Abstract
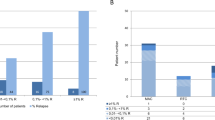
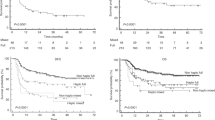
One of the major complications after allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT) in patients with malignant disease is a high frequency of relapse. We have prospectively analyzed the clinical impact of recipient-derived chimeric cells in 30 patients with acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome after SCT. In order to improve sensitivity and specificity, all samples were cell-separated by using immunomagnetic beads according to the patient's leukemia phenotype, expressed at diagnosis or relapse before SCT. Twelve out of 30 patients experienced a clinical relapse after SCT. Median follow-up time for patients alive and without relapse (n = 15) was 30 (16–47) months. Mixed chimerism in peripheral blood (PB) and bone marrow (BM) ⩾1 month post SCT, in the leukemia-affected cell lineage, was detected in 14/30 patients. Ten of these 14 patients relapsed as compared to 2/16 with donor chimerism (DC) (P <0.01). All eight patients with MC in peripheral blood ⩾1 month after SCT relapsed vs 4/22 DC patients (P < 0.001). MC was detected a median of 66 (23–332) days before hematological relapse. No correlation was found between T cell MC and relapse. In this study, chimerism analysis showed a higher sensitivity and specificity vsmorphological examination. In conclusion, this study may provide a rational basis for treatment with adoptive immunotherapy at an earlier time after SCT than at present, in patients with AML and MDS, in order to treat recurrences of malignant disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomas ED, Buckner CD, Banaji M, Clift RA, Fefer A, Flournoy N, Goodell BW, Hickman RO, Lerner KG, Neiman PE, Sale GE, Sanders JE, Singer J, Stevens M, Storb R, Weiden PL . One hundred patients with acute leukemia treated by chemotherapy, total body irradiation, and allogeneic marrow transplantation Blood 1977 49: 511–533
Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, Storb R, Witherspoon RP, Fefer A, Fisher L, Buckner CD, Anasetti C, Appelbaum FR, Badger C, Beatty P, Bensinger W, Berenson R, Bigelow C, Cheever MA, Clift R, Deeg HJ, Doney K, Greenberg P, Hansen JA, Hill R, Loughran T, Martin P, Neiman P, Petersen FB, Sanders J, Singer J, Stewart P, Thomas ED . Influence of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease on relapse and survival after bone marrow transplantation from HLA-identical siblings as treatment of acute and chronic leukemia (published erratum appears in Blood 1989 Aug 15;74(3):1180) Blood 1989 73: 1720–1728
Kolb HJ . Donor leukocyte transfusions for treatment of leukemic relapse after bone marrow transplantation. EBMT Immunology and Chronic Leukemia Working Parties Vox Sang 1998 74: 321–329
Dazzi F, Szydlo RM, Goldman JM . Donor lymphocyte infusions for relapse of chronic myeloid leukemia after allogeneic stem cell transplant: where we now stand Exp Hematol 1999 27: 1477–1486
van Rhee F, Lin F, Cullis JO, Spencer A, Cross NC, Chase A, Garicochea B, Bungey J, Barrett J, Goldman JM . Relapse of chronic myeloid leukemia after allogeneic bone marrow transplant: the case for giving donor leukocyte transfusions before the onset of hematologic relapse Blood 1994 83: 3377–3383
Bader P, Klingebiel T, Schaudt A, Theurer-Mainka U, Handgretinger R, Lang P, Niethammer D, Beck JF . Prevention of relapse in pediatric patients with acute leukemias and MDS after allogeneic SCT by early immunotherapy initiated on the basis of increasing mixed chimerism: a single center experience of 12 children Leukemia 1999 13: 2079–2086
Ryan D, Van Dongen J . Detection of residual disease in acute leukemia using immunological markers. In: Bennet J, Foon K (eds) Immunologic Approaches to the Classification and Management of Lymphomas and Leukemias Kluwer Academic: Norwell, MA 1988 p 173
Campana D, Pui CH . Detection of minimal residual disease in acute leukemia: methodologic advances and clinical significance (see comments) Blood 1995 85: 1416–1434
van Dongen JJ, Macintyre EA, Gabert JA, Delabesse E, Rossi V, Saglio G, Gottardi E, Rambaldi A, Dotti G, Griesinger F, Parreira A, Gameiro P, Diaz MG, Malec M, Langerak AW, San Miguel JF, Biondi A . Standardized RT-PCR analysis of fusion gene transcripts from chromosome aberrations in acute leukemia for detection of minimal residual disease. Report of the BIOMED-1 Concerted Action: investigation of minimal residual disease in acute leukemia Leukemia 1999 13: 1901–1928
Socie G, Lawler M, Gluckman E, McCann SR, Brison O . Studies on hemopoietic chimerism following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in the molecular biology era Leuk Res 1995 19: 497–504
Schattenberg A, De Witte T, Salden M, Vet J, Van Dijk B, Smeets D, Hoogenhout J, Haanen C . Mixed hematopoietic chimerism after allogeneic transplantation with lymphocyte-depleted bone marrow is not associated with a higher incidence of relapse Blood 1989 73: 1367–1372
van Leeuwen JE, van Tol MJ, Joosten AM, Wijnen JT, Khan PM, Vossen JM . Mixed T-lymphoid chimerism after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for hematologic malignancies of children is not correlated with relapse Blood 1993 82: 1921–1928
van Leeuwen JE, van Tol MJ, Joosten AM, Wijnen JT, Verweij PJ, Khan PM, Vossen JM . Persistence of host-type hematopoiesis after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for leukemia is significantly related to the recipient's age and/or the conditioning regimen, but it is not associated with an increased risk of relapse Blood 1994 83: 3059–3067
Bader P, Holle W, Klingebiel T, Handgretinger R, Benda N, Schlegel PG, Niethammer D, Beck J . Mixed hematopoietic chimerism after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: the impact of quantitative PCR analysis for prediction of relapse and graft rejection in children Bone Marrow Transplant 1997 19: 697–702
Bader P, Beck J, Frey A, Schlegel PG, Hebarth H, Handgretinger R, Einsele H, Niemeyer C, Benda N, Faul C, Kanz L, Niethammer D, Klingebiel T . Serial and quantitative analysis of mixed hematopoietic chimerism by PCR in patients with acute leukemias allows the prediction of relapse after allogeneic BMT Bone Marrow Transplant 1998 21: 487–495
Lawler M, Humphries P, McCann SR . Evaluation of mixed chimerism by in vitro amplification of dinucleotide repeat sequences using the polymerase chain reaction Blood 1991 77: 2504–2514
Ramirez M, Diaz MA, Garcia-Sanchez F, Velasco M, Casado F, Villa M, Vicario JL, Madero L . Chimerism after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Bone Marrow Transplant 1996 18: 1161–1165
Khalidi HS, Medeiros LJ, Chang KL, Brynes RK, Slovak ML, Arber DA . The immunophenotype of adult acute myeloid leukemia: high frequency of lymphoid antigen expression and comparison of immunophenotype, French–American–British classification, and karyotypic abnormalities Am J Clin Pathol 1998 109: 211–220
Lauria F, Raspadori D, Ventura MA, Rondelli D, Testoni N, Tosi P, Michieli M, Damiani D, Motta MR, Tura S . The presence of lymphoid-associated antigens in adult acute myeloid leukemia is devoid of prognostic relevance Stem Cells 1995 13: 428–434
Olerup O, Zetterquist H . HLA-DR typing by PCR amplification with sequence-specific primers (PCR- SSP) in 2 hours: an alternative to serological DR typing in clinical practice including donor-recipient matching in cadaveric transplantation (see comments) Tissue Antigens 1992 39: 225–235
Oakhill A, Pamphilon DH, Potter MN, Steward CG, Goodman S, Green A, Goulden P, Goulden NJ, Hale G, Waldmann H, Cornish JM . Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for children with relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in second complete remission Br J Haematol 1996 94: 574–578
Ringden O, Remberger M, Ruutu T, Nikoskelainen J, Volin L, Vindelov L, Parkkali T, Lenhoff S, Sallerfors B, Mellander L, Ljungman P, Jacobsen N . Increased risk of chronic graft-versus-host disease, obstructive bronchiolitis, and alopecia with busulfan versus total body irradiation: long-term results of a randomized trial in allogeneic marrow recipients with leukemia. Nordic Bone Marrow Transplantation Group Blood 1999 93: 2196–2201
Remberger M, Svahn BM, Hentschke P, Lofgren C, Ringden O . Effect on cytokine release and graft-versus-host disease of different anti-T cell antibodies during conditioning for unrelated haematopoietic stem cell transplantation Bone Marrow Transplant 1999 24: 823–830
Ringden O, Soderdahl G, Mattsson J, Uzunel M, Remberger M, Hentschke P, Hagglund H, Sparrelid E, Elmhorn-Rosenborg A, Duraj F, Zetterquist H, Ericzon BG . Transplantation of autologous and allogeneic bone marrow with liver from a cadaveric donor for primary liver cancer (see comments) Transplantation 2000 69: 2043–2048
Storb R, Deeg HJ, Whitehead J, Appelbaum F, Beatty P, Bensinger W, Buckner CD, Clift R, Doney K, Farewell V, Hansen J, Hill R, Lum L, Martin P, McGuffin R, Sanders J, Stewart P, Sullivan K, Witherspoon R, Yee G, Thomas ED . Methotrexate and cyclosporine compared with cyclosporine alone for prophylaxis of acute graft versus host disease after marrow transplantation for leukemia N Engl J Med 1986 314: 729–735
Ringden O, Remberger M, Carlens S, Hagglund H, Mattsson J, Aschan J, Lonnqvist B, Klaesson S, Winiarski J, Dalianis T, Olerup O, Sparrelid E, Elmhorn-Rosenborg A, Svahn BM, Ljungman P . Low incidence of acute graft-versus-host disease, using unrelated HLA-A-, HLA-B-, and HLA-DR-compatible donors and conditioning, including anti-T-cell antibodies Transplantation 1998 66: 620–625
Ringden O, Remberger M, Persson U, Ljungman P, Aldener A, Andstrom E, Aschan J, Bolme P, Dahllof G, Dalianis T, Gahrton G, Hagglund H, Lonnqvist B, Olerup O, Shanwell A, Sparrelid E, Winiarski J, Moller E, Oberg M . Similar incidence of graft-versus-host disease using HLA-A, -B and -DR identical unrelated bone marrow donors as with HLA-identical siblings Bone Marrow Transplant 1995 15: 619–625
Budowle B, Chakraborty R, Giusti AM, Eisenberg AJ, Allen RC . Analysis of the VNTR locus D1S80 by the PCR followed by high-resolution PAGE Am J Hum Genet 1991 48: 137–144
Eubanks JH, Selleri L, Hart R, Rosette C, Evans GA . Isolation, localization, and physical mapping of a highly polymorphic locus on human chromosome 11q13 Genomics 1991 11: 720–729
Decorte R, Cuppens H, Marynen P, Cassiman JJ . Rapid detection of hypervariable regions by the polymerase chain reaction technique DNA Cell Biol 1990 9: 461–469
Jeffreys AJ, Wilson V, Neumann R, Keyte J . Amplification of human minisatellites by the polymerase chain reaction: towards DNA fingerprinting of single cells Nucleic Acids Res 1988 16: 10953–10971
Buchmayer H, Rumpold H, Mannhalter C . Identification of a variable number tandem repeat region in the human T cell receptor alpha-delta (TCRAD) locus Hum Genet 1996 98: 333–335
Demers DB, Curry ET, Egholm M, Sozer AC . Enhanced PCR amplification of VNTR locus D1S80 using peptide nucleic acid (PNA) Nucleic Acids Res 1995 23: 3050–3055
Mattsson J, Uzunel M, Remberger M, Ljungman P, Kimby E, Ringdén O, Zetterquist H . Minimal residual disease is common after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in patients with B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and may be controlled by graft-versus-host disease Leukemia 2000 14: 247–254
Zetterquist H, Mattsson J, Uzunel M, Näsman-Björk I, Svenberg P, Tammik L, Bayat G, Winiarski J, Ringdén O . Mixed chimerism in the B cell lineage is a rapid and sensitive indicator of minimal residual disease in bone marrow transplant recipients with pre-B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia Bone Marrow Transplant 2000 25: 843–851
Kaplan E, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations J Am Stat Assoc 1958 53: 457–481
Kalbfleisch J, Prentice R . The Statistical Analysis of Failure Time Data John Wiley and Sons: New York 1980
Galen R, Gambino S . The Predictive Value and Efficiency of Medical Diagnosis John Wiley: New York 1975
Gerhardt W, Keller H . Evaluation of test data from clinical studies Scand J Clin Lab Invest 1986 (Suppl. 181): 1–74
Horowitz MM, Gale RP, Sondel PM, Goldman JM, Kersey J, Kolb HJ, Rimm AA, Ringden O, Rozman C, Speck B, Truitt RL, Zwaan FE, Bortin MM . Graft-versus-leukemia reactions after bone marrow transplantation Blood 1990 75: 555–562
Pratt W, Ruddon R, Ensminger W, Maybaum J . Determinants of Drug Responsiveness Oxford University Press: New York, NY 1994
Kolb HJ, Schattenberg A, Goldman JM, Hertenstein B, Jacobsen N, Arcese W, Ljungman P, Ferrant A, Verdonck L, Niederwieser D, Vanrhee F, Mittermueller J, Dewitte T, Holler E, Ansari H . Graft-versus-leukemia effect of donor lymphocyte transfusions in marrow grafted patients. European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Working Party Chronic Leukemia (see comments) Blood 1995 86: 2041–2050
Elmaagacli AH, Beelen DW, Kroll M, Trzensky S, Stein C, Schaefer UW . Detection of CBFbeta/MYH11 fusion transcripts in patients with inv(16) acute myeloid leukemia after allogeneic bone marrow or peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation Bone Marrow Transplant 1998 21: 159–166
Dubovsky J, Daxberger H, Fritsch G, Printz D, Peters C, Matthes S, Gadner H, Lion T, Muller-Berat N . Kinetics of chimerism during the early post-transplant period in pediatric patients with malignant and non-malignant hematologic disorders: implications for timely detection of engraftment, graft failure and rejection Leukemia 1999 13: 2059–2060
Lamb LS Jr, Robbins NF, Abhyankar S, Joyce M, Stetler-Stevenson M, Henslee-Downey PJ, Gee AP . Flow cytometric cell sorting combined with molecular chimerism analysis to detect minimal recurrent leukemia: good news and bad news Bone Marrow Transplant 1997 19: 1157–1161
Lion T, Daxberger H, Dubovsky J, Filipcik P, Fritsch G, Printz D, Peters C, Matthes-Martin S, Lawitschka A, Gadner H . Analysis of chimerism within specific leukocyte subsets for detection of residual or recurrent leukemia in pediatric patients after allogeneic stem cell transplantation Leukemia 2001 15: 307–310
Thiede C, Bornhäuser M, Oelschlagel U, Brendel C, Leo R, Daxberger H, Mohr B, Florek M, Kroschinsky F, Geissler G, Naumann R, Ritter M, Prange-Krex G, Lion T, Neubauer A, Ehninger G . Sequential monitoring of chimerism and detection of minimal residual disease after allogeneic blood stem cell transplantation (BSCT) using multiplex PCR amplification of short tandem repeat-markers Leukemia 2001 15: 293–302
Goulden NJ, Knechtli CJ, Garland RJ, Langlands K, Hancock JP, Potter MN, Steward CG, Oakhill A . Minimal residual disease analysis for the prediction of relapse in children with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia Br J Haematol 1998 100: 235–244
Tobal K, Johnson PR, Saunders MJ, Harrison CJ, Liu Yin JA . Detection of CBFB/MYH11 transcripts in patients with inversion and other abnormalities of chromosome 16 at presentation and remission Br J Haematol 1995 91: 104–108
Simmons PJ, Przepiorka D, Thomas ED, Torok-Storb B . Host origin of marrow stromal cells following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation Nature 1987 328: 429–432
Potter MN, Steward CG, Oakhill A . The significance of detection of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia Br J Haematol 1993 83: 412–418
Bader P, Stoll K, Huber S, Geiselhart A, Handgretinger R, Niemeyer C, Einsele H, Schlegel PG, Niethammer D, Beck J, Klingebiel T . Characterization of lineage-specific chimaerism in patients with acute leukaemia and myelodysplastic syndrome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation before and after relapse Br J Haematol 2000 108: 761–768
Sondel PM, Hank JA, Molenda J, Blank J, Borcherding W, Longo W, Trigg ME, Hong R, Bozdech MJ . Relapse of host leukemic lymphoblasts following engraftment by an HLA-mismatched marrow transplant: mechanisms of escape from the ‘graft versus leukemia’ effect Exp Hematol 1985 13: 782–790
Dermime S, Mavroudis D, Jiang YZ, Hensel N, Molldrem J, Barrett AJ . Immune escape from a graft-versus-leukemia effect may play a role in the relapse of myeloid leukemias following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation Bone Marrow Transplant 1997 19: 989–999
Kolb HJ, Holler E . Adoptive immunotherapy with donor lymphocyte transfusions Curr Opin Oncol 1997 9: 139–145
Ruiz-Cabello F, Klein E, Garrido F . MHC antigens on human tumors Immunol Lett 1991 29: 181–189
Bader P, Beck J, Schlegel PG, Handgretinger R, Niethammer D, Klingebiel T . Additional immunotherapy on the basis of increasing mixed hematopoietic chimerism after allogeneic BMT in children with acute leukemia: is there an option to prevent relapse? Bone Marrow Transplant 1997 20: 79–81
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Giti Bayat and Susanne Öhman for their excellent technical assistance. We also want to thank the staff in the Center for Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation, Division of Hematology in the Dept of Medicine and Dept of Pediatrics for competent and compassionate patient care. This study was supported by grants from the Swedish Cancer Foundation (0070-B96–10XAC), the Children's Cancer Foundation (1994–060), (1998–002), the Swedish Medical Research Council (K97–06X-05971–17A), the Tobias foundation, the FRF foundation and Ellen Bechrach foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattsson, J., Uzunel, M., Tammik, L. et al. Leukemia lineage-specific chimerism analysis is a sensitive predictor of relapse in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Leukemia 15, 1976–1985 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402311
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402311
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Monitoring minimal residual/relapsing disease after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)
-
Chimerism analysis in peripheral blood using indel quantitative real-time PCR is a useful tool to predict post-transplant relapse in acute leukemia
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2015)
-
Immunosuppressive CD14+HLA-DRlow/neg IDO+ myeloid cells in patients following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Leukemia (2013)
-
CD34+ lineage specific donor cell chimerism for the diagnosis and treatment of impending relapse of AML or myelodysplastic syndrome after allo-SCT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2013)
-
Evaluation of BM cytomorphology after allo-SCT in patients with AML
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2012)