Abstract
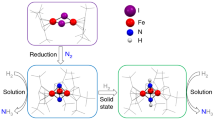
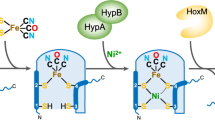
Nitrile hydratase (NHase), which catalyzes the hydration of nitriles to amides, has been used in the industrial production of acrylamide and nicotinamide. Recent studies on NHases, which are roughly classified into iron and cobalt types according to the metal involved, have clarified the photoactivation mechanism, the novel Iigand structure of the metal-binding sites, the unique mechanism of the enzyme hyper-induction, and the occurrence of an accessory gene involved in cobalt-containing NHase formation. These detailed analyses have led to the development of biotechnological applications of NHase, including biotransformation and bioremediation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kobayashi, M., Nagasawa, T., and Yamada, H. 1992. Enzymatic synthesis of acrylamide: a success story not yet over. Trends Biotechnol. 10: 402–408.
Yamada, H. and Kobayashi, M. 1996. Nitrile hydratase and its application to industrial production of acryamide. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 60: 1391–1400.
Kobayashi, M. and Shimizu, S. 1994. Versatile nitrilases: nitrile-hydrolyzing enzymes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 120: 217–224.
Komeda, H., Hori, Y., Kobayashi, M., and Shimizu, S. 1996. Transcriptional regulation of the Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1 nitA gene encoding a nitrilase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 10572–10577.
Asano, Y., Tani, Y., and Yamada, H. 1980. A new enzyme “nitrile hydratase” which degrades acetonitrile in combination with amidase. Agric. Bid. Chem. 44: 2251–2252.
Nagasawa, T. and Yamada, H. 1989. Microbial transformations of nitriles. Trends Biotechnol. 7: 153–158.
Sugiura, Y., Kuwahara, J., Nagasawa, T., and Yamada, H. 1987. Nitrile hydratase: the first non-heme iron enzyme with a typical low-spin Fe(lll)-active center. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 109: 5848–5850.
Sugiura, Y., Kuwahara, J., Nagasawa, T., and Yamada, H. 1988. Significant interaction between low-spin iron(lll) site and pyrroloquinoline quinone in active center of nitrile hydratase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 154: 522–528.
Nelson, M.J., Jin, H., Turner, I.M.Jr., Grove, G., Scarrow, R.C., Brennan, B.A., and Que L. Jr 1991. A novel iron-sulfur center in nitrile hydratase from Brevibacterium sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113: 7072–7073.
Brennan, B.A., Cummings, J.G., Chase, D.B., Turner, I.M.Jr., and Nelson, M. 1996. Raman spectroscopy of nitrile hydratase, a novel iron-sulfur enzyme. Biochemistry 35: 10068–10077.
Scarrow, R.C., Brennan, B.A., Cummings, J.G., Jin, H., Duong, D.J., Kindt, J.T., and Nelson, M.J. 1996. X-ray spectroscopy of nitrile hydratase at pH 7 and 9. Biochemistry 35: 10078–10088.
Jin, H., Turner, I.M.Jr., Nelson, M.J., Gurbiel, R.J., Doan, P.E., and Hoffman, B.M. 1993. Coordination sphere of the ferric ion in nitrile hydratase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115: 5290–5291.
Doan, P.E., Nelson, M.J., Jin, H., and Hoffman, B.M. 1996. An implicit TRIPLE effect in Mims pulsed ENDOR: a sensitive new technique for determining signs of hyper-fine couplings. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118: 7014–7015.
Mayaux, J.-F., Cerbelaud, E., Soubrier, R., Faucher, D., and Petre, D., 1990. Purification, cloning, and primary structure of an enatiomer-selective amidase from Brevibacteriumsp. strain R312: structural evidence for genetic coupling with nitrile hydratase. J. Bacteriol. 172: 6764–6773.
Nakajima, Y., Doi, T., Satoh, Y., Fujiwara, A., and Watanabe, l., 1987. Photoactivation of nitrile hydratase in Corynebacterium sp. N-774. Chemical Letters 9: 1767–1770.
Ikehata, O., Nishiyama, M., Horinouchi, S., and Beppu, T. 1989. Primary structure of a nitrile hydratase deduced from the nucleotide sequence of a Rhodococcusspecies and its expression in Escherichia coli.. Eur. J. Biochem. 181: 563–570.
Noguchi, T., Hoshino, M., Tsujimura, M., Odaka, M., Inoue, Y., and Endo, I. 1996. Resonance Raman evidence that photodissociation of nitric oxide from the non-heme iron center activates nitrile hydratase from Rhodococcussp. N-771. Biochemistry 35: 16777–16781.
Honda, J., Nagamune, T., Teratani, Y., Hirata, A., Sasabe, H., and Endo, I. 1992. Photosensitive nitrile hydratase from Rhodococcus sp. N-771; structure and function of the enzyme. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 672: 29–36.
Nagamune, T., Kurata, H., Hirata, M., Honda, J., Hirata, A., Endo, I. 1990. Photosensitive phenomena of nitrile hydratase of Rhodococcus sp. N-771. Photochem. Photobiol. 51: 87–90.
Nagamune, T., Kurata, H., Hirata, M., Honda, J., Koike, H., Ikuchi, M. et al. 1990. Purification of inactivated photoresponsive nitrile hydratase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 168: 437–142.
Honda, J., Kandori, H., Odaka, M., Nagamune, T., Shichida, Y., Sasabe, H., and Endo, l. 1994. Spectroscopic observation of the intramolecular electron transfer in the photoactivation processes of nitrile hydratase. Biochemistry 33: 3577–3583.
Tsujimura, M., Odaka, M., Nagashima, S., Yohda, M., and Endo, I. 1996. Photoreactive nitrile hydratase: the photoreaction site is located on the α subunit. J. Biochem. 119: 407–113.
Odaka, M., Noguchi, T., Nagashima, S., Yohda, M., Yabuki, S. Hoshino, M. et al. 1996. Location of the non-heme iron center on the α subunit of photoreactive nitrile hydratase from Rhodococcus sp. N-771. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 221: 146–150.
Noguchi, T., Honda, J., Nagamune, T., Sasabe, H., Inoue, Y., and Endo, I. 1995. Photosensitive nitrile hydratase intrinsically possesses nitric oxide bound to the non-heme iron center: evidence by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 358: 9–12.
Odaka, M., Fujii, K., Hoshino, M., Noguchi, T., Tsujimura, M., Nagashima, S. et al. 1997. Activity regulation of photoreactive nitrile hydratase by nitric oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119: 3785–3791.
Bonnet, D., Artaud, I., Moali, C. Petre, D., and Mansuy, I. 1997. Highly efficient control of iron-containing nitrile hydratases by stoichiometric amounts of nitric oxide and light. FEBS Lett. 409: 216–220.
Huang, W., Jia, J., Cummings, J., Nelson, M., Schneider, G., and Lindqvist, Y. 1997. Crystal structure of nitrile hydratase reveals a novel iron centre in a novel fold.Structure 5: 691–699.
Tsujimura, M., Dohmae, N., Odaka, M., Chijimatsu, M., Takio, K., Yohda, M. et al. 1997. Structure of the photoreactive iron center of the nitrile hydratase from Rhodococcus sp N-771: evidence of a novel posttranslational modification in the cysteine ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 29454–29459.
Nagashima, S., Nakasako, M., Dohmae, N., Tsujimura, M., Takio, K., Odaka, M. et al. 1998. Novel non-heme iron center of nitrile hydratase with a claw setting of oxygen atoms. Nat Struct. Biol. 5: 347–351.
Shoner, S.C., Barnhart, D., and Kovacs, J.A. 1995. A model for the low-spin, non-heme, thiolate-ligated iron site of nitrile hydratase. Inorganic Chemistry 34: 4517–4518.
Ellison, J.J., Nienstedt, A., Shoner, S.C., Barnhart, D., Cowen, J.A., and Kovacs, J.A. 1998. Reactivity of five-coordinate models for the thiolate-ligated Fe site of nitrile hydratase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120: 5691–5700.
Nagasawa, T., Takeuchi, K., and Yamada, H., 1991. Characterization of a new cobalt-containing nitrile hydratase purified from urea-induced cells of Rhodococcusrhodochrous J1. Eur. J. Biochem. 196: 581–589.
Komeda, H., Kobayashi, M. and Shimizu, S. 1996. Characterization of the gene cluster of high-molecular-mass nitrile hydratase (H-NHase) induced by its reaction product in Rhodococcus rhodochrousJ1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 4267–4272.
Komeda, H., Kobayashi, M., and Shimizu, S. 1996. A novel gene cluster including the Rhodococcus rhodochrousJ1 nhlBAgenes encoding a low molecular mass nitrile hydratase (L-NHase) induced by its reaction product. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 15796–15802.
Brennan, B.A., Alms, G., Nelson, M., Dumey, L.T., and Scarrow, R.C. 1996. Nitrile hydratase from Rhodococcus rhodochrousJ1 contains a non-corrin cobalt ion with two sulfur ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118: 9194–9195.
Payne, M.S., Wu, S., Fallon, R.D., Tudor, G., Stieglitz, B., Turner, I.M., and Nelson, M.J. 1997. A stereoselective cobalt-containing nitrile hydratase. Biochemistry 36: 5447–5454.
Kobayashi, M., Nishiyama, M., Nagasawa, T., Horinouchi, S., Beppu, T., and Yamada, H. 1991. Cloning, nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coliof two cobalt-containing nitrile hydratase genes from Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1. Biochim. Biophys. Ada 1129: 23–33.
Kobayashi, M., Suzuki, T., Fujita, T., Masuda, M., and Shimizu, S., 1995. Occurrence of enzymes involved in biosynthesis of indole-3-acetic acid from indole-3-acetoni-trile in plant-associated bacteria, Agrobacterium and Rhizobium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 714–718.
Nishiyama, M., Horinouchi, S., Kobayashi, M., Nagasawa, T., Yamada, H., and Beppu, T., 1991. Cloning and characterization of genes responsible for metabolism of nitrile compounds from Pseudomonas chlororaphis B23. j. Bacteriol. 173: 2465–2472.
Kobayashi, M., Komeda, H., Shimizu, S., Yamada, H. and Beppu, T. 1997. Characterization and distribution of IS7764 that exists in the high molecular mass nitrile hydratase gene cluster of the industrial microbe Rhodococcus rhodochrousJ1. Proceedings of the Japan Academy 73B: 104–108.
Kobayashi, M., Komeda, H., Shimizu, S., Yamada, H., and Beppu, T. et al. 1993. Amidase coupled with low-Mr-nitrile hydratase from Rhodococcus rhodochrousJ1: Sequencing and expression of the gene and purification and characterization of the gene product. Eur. J. Biochem. 217: 327–336.
Komeda, H., Kobayashi, M. and Shimizu, S. 1997. A novel transporter involved in cobalt uptake.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 36–41.
Eitinger, T., Wolfram, L., Degen, O., and Anthon, C. 1997. A Ni2+ binding motif is the basis of high affinity transport of the Alcaligenes eutrophusnickel permease. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 17139–17144.
Fu, C., Javedan, S., Moshiri, R., and Maier, R.J. 1994. Bacterial genes involved in incorporation of nickel into a hydrogenase enzyme. Proc. Watt Acad. Sci. USA 91: 5099–5103.
Mobley, H.L.T., Garner, R.M., Bauerfeind, P. 1995. Helicobacterpylori nickel-transport gene nixA:synthesis of catalytically active urease in Escherichia coliindependent of growth conditions. Mol. Microbiol. 16: 97–109.
Maeda, M., Hidaka, M., Nakamura, A., Masaki, H., and Uozumi, T., 1994. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of thermophilic Bacillus sp. strain TB-90 urease gene complex in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 176: 432–442.
Kobayashi, M., Fujiwara, Y., Goda, M., Komeda, H., and Shimizu, S., 1997. Identification of active sites in amidase: Evolutionary relationship between amide bond- and peptide bond-cleaving enzymes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 11986–11991.
Battistel, E., Bernardi, A., and Maestri, P. 1997. Enzymatic decontamination of aqueous polymer emulsions containing acrylonitrile. Biotechnology Letters 19: 131–134.
Wyatt, J.M. and Knowles, C.J. 1995. Microbial degradation of acrylonitrile waste effluents: the degradation of effluents and condensates from the manufacture of acrylonitrile. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, pp. 227–248.
Stalker, D.M., McBride, K.E., and Malyj, L.D. 1988. Herbicide resistence in trans-genic plants expressing a bacterial detoxification gene. Science 242: 41–423.
Stalker, D.M., Kiser, J.A., Baldwin, G., Coulombe, B., and Houck, C.M. 1996. Cotton weed control using the BXN(tm) system, pp. 93–105 in Herbicide-resistant crops, Duke, S.O. (ed.). Lewis Publishers, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, M., Shimizu, S. Metalloenzyme nitrile hydratase: Structure, regulation, and application to biotechnology. Nat Biotechnol 16, 733–736 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0898-733
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0898-733
This article is cited by
-
Biodegradation of sulfoxaflor and photolysis of sulfoxaflor by ultraviolet radiation
Biodegradation (2023)
-
Merging enzymes with chemocatalysis for amide bond synthesis
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Biodegradation of flonicamid by Ensifer adhaerens CGMCC 6315 and enzymatic characterization of the nitrile hydratases involved
Microbial Cell Factories (2021)
-
Synthesis, Characterization and Molecular Structure of Iron(III) Complex with Tridentate Diazene Ligand Having O,N,S Donor Set: Coexistence of Octahedral and Tetrahedral Iron(III) Sites in the Asymmetric Unit
Journal of Chemical Crystallography (2020)
-
Bioconversion of acrylonitrile using nitrile hydratase activity of Bacillus sp. APB-6
3 Biotech (2018)