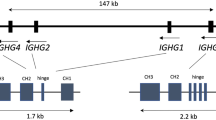
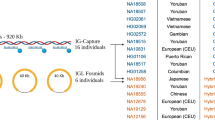
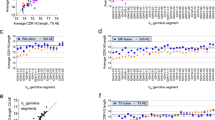
Abstract
The immunoglobulin lambda (IGL) repertoires from two unrelated human blood samples, three NOD-scid-IL2Rγnull mice engrafted with human hematopoietic stem cells and two pairs of monozygotic twin blood samples were determined by Roche 454 sequencing to generate a total of about 700 000 IGL sequences. We applied bioinformatic analysis to examine IGL repertoires wherein, surprisingly, ⩾20% of CDR-L3 peptide sequences were ‘public’ (shared across individuals); moreover, full-length IGL protein sequences (VJ recombinants) were also present in the public domain. Subtle yet significant differences in CDR-L3 nontemplated nucleotide addition, IGL V-gene family usage, and amino-acid composition distinguished the public CDR-L3 groups from the private groups. These data suggest that public CDR-L3 intervals can arise by intrinsic genetic mechanisms irrespective of different B-cell developmental milieu (human versus humanized mouse). Furthermore, the occurrence of identical public IGL protein sequences indirectly suggest the positive selection (evolutionary, somatic or both) of particular IGL chains independent of the immunoglobulin heavy chain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lai E, Wilson RK, Hood LE . Physical maps of the mouse and human immunoglobulin-like loci. Adv Immunol 1989; 46: 1–59.
Rajewsky K . Clonal selection and learning in the antibody system. Nature 1996; 381: 751–758.
Sanz I . Multiple mechanisms participate in the generation of diversity of human H chain CDR3 regions. J Immunol 1991; 147: 1720–1729.
Tonegawa S . Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature 1983; 302: 575–581.
Schroeder HW Jr, Cavacini L . Structure and function of immunoglobulins. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010; 125 (2, Supplement 2): S41–S52.
Boyd SD, Marshall EL, Merker JD, Maniar JM, Zhang LN, Sahaf B et al. Measurement and clinical monitoring of human lymphocyte clonality by massively parallel VDJ pyrosequencing. Sci Transl Med 2009; 1: 12ra23.
Glanville J, Zhai W, Berka J, Telman D, Huerta G, Mehta GR et al. Precise determination of the diversity of a combinatorial antibody library gives insight into the human immunoglobulin repertoire. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106 (48): 20216–20221.
Arnaout R, Lee W, Cahill P, Honan T, Sparrow T, Weiand M et al. High-resolution description of antibody heavy-chain repertoires in humans. PLoS One 2011; 6: e22365.
Brezinschek H, Brezinschek R, Lipsky P . Analysis of the heavy chain repertoire of human peripheral B cells using single-cell polymerase chain reaction. J Immunol 1995; 155: 190–202.
Glanville J, Kuo TC, Von Büdingen H-C, Guey L, Berka J, Sundar PD et al. Naive antibody gene-segment frequencies are heritable and unaltered by chronic lymphocyte ablation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108 (50): 20066–20071.
Schelonka RL, Tanner J, Zhuang Y, Gartland GL, Zemlin M, Schroeder HW . Categorical selection of the antibody repertoire in splenic B cells. Eur J Immunol 2007; 37: 1010–1021.
Suzuki I, Pfister L, Glas A, Nottenburg C, Milner EC . Representation of rearranged VH gene segments in the human adult antibody repertoire. J Immunol 1995; 154: 3902–3911.
Yamada M, Wasserman R, Reichard BA, Shane S, Caton AJ, Rovera G . Preferential utilization of specific immunoglobulin heavy chain diversity and joining segments in adult human peripheral blood B lymphocytes. J Exp Med 1991; 173: 395–407.
Boyd SD, Gaeta BA, Jackson KJ, Fire AZ, Marshall EL, Merker JD et al. Individual variation in the germline Ig gene repertoire inferred from variable region gene rearrangements. J Immunol 2010; 184: 6986–6992.
Cox JP, Tomlinson IM, Winter G . A directory of human germ-line V kappa segments reveals a strong bias in their usage. Eur J Immunol 1994; 24: 827–836.
Foster SJ, Brezinschek HP, Brezinschek RI, Lipsky PE . Molecular mechanisms and selective influences that shape the kappa gene repertoire of IgM+ B cells. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 1614–1627.
Jackson KJL, Wang Y, Gaeta BA, Pomat W, Siba P, Rimmer J et al. Divergent human populations show extensive shared IGK rearrangements in peripheral blood B cells. Immunogenetics 2011; 64: 3–14.
Ignatovich O, Tomlinson IM, Jones PT, Winter G . The creation of diversity in the human immunoglobulin Vλ repertoire. J Mol Biol 1997; 268: 69–77.
Bridges SL . Frequent N addition and clonal relatedness among immunoglobulin lambda light chains expressed in rheumatoid arthritis synovia and PBL, and the influence of V lambda gene segment utilization on CDR3 length. Mol Med 1998; 4: 525–553.
Ignatovich O, Tomlinson IM, Popov AV, Brüggemann M, Winter G . Dominance of intrinsic genetic factors in shaping the human immunoglobulin Vλ repertoire. J Mol Biol 1999; 294: 457–465.
Farner NL, Dörner T, Lipsky PE . Molecular mechanisms and selection influence the generation of the human VλJλ repertoire. J Immunol 1999; 162: 2137–2145.
Lee J, Monson NL, Lipsky PE . The VλJλ repertoire in human fetal spleen: evidence for positive selection and extensive receptor editing. J Immunol 2000; 165: 6322–6333.
Richl P, Stern U, Lipsky PE, Girschick HJ . The lambda gene immunoglobulin repertoire of human neonatal B cells. Mol Immunol 2008; 45: 320–327.
Frippiat JP, Williams SC, Tomlinson IM, Cook GP, Cherif D, Le Paslier D et al. Organization of the human immunoglobulin lambda light-chain locus on chromosome 22q11.2. Hum Mol Genet 1995; 4: 983–991.
Kawasaki K, Minoshima S, Nakato E, Shibuya K, Shintani A, Schmeits JL et al. One-megabase sequence analysis of the human immunoglobulin lambda gene locus. Genome Res 1997; 7: 250–261.
Kawasaki K, Minoshima S, Schooler K, Kudoh J, Asakawa S, De Jong PJ et al. The organization of the human immunoglobulin lambda gene locus. Genome Res 1995; 5: 125–135.
Williams SC, Frippiat J-P, Tomlinson IM, Ignatovich O, Lefranc M-P, Winter G . Sequence and evolution of the human germline Vλ repertoire. J Mol Biol 1996; 264: 220–232.
Saada R, Weinberger M, Shahaf G, Mehr R . Models for antigen receptor gene rearrangement: CDR3 length. Immunol Cell Biol 2007; 85: 323–332.
Ippolito GC, Hoi KH, Reddy ST, Carroll SM, Ge X, Rogosch T et al. Antibody repertoires in humanized NOD-scid-IL2Rγnull mice and human B cells reveals human-like diversification and tolerance checkpoints in the mouse. PLoS One 2012; 7: 4 e35497.
Padlan EA . Anatomy of the antibody molecule. Mol Immunol 1994; 31: 169–217.
Wilson IA, Stanfield RL . Antibody-antigen interactions: new structures and new conformational changes. Curr Opin Struct Biol 1994; 4: 857–867.
Chothia C, Lesk AM . Canonical structures for the hypervariable regions of immunoglobulins. J Mol Biol 1987; 196: 901–917.
Kuroda D, Shirai H, Kobori M, Nakamura H . Systematic classification of CDR-L3 in antibodies: implications of the light chain subtypes and the VL–VH interface. Proteins Structure Function Bioinformatics 2009; 75: 139–146.
Schoettler N, Ni D, Weigert M . B cell receptor light chain repertoires show signs of selection with differences between groups of healthy individuals and SLE patients. Mol Immunol 2012; 51: 273–282.
DeKosky BJ, Ippolito GC, Deschner RP, Lavinder JJ, Wine Y, Rawlings BM et al. High-throughput sequencing of the paired human immunoglobulin heavy and light chain repertoire. Nat Biotech 2013; 31: 166–169.
Reddy ST, Ge X, Miklos AE, Hughes RA, Kang SH, Hoi KH et al. Monoclonal antibodies isolated without screening by analyzing the variable-gene repertoire of plasma cells. Nat Biotech 2010; 28: 965–969.
Brochet X, Lefranc M-P, Giudicelli V . IMGT/V-QUEST: the highly customized and integrated system for IG and TR standardized V-J and V-D-J sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36 (Web Server issue): W503–W508.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Jaime O’Neal and Chhaya Das for their technical assistance. We also acknowledge Arvind Rajpal, Tracy Kuo and Marina Sirota for providing the Rinat–Pfizer twin sequences. We are grateful to George Georgiou for his insightful commentary and general support and collegiality.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoi, K., Ippolito, G. Intrinsic bias and public rearrangements in the human immunoglobulin Vλ light chain repertoire. Genes Immun 14, 271–276 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2013.10
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2013.10
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Profiling immunoglobulin repertoires across multiple human tissues using RNA sequencing
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Comparisons of the antibody repertoires of a humanized rodent and humans by high throughput sequencing
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Message from the new Editors-in-Chief
Genes & Immunity (2019)
-
On being the right size: antibody repertoire formation in the mouse and human
Immunogenetics (2018)
-
Reliability of immune receptor rearrangements as genetic markers for minimal residual disease monitoring
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2016)