251: 285-296.
Lowrance, R., R. Todd, J. FaIL, O. Hendrickson, R. Leonard & L. Rasmussen, 1984. Riparian forests as nutrient filters in agricultural watersheds. BioScience 34: 374-377.
Mariotti, A., 1982. Apports de la géochimie isotopique à la connaissance du cycle de l'azote. Thesis. Université Pierre et Marie Curie.
Muxart, T. (coord), 1996. Exportation de MES et de polluants. Chap. 7: 75-124. In 'Thème Bassins versants ruraux'. Rapport PIREN-Seine 1996/1: 181pp.
Ministère de l'Agriculture et des Forêts, 1988. Recensement Général de l'Agriculture, 1988.
Peterjohn, W. T., D. L. Correll, 1984. Nutrient dynamics in an agricultural watershed: observation on the role of a riparian forest. Ecology 65: 1466-1475.
Qotbi, A., 1996. Etude de la dynamique du phytoplancton et des nutriments dans une rivière aménagée: le Lot (France). Modélisation mathématique et simulation de scénarios. Thesis. Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse (France).
Ryding, S. O. & W. Rast, 1989. The control of eutrophication of lakes and reservoirs. Man & the Biosphere Series, Jeffers J.N.R. (ed.), UNESCO, Paris: 314 pp.
Strahler, A. H., 1957. Quantitative analysis of watershed geomorphology. Geophys. Union Trans. 38: 913-920.
Thibert, S., 1996. Exportations naturelles et anthropiques des ions majeurs et des éléments nutritifs dans le bassin de la Seine. Approches méthodologiques. Thèse. Université de Paris VI.
Vought, L. B. M., J. Dahl, C. L. Pedersen & J. O. Lacoursiere, 1994. Nutrient retention in riparian ecotones. Ambio 23: 342-347.
Whitehead, P. G., E. J. Wilson & D. Butterfield, 1998. A semidistributed Integrated Nitrogen model for multiple source assessment in Catchments (INCA): Part I -model structure and process equations. Sci. Tot. Envir. 210/211: 547-558.
Whitehead, P. G., E. J. Wilson, D. Butterfield & K. Seed, 1998. A semi-distributed Integrated Nitrogen model for multiple source assessment in Catchments (INCA): Part II - application to large river basins in South Wales and eastern England. Sci. Tot. Envir. 210/211: 559-583
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Billen, G., Garnier, J. Nitrogen transfers through the Seine drainage network: a budget based on the application of the `Riverstrahler' model. Hydrobiologia 410, 139–150 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003838116725
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003838116725