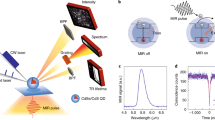
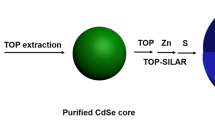
Abstract
High particle uniformity, high photoluminescence quantum yields, narrow and symmetric emission spectral lineshapes and minimal single-dot emission intermittency (known as blinking) have been recognized as universal requirements for the successful use of colloidal quantum dots in nearly all optical applications. However, synthesizing samples that simultaneously meet all these four criteria has proven challenging. Here, we report the synthesis of such high-quality CdSe–CdS core–shell quantum dots in an optimized process that maintains a slow growth rate of the shell through the use of octanethiol and cadmium oleate as precursors. In contrast with previous observations, single-dot blinking is significantly suppressed with only a relatively thin shell. Furthermore, we demonstrate the elimination of the ensemble luminescence photodarkening that is an intrinsic consequence of quantum dot blinking statistical ageing. Furthermore, the small size and high photoluminescence quantum yields of these novel quantum dots render them superior in vivo imaging agents compared with conventional quantum dots. We anticipate these quantum dots will also result in significant improvement in the performance of quantum dots in other applications such as solid-state lighting and illumination.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dahan, M. et al. Diffusion dynamics of glycine receptors revealed by single-quantum dot tracking. Science 302, 442–445 (2003).
Stroh, M. et al. Quantum dots spectrally distinguish multiple species within the tumour milieu in vivo. Nature Med. 11, 678–682 (2005).
Chan, W. C. W. et al. Luminescent quantum dots for multiplexed biological detection and imaging. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 13, 40–46 (2002).
Jaiswal, J. K. & Simon, S. M. Potentials and pitfalls of fluorescent quantum dots for biological imaging. Trends Cell Biol. 14, 497–504 (2004).
Colvin, V. L., Schlamp, M. C. & Alivisatos, A. P. Light-emitting-diodes made from cadmium selenide nanocrystals and a semiconducting polymer. Nature 370, 354–357 (1994).
Jang, H. S. et al. White light-emitting diodes with excellent colour rendering based on organically capped CdSe quantum dots and Sr3SiO5: Ce3+, Li+ phosphors. Adv. Mater. 20, 2696–2702 (2008).
Lim, J. et al. Preparation of highly luminescent nanocrystals and their application to light-emitting diodes. Adv. Mater. 19, 1927–1932 (2007).
Resch-Genger, U., Grabolle, M., Cavaliere-Jaricot, S., Nitschke, R. & Nann, T. Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nature Methods 5, 763–775 (2008).
Brokmann, X., Giacobino, E., Dahan, M. & Hermier, J. P. Highly efficient triggered emission of single photons by colloidal CdSe/ZnS nanocrystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 712–714 (2004).
Fisher, B., Caruge, J. M., Zehnder, D. & Bawendi, M. Room-temperature ordered photon emission from multiexciton states in single CdSe core–shell nanocrystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 087403 (2005).
Popovic, Z. et al. A nanoparticle size series for in vivo fluorescence imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 8649–8652 (2010).
Reiss, P., Protiere, M. & Li, L. Core/shell semiconductor nanocrystals. Small 5, 154–168 (2009).
Jun, S., Jang, E. J. & Chung, Y. S. Alkyl thiols as a sulphur precursor for the preparation of monodisperse metal sulphide nanostructures. Nanotechnology 17, 4806–4810 (2006).
Nirmal, M. et al. Fluorescence intermittency in single cadmium selenide nanocrystals. Nature 383, 802–804 (1996).
Kuno, M. et al. Fluorescence intermittency in single InP quantum dots. Nano Lett. 1, 557–564 (2001).
Frantsuzov, P., Kuno, M., Janko, B. & Marcus, R. A. Universal emission intermittency in quantum dots, nanorods and nanowires. Nature Phys. 4, 519–522 (2008).
Hohng, S. & Ha, T. Near-complete suppression of quantum dot blinking in ambient conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 1324–1325 (2004).
Fomenko, V. & Nesbitt, D. J. Solution control of radiative and nonradiative lifetimes: A novel contribution to quantum dot blinking suppression. Nano Lett. 8, 287–293 (2008).
Hammer, N. I. et al. Coverage-mediated suppression of blinking in solid state quantum dot conjugated organic composite nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 14167–14171 (2006).
Mahler, B. et al. Towards non-blinking colloidal quantum dots. Nature Mater. 7, 659–664 (2008).
Chen, Y. et al. ‘Giant’ multishell CdSe nanocrystal quantum dots with suppressed blinking. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 5026–5027 (2008).
Wang, X. et al. Non-blinking semiconductor nanocrystals. Nature 459, 686–689 (2009).
Li, J. J. et al. Large-scale synthesis of nearly monodisperse CdSe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals using air-stable reagents via successive ion layer adsorption and reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 12567–12575 (2003).
Munro, A. M., Jen-La Plante, I., Ng, M. S. & Ginger, D. S. Quantitative study of the effects of surface ligand concentration on CdSe nanocrystal photoluminescence. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 6220–6227 (2007).
Wuister, S. F., Donega, C. D. & Meijerink, A. Influence of thiol capping on the exciton luminescence and decay kinetics of CdTe and CdSe quantum. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 17393–17397 (2004).
Gomez, D. E., van Embden, J. & Mulvaney, P. Spectral diffusion of single semiconductor nanocrystals: The influence of the dielectric environment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 154106 (2006).
Van Embden, J., Jasieniak, J. & Mulvaney, P. Mapping the optical properties of CdSe/CdS heterostructure nanocrystals: The effects of core size and shell thickness. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 14299–14309 (2009).
Clark, M. D., Kumar, S. K., Owen, J. S. & Chan, E. M. Focusing nanocrystal size distributions via production control. Nano Lett. 11, 1976–1980 (2011).
Chen, O. et al. Synthesis of metal-selenide nanocrystals using selenium dioxide as the selenium precursor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 8638–8641 (2008).
Mahler, B., Lequeux, N. & Dubertret, B. Ligand-controlled polytypism of thick-shell CdSe/CdS nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 953–959 (2010).
Chen, O. et al. Surface-functionalization-dependent optical properties of II–VI semiconductor nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 17504–17512 (2011).
Marshall, L. F., Cui, J., Brokmann, X. & Bawendi, M. G. Extracting spectral dynamics from single chromophores in solution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 053005 (2010).
Brokmann, X., Bawendi, M., Coolen, L. & Hermier, J. P. Photon-correlation Fourier spectroscopy. Opt. Express 14, 6333–6341 (2006).
Kuno, M., Fromm, D. P., Hamann, H. F., Gallagher, A. & Nesbitt, D. J. ‘On’/‘off’ fluorescence intermittency of single semiconductor quantum dots. J. Chem. Phys. 115, 1028–1040 (2001).
Empedocles, S. A., Neuhauser, R., Shimizu, K. & Bawendi, M. G. Photoluminescence from single semiconductor nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 11, 1243–1256 (1999).
Brokmann, X. et al. Statistical ageing and nonergodicity in the fluorescence of single nanocrystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 120601 (2003).
Chung, I. H. & Bawendi, M. G. Relationship between single quantum-dot intermittency and fluorescence intensity decays from collections of dots. Phys. Rev. B 70, 165304 (2004).
Nair, G., Zhao, J. & Bawendi, M. G. Biexciton quantum yield of single semiconductor nanocrystals from photon statistics. Nano Lett. 11, 1136–1140 (2011).
Park, Y. S. et al. Near-unity quantum yields of biexciton emission from CdSe/CdS nanocrystals measured using single-particle spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 187401 (2011).
Zhao, J., Chen, O., Strasfeld, D. B. & Bawendi, M. G. Biexciton quantum yield heterogeneities in single CdSe (CdS) core (shell) nanocrystals and its correlation to exciton blinking. Nano Lett. 12, 4477–4483 (2012).
Spinicelli, P. et al. Bright and grey states in CdSe-CdS nanocrystals exhibiting strongly reduced blinking. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 136801 (2009).
Cichos, F., von Borczyskowski, C. & Orrit, M. Power-law intermittency of single emitters. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 12, 272–284 (2007).
Gomez, D. E., Califano, M. & Mulvaney, P. Optical properties of single semiconductor nanocrystals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 8, 4989–5011 (2006).
Ghosh, Y. et al. New insights into the complexities of shell growth and the strong influence of particle volume in nonblinking ‘giant’ core/shell nanocrystal quantum dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 9634–9643 (2012).
Malko, A. V. et al. Pump-intensity- and shell-thickness-dependent evolution of photoluminescence blinking in individual core/shell CdSe/CdS nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 11, 5213–5218 (2011).
Gomez, D. E., van Embden, J., Jasieniak, J., Smith, T. A. & Mulvaney, P. Blinking and surface chemistry of single CdSe nanocrystals. Small 2, 204–208 (2006).
CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 85th edn (CRC, 2005).
Bardou, F., Bouchaud, J. P., Aspect, A. & Cohen-Tannoudji, C. Levy Statistics and Laser Cooling (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2001).
Lee, S. F. & Osborne, M. A. Brightening, blinking, bluing and bleaching in the life of a quantum dot: Friend or foe? ChemPhysChem 10, 2174–2191 (2009).
Zhang, J., Campbell, R. E., Ting, A. Y. & Tsien, R. Y. Creating new fluorescent probes for cell biology. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 906–918 (2002).
Brown, E. B. et al. In vivo measurement of gene expression, angiogenesis and physiological function in tumours using multiphoton laser scanning microscopy. Nature Med. 7, 864–868 (2001).
Liu, W. et al. Compact biocompatible quantum dots via RAFT-mediated synthesis of imidazole-based random copolymer ligand. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 472–483 (2010).
Acknowledgements
The work received support from the NIH through grants 5-U54-CA119349 (M.G.B.) and 5R01CA126642 (M.G.B., D.F., R.K.J.), the ARO through the Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies (W911NF-07-D-0004), and the NSF through a Collaborative Research in Chemistry Program (CHE-0714189) (M.G.B.). This work made use of the MRSEC Shared Experimental Facilities at MIT, supported by the National Science Foundation under award number DMR-08-19762 and the MIT DCIF NMR spectrometer funded through National Science Foundation Grants CHE-9808061 and DBI-9729592.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
O.C. and M.G.B. conceived and designed the project. O.C. performed the bulk of the experimental work with help from J.Z., V.P.C., J.C., C.W., D.K.H., H.W. and H-S.H. The data was analysed by O.C., J.Z., V.P.C., J.C., C.W. and M.G.B. All authors discussed the results and took part in producing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 1920 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, O., Zhao, J., Chauhan, V. et al. Compact high-quality CdSe–CdS core–shell nanocrystals with narrow emission linewidths and suppressed blinking. Nature Mater 12, 445–451 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3539
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3539
This article is cited by
-
Designer phospholipid capping ligands for soft metal halide nanocrystals
Nature (2024)
-
Unveiling the dual role of silver-associated defects: the manipulators of luminescence and carrier dynamics in eco-friendly AgIn0.5Ga0.5S2
Science China Materials (2024)
-
Highly stable and pure single-photon emission with 250 ps optical coherence times in InP colloidal quantum dots
Nature Nanotechnology (2023)
-
Heteroepitaxial chemistry of zinc chalcogenides on InP nanocrystals for defect-free interfaces with atomic uniformity
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Enrichment of anchoring sites by introducing supramolecular halogen bonds for the efficient perovskite nanocrystal LEDs
Light: Science & Applications (2023)