Abstract
OBJECTIVE: Abdominal fat is of major importance in terms of body fat distribution but is poorly reflected in conventional body impedance measurements. We developed a new technique for assessing the abdominal subcutaneous fat layer thickness (SFL) with single-frequency determination of the electrical impedance across the waist (SAI).
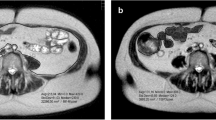
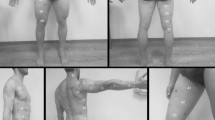
SUBJECTS AND MEASUREMENTS: The method uses a tetrapolar arrangement of surface electrodes which are placed symmetrically to the umbilicus in a plane perpendicular to the body axis. Twenty-four test subjects (12 male, 12 female) underwent SAI and abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The SFL below the sensing electrodes was determined from MRI and correlated with the SAI data at four different frequencies (5, 20, 50 and 204 kHz).
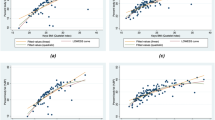
RESULTS: A highly significant linear correlation (r2=0.99) between SFL and SAI over a wide range of the abdominal SFL was found. Separate regression models for female and male subjects did not differ significantly, except at 50 kHz.
CONCLUSION: SAI represents a good predictor of the SFL and provides an excellent tool for the assessment of central obesity.
International Journal of Obesity (2001) 25, 502–511
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Björnthorp P . Metabolic implications of body fat distribution Diabetes Care 1991 14: 1132.
Després JP, Moorjani S, Lupien PJ, Tremblay A, Nadeau A, Bouchard C . Regional distribution of body fat, plasma lipoproteins and cardiovascular disease Arteriosclerosis 1990 10: 497–511.
Krotkiewski M, Björntorp P, Sjöström L, Smith U . Impact of obesity on metabolism in men and women. Importance of regional adipose tissue distribution J Clin Invest 1983 72: 1150–1162.
Vague J . The degree of masculine differentiation of obesities: a factor determining predisposition to diabetes, atherosclerosis, gout and uric calculous disease Am J Clin Nutr 1956 4: 20–34.
Anderson KM, Wilson PWF, Odell PM, Kannel WB . An updated coronary risk profile. A statement for health professionals Circulation 1991 83: 356–362.
Donahue RP, Abbott RD, Bloom E, Reed DM, Yano K . Central obesity and coronary heart disease in men Lancet 1987 21 (8569): 821–824.
Ducimetiere P, Richard J, Cambien F . The pattern of subcutaneous fat distribution in middle-aged men and the risk of coronary heart disease: the Paris prospective study Int J Obes 1986 10: 229–240.
Twisk JWR, Kemper HCG, van Mechelen W, Post GB, van Lenthe FJ . Body fatness: longitudinal relationship of body mass index and the sum of skinfolds with other risk factors for coronary heart disease Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998 22: 915–922.
Larsson B, Svärdssud K, Welin L, Wilhelmsen L, Björntorp P, Tibblin G . Abdominal adipose tissue distribution, obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: 13 year follow up of participants in the study of men born 1913 Br Med J 1994 288: 1401–1404.
Megnien JL, Denarie N, Cocaul M, Simon A, Levenson J . Predictive value of waist-to-hip ratio on cardiovascular risk events Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999 23: 90–97.
Akers R, Buskirk ER . An underwater weighing system utilizing ‘force cube’ transducers J Appl Physiol 1969 26: 649–652.
Forbes GB . Human body composition Springer: New York 1987.
Lukaski HC . Methods for the assessment of human body composition: traditional and new Am J Clin Nutr 1987 46: 537–556.
Fuller MF, Fowler PA, McNeill G, Foster MA . Imaging techniques for the assessment of body composition J Nutr 1994 124: S1546–1550.
Sjostrom L, Kvist H, Cederblad A, Tylen U . Determination of total adipose tissue and body fat in women by computed tomography, 40K, and tritium Am J Physiol 1986 250: E736–745.
Sohlstrom A, Wahlund LO, Forsum E . Adipose tissue distribution as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging and total body fat by magnetic resonance imaging, underwater weighing, and body-water dilution in healthy women Am J Clin Nutr 1993 58: 830–838.
Thomas EL, Saeed N, Hajnal JV, Brynes A, Goldstone AP, Frost G, Bell JD . Magnetic resonance imaging of total body fat Appl Physiol 1998 85: 1778–1785.
Abe T et al. Total and segmental subcutaneous adipose tissue volume measured by ultrasound Med Sci Sports Exercise 1996 28: 908–912.
Harrison GG, Van Atallie TB . Estimation of body composition: a new approach based on electromagnetic principles Am J Clin Nutr 1982 35: 1176–1179.
Kuschner RF . Bioelectrical impedance analysis: a review of principles and applications J Am Coll Nutr 1992 11: 199–209.
Van Loan MD, Withers P, Matthie J, Mayclin PL . Use of bio-impedance spectroscopy (BIS) to determine extracellular fluid (ECF), intracellular fluid (ICF), total body water (TBW), and fat-free mass (FFM). In: Ellis, KJ, Eastman JD (eds). Human body composition: in vivo methods, models, and assessment Plenum: New York 1993.
Organ LW, Bradham GB, Gore DW, Lozier SL . Segmental bioelectrical impedance analysis: theory and application of a new technique J Appl Physiol 1994 77: 98–112.
Baumgartner RN, Ross R, Heymsfield SB . Does adipose tissue influence bioelectric impedance in obese men and women? J Appl Physiol 1998 84: 257–262.
Gonzalez CA, Zuniga O, Padilla LE . Detection of animal tissue thickness using simple vertical electric sounding (VES) Physiol Measmt 1997 18: 85–91.
Elia M, Ward LC . New techniques in nutritional assessment: body composition methods Proc Nutr Soc 1999 58: 33–38.
Geddes LA, Baker LE . The specific resistance of biological material—a compendium of data for the biomedical engineer and physiologist Med Biol Engng 1967 5: 271–293.
Scharfetter H, Monif M, Laszlo Z, Lambauer T, Hutten H, Hinghofer-Szalkay H . Effect of postural changes on the reliability of volume estimations from bioimpedance spectroscopy data Kidney Int 1997 51: 1078–1087.
Newell JC, Isaacson D, Gisser DC . Rapid assessment of electrode characteristics for impedance imaging Biomed Engng 1990 37: 735–738.
Scharfetter H, Hartinger P, Hinghofer-Szalkay H, Hutten H . A model of artifacts produced by stray capacitance during whole body or segmental bioimpedance spectroscopy Physiol Measmt 1998 19: 247–261.
Lozano A, Rosell J, Pallas-Areny R . Errors in prolonged electrical impedance measurements due to electrode repositioning and postural changes Physiol Measmt 1995 16: 121–130.
Rigaud B, Hamzaoui L, Frikha MR, Chauveau N, Morucci JP . In vitro tissue characterization and modelling using electrical impedance measurements in the 100 Hz–10 MHz frequency range Physiol Measmt 1995 16 (3 Suppl A): A15–28.
Rexrode KM, Carey VJ, Hennekens CH, Walters EE, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Manson JAE . Abdominal adiposity and coronary heart disease in women JAMA 1998 280: 1843–1848.
Eckel RH, Krauss RM . American Heart Association call to action: obesity as a major risk factor for coronary heart disease Circulation 1998 97: 2099–2100.
Molarius A, Seidell JC, Sans S, Tuomilehto J, Kuulasmaa K . Waist and hip circumferences, and waist-hip ratio in 19 populations of the WHO MONICA project Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999 23: 116–125.
Okosun IS, Prewitt TE, Liao Y, Cooper RS . Association of waist circumference with ApoB to ApoAI ratio in black and white Americans Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999 23: 498–504.
Han TS, van Leer ED, Seidell JC, Lean MEJ . Waist circumference as a screening tool for cardiovascular risk factors: evaluation of receiver operating characteristics (ROC) Obes Res 1996 4: 533–547.
Zipp P . Die Bemessung der Elektroden-Haut-Kontaktfläche und der Verstärkereingangsimpedanz bei der quantitativen Oberflächenelektrographie (EKG und EMG) Biomed Technol 1978 23: 130–140.
Acknowledgements
Experiments were done at Institute for Adaptive and Spaceflight Physiology, Austrian Society for Aerospace Medicine (ASM), Graz, Austria. The authors thank Ulrike Marauli, Andreas Rothaler and Melitta Unterlerchner for their excellent technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scharfetter, H., Schlager, T., Stollberger, R. et al. Assessing abdominal fatness with local bioimpedance analysis: basics and experimental findings. Int J Obes 25, 502–511 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801556
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801556
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Normal-weight obesity is associated with increased risk of subclinical atherosclerosis
Cardiovascular Diabetology (2015)
-
Subclinical vascular inflammation in subjects with normal weight obesity and its association with body Fat: an 18 F-FDG-PET/CT study
Cardiovascular Diabetology (2014)
-
The Negative Association of Obesity with Subjective Well-Being: Is it All About Health?
Journal of Happiness Studies (2014)
-
Estimation of abdominal fat compartments by bioelectrical impedance: the validity of the ViScan measurement system in comparison with MRI
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2010)
-
Is bioelectrical impedance accurate for use in large epidemiological studies?
Nutrition Journal (2008)